Lubna landfill
Lubna landfill
Lubna landfill
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
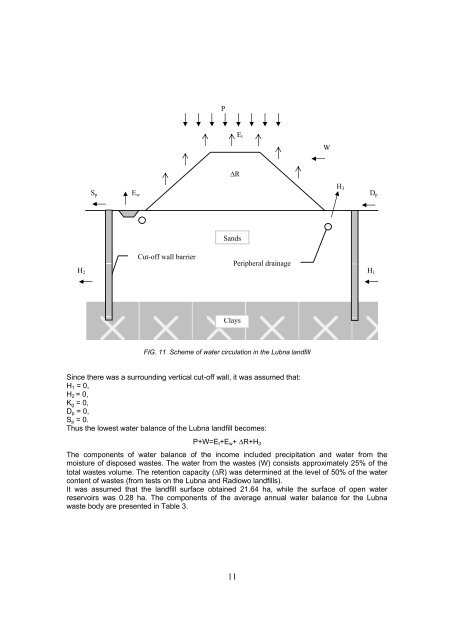
PE tW∆RS pE wH 3D pSandsH 2Cut-off wall barrierPeripheral drainageH 1ClaysFIG. 11 Scheme of water circulation in the <strong>Lubna</strong> <strong>landfill</strong>Since there was a surrounding vertical cut-off wall, it was assumed that:H 1 = 0,H 2 = 0,K g = 0,D p = 0,S p = 0.Thus the lowest water balance of the <strong>Lubna</strong> <strong>landfill</strong> becomes:P+W=E t +E w + ∆R+H 3The components of water balance of the income included precipitation and water from themoisture of disposed wastes. The water from the wastes (W) consists approximately 25% of thetotal wastes volume. The retention capacity (∆R) was determined at the level of 50% of the watercontent of wastes (from tests on the <strong>Lubna</strong> and Radiowo <strong>landfill</strong>s).It was assumed that the <strong>landfill</strong> surface obtained 21.64 ha, while the surface of open waterreservoirs was 0.28 ha. The components of the average annual water balance for the <strong>Lubna</strong>waste body are presented in Table 3.11