LF95 Linux User's Guide - Lahey Computer Systems
LF95 Linux User's Guide - Lahey Computer Systems
LF95 Linux User's Guide - Lahey Computer Systems
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
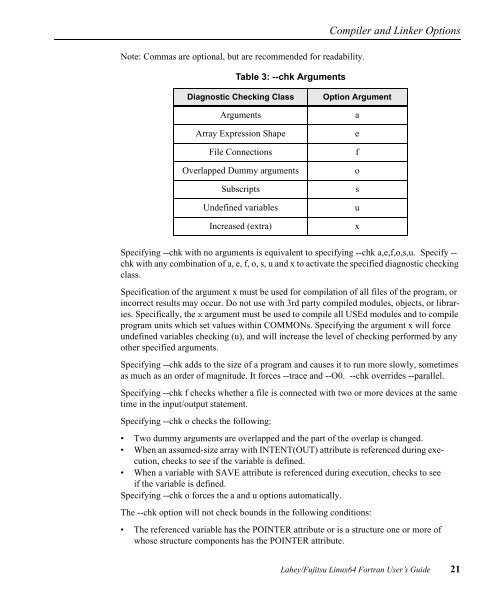
Note: Commas are optional, but are recommended for readability.Table 3: --chk ArgumentsCompiler and Linker OptionsDiagnostic Checking ClassArgumentsArray Expression ShapeFile ConnectionsOverlapped Dummy argumentsSubscriptsUndefined variablesIncreased (extra)Option ArgumentaefosuxSpecifying --chk with no arguments is equivalent to specifying --chk a,e,f,o,s,u. Specify --chk with any combination of a, e, f, o, s, u and x to activate the specified diagnostic checkingclass.Specification of the argument x must be used for compilation of all files of the program, orincorrect results may occur. Do not use with 3rd party compiled modules, objects, or libraries.Specifically, the x argument must be used to compile all USEd modules and to compileprogram units which set values within COMMONs. Specifying the argument x will forceundefined variables checking (u), and will increase the level of checking performed by anyother specified arguments.Specifying --chk adds to the size of a program and causes it to run more slowly, sometimesas much as an order of magnitude. It forces --trace and --O0. --chk overrides --parallel.Specifying --chk f checks whether a file is connected with two or more devices at the sametime in the input/output statement.Specifying --chk o checks the following:• Two dummy arguments are overlapped and the part of the overlap is changed.• When an assumed-size array with INTENT(OUT) attribute is referenced during execution,checks to see if the variable is defined.• When a variable with SAVE attribute is referenced during execution, checks to seeif the variable is defined.Specifying --chk o forces the a and u options automatically.The --chk option will not check bounds in the following conditions:• The referenced variable has the POINTER attribute or is a structure one or more ofwhose structure components has the POINTER attribute.<strong>Lahey</strong>/Fujitsu <strong>Linux</strong>64 Fortran User’s <strong>Guide</strong> 21