Kaiser Family Foundation Survey on State Medicaid Managed Care ...
Kaiser Family Foundation Survey on State Medicaid Managed Care ...
Kaiser Family Foundation Survey on State Medicaid Managed Care ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
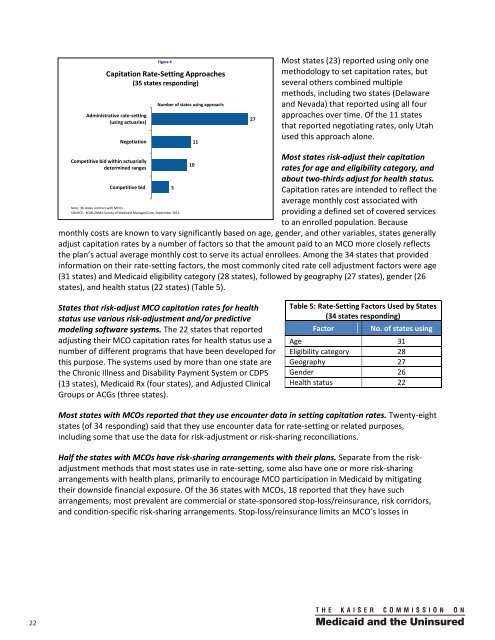
Figure 4Capitati<strong>on</strong> Rate-Setting Approaches(35 states resp<strong>on</strong>ding)Administrative rate-setting(using actuaries)Negotiati<strong>on</strong>Number of states using approach:1127Most states (23) reported using <strong>on</strong>ly <strong>on</strong>emethodology to set capitati<strong>on</strong> rates, butseveral others combined multiplemethods, including two states (Delawareand Nevada) that reported using all fourapproaches over time. Of the 11 statesthat reported negotiating rates, <strong>on</strong>ly Utahused this approach al<strong>on</strong>e.Competitive bid within actuariallydetermined rangesCompetitive bidNote: 36 states c<strong>on</strong>tract with MCOs.SOURCE: KCMU/HMA <str<strong>on</strong>g>Survey</str<strong>on</strong>g> of <strong>Medicaid</strong> <strong>Managed</strong> <strong>Care</strong>, September 2011.510Most states risk-adjust their capitati<strong>on</strong>rates for age and eligibility category, andabout two-thirds adjust for health status.Capitati<strong>on</strong> rates are intended to reflect theaverage m<strong>on</strong>thly cost associated withproviding a defined set of covered servicesto an enrolled populati<strong>on</strong>. Becausem<strong>on</strong>thly costs are known to vary significantly based <strong>on</strong> age, gender, and other variables, states generallyadjust capitati<strong>on</strong> rates by a number of factors so that the amount paid to an MCO more closely reflectsthe plan’s actual average m<strong>on</strong>thly cost to serve its actual enrollees. Am<strong>on</strong>g the 34 states that providedinformati<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong> their rate-setting factors, the most comm<strong>on</strong>ly cited rate cell adjustment factors were age(31 states) and <strong>Medicaid</strong> eligibility category (28 states), followed by geography (27 states), gender (26states), and health status (22 states) (Table 5).<strong>State</strong>s that risk-adjust MCO capitati<strong>on</strong> rates for healthstatus use various risk-adjustment and/or predictivemodeling software systems. The 22 states that reportedadjusting their MCO capitati<strong>on</strong> rates for health status use anumber of different programs that have been developed forthis purpose. The systems used by more than <strong>on</strong>e state arethe Chr<strong>on</strong>ic Illness and Disability Payment System or CDPS(13 states), <strong>Medicaid</strong> Rx (four states), and Adjusted ClinicalGroups or ACGs (three states).Table 5: Rate-Setting Factors Used by <strong>State</strong>s(34 states resp<strong>on</strong>ding)FactorNo. of states usingAge 31Eligibility category 28Geography 27Gender 26Health status 22Most states with MCOs reported that they use encounter data in setting capitati<strong>on</strong> rates. Twenty-eightstates (of 34 resp<strong>on</strong>ding) said that they use encounter data for rate-setting or related purposes,including some that use the data for risk-adjustment or risk-sharing rec<strong>on</strong>ciliati<strong>on</strong>s.Half the states with MCOs have risk-sharing arrangements with their plans. Separate from the riskadjustmentmethods that most states use in rate-setting, some also have <strong>on</strong>e or more risk-sharingarrangements with health plans, primarily to encourage MCO participati<strong>on</strong> in <strong>Medicaid</strong> by mitigatingtheir downside financial exposure. Of the 36 states with MCOs, 18 reported that they have sucharrangements; most prevalent are commercial or state-sp<strong>on</strong>sored stop-loss/reinsurance, risk corridors,and c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>-specific risk-sharing arrangements. Stop-loss/reinsurance limits an MCO’s losses in22 00