- Page 3:
ENCYCLOPEDIA OFHOMEOPATHY
- Page 6 and 7:
LONDON, NEW YORK, MUNICH, MELBOURNE
- Page 8 and 9:
INTRODUCTIONHomeopathy is a holisti
- Page 10 and 11:
8 •ENCYCLOPEDIA OF HOMEOPATHYHOW
- Page 13 and 14:
theory& practice
- Page 15 and 16:
HISTORY OF HOMEOPATHY• 13illness
- Page 17 and 18:
HISTORY OF HOMEOPATHY • 15intelle
- Page 19 and 20:
HISTORY OF HOMEOPATHY • 17The Bri
- Page 21 and 22:
HISTORY OF HOMEOPATHY• 19Many of
- Page 23 and 24:
HISTORY OF HOMEOPATHY • 21cases m
- Page 25 and 26:
HISTORY OF HOMEOPATHY• 23daily re
- Page 27:
DEVELOPMENT OF HOMEOPATHY• 25arth
- Page 30 and 31:
28 •MATERIA MEDICAHOW REMEDIES AR
- Page 33 and 34:
major plantremediesplants have been
- Page 35 and 36:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 33Agaricus
- Page 37 and 38:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 35Aloe fero
- Page 39 and 40:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 37Arnica mo
- Page 41 and 42:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 39Atropa be
- Page 43 and 44:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 41Berberis
- Page 45 and 46:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 43Cannabis
- Page 47 and 48:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 45Cephaelis
- Page 49 and 50:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 47Chelidoni
- Page 51 and 52:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 49Cinchona
- Page 53 and 54:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 51Conium ma
- Page 55 and 56:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 53Datura st
- Page 57 and 58:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 55Helleboru
- Page 59 and 60:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 57Ignatia a
- Page 61 and 62:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 59Lycopodiu
- Page 63 and 64:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 61Pulsatill
- Page 65 and 66:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 63Strychnos
- Page 67:
MAJOR PLANT REMEDIES• 65Veratrum
- Page 70 and 71:
68 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESAcidum
- Page 72 and 73:
70 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESAcidum
- Page 74 and 75:
72 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESAluminu
- Page 76 and 77:
74 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESArgentu
- Page 78 and 79:
76 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESBarium
- Page 80 and 81:
78 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESCalcium
- Page 82 and 83:
80 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESCuprum
- Page 84 and 85:
82 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESFerrum
- Page 86 and 87:
84 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESHepar s
- Page 88 and 89:
86 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESIodumIO
- Page 90 and 91:
88 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESKalium
- Page 92 and 93:
90 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESMagnesi
- Page 94 and 95:
92 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESNatrum
- Page 96 and 97:
94 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESPhospho
- Page 98 and 99:
96 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESPlumbum
- Page 100 and 101:
98 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESStibium
- Page 102 and 103:
100 •MAJOR MINERAL REMEDIESTartar
- Page 105 and 106:
major animalremediesthis small but
- Page 107 and 108:
MAJOR ANIMAL REMEDIES• 105Canthar
- Page 109 and 110:
MAJOR ANIMAL REMEDIES• 107Crotalu
- Page 111 and 112:
MAJOR ANIMAL REMEDIES• 109Lachesi
- Page 113 and 114:
MAJOR ANIMAL REMEDIES• 111Psorinu
- Page 115 and 116:
MAJOR ANIMAL REMEDIES• 113Syphili
- Page 117:
MAJOR ANIMAL REMEDIES• 115Tubercu
- Page 120 and 121:
118 • MINOR REMEDIESAbies canaden
- Page 122 and 123:
120 • MINOR REMEDIESAcidum oxalic
- Page 124 and 125:
122 • MINOR REMEDIESAgkistrodon c
- Page 126 and 127:
124 • MINOR REMEDIESAmylium nitro
- Page 128 and 129:
126 •MINOR REMEDIESARGENTUM METAL
- Page 130 and 131:
128 • MINOR REMEDIESAsclepias tub
- Page 132 and 133:
130 • MINOR REMEDIESBismuthum met
- Page 134 and 135:
132 • MINOR REMEDIESmalnutrition
- Page 136 and 137: 134 • MINOR REMEDIESCarbonium sul
- Page 138 and 139: 136 •MINOR REMEDIESChininum sulph
- Page 140 and 141: 138 • MINOR REMEDIESComocladia de
- Page 142 and 143: 140 • MINOR REMEDIESCuprum arseni
- Page 144 and 145: 142 • MINOR REMEDIESEquisetum hye
- Page 146 and 147: 144 • MINOR REMEDIESGalipea offic
- Page 148 and 149: 146 • MINOR REMEDIESHumulus lupul
- Page 150 and 151: 148 •MINOR REMEDIESThe remedy iso
- Page 152 and 153: 150 • MINOR REMEDIESKalium chlora
- Page 154 and 155: 152 • MINOR REMEDIESLatrodectus m
- Page 156 and 157: 154 • MINOR REMEDIESMagnesium sul
- Page 158 and 159: 156 • MINOR REMEDIESMygale lasiod
- Page 160 and 161: 158 • MINOR REMEDIESNicotiana tab
- Page 162 and 163: 160 • MINOR REMEDIESPiper cubebaC
- Page 164 and 165: 162 • MINOR REMEDIESRaphanus sati
- Page 166 and 167: 164 • MINOR REMEDIESSambucus nigr
- Page 168 and 169: 166 • MINOR REMEDIESSerenoa repen
- Page 170 and 171: 168 • MINOR REMEDIESStrychnos tox
- Page 172 and 173: 170 • MINOR REMEDIESTrinitrum syn
- Page 174 and 175: 172 • MINOR REMEDIESVetiveria ziz
- Page 177 and 178: seriousailments
- Page 179 and 180: SERIOUS AILMENTS• 177ASSESSING A
- Page 181 and 182: NERVOUS SYSTEM• 179MULTIPLE SCLER
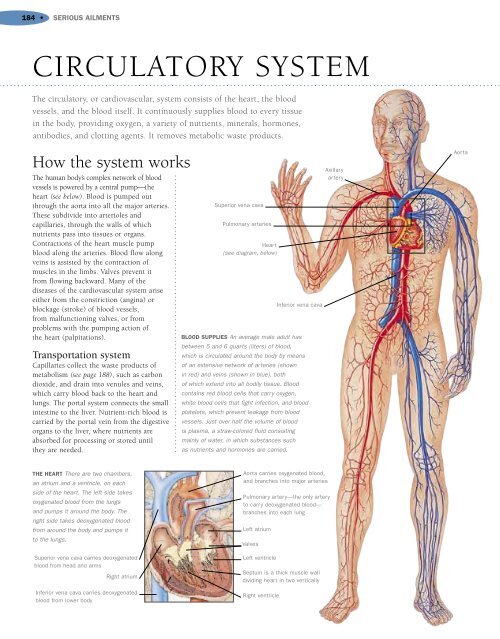
- Page 183 and 184: RESPIRATORY SYSTEM• 181ASTHMAAn a
- Page 185: RESPIRATORY SYSTEM• 183PNEUMONIAP
- Page 189 and 190: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM• 187STROKEA ce
- Page 191 and 192: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM• 189IRRITABLE BO
- Page 193 and 194: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM• 191DIABETESThe
- Page 195 and 196: SKIN & BONES• 193ROSACEARosacea,
- Page 197 and 198: SKIN & BONES• 195PSORIASISThis fa
- Page 199 and 200: SKIN & BONES• 197RHEUMATOID ARTHR
- Page 201 and 202: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS• 199FIBROIDS
- Page 203 and 204: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS• 201BREAST P
- Page 205 and 206: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS• 203INFERTIL
- Page 207 and 208: IMMUNE SYSTEM• 205CHRONIC FATIGUE
- Page 209 and 210: IMMUNE SYSTEM• 207mouth. Arsen. a
- Page 211 and 212: IMMUNE SYSTEM• 209of a person, es
- Page 213 and 214: MIND & EMOTIONS• 211PHOBIASA phob
- Page 215: MIND & EMOTION• 213GRIEFGrief is
- Page 218 and 219: 216 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPCHOOSIN
- Page 220 and 221: 218 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPNERVOUS
- Page 222 and 223: 220 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPTHE EYE
- Page 224 and 225: 222 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPTHE EAR
- Page 226 and 227: 224 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPRESPIRA
- Page 228 and 229: 226 • HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPDISORD
- Page 230 and 231: 228 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPDISORDE
- Page 232 and 233: 230 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPCIRCULA
- Page 234 and 235: 232 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPTHE MOU
- Page 236 and 237:
234 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPDIGESTI
- Page 238 and 239:
236 • HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPDISORD
- Page 240 and 241:
238 • HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPDISORD
- Page 242 and 243:
240 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPTHE SKI
- Page 244 and 245:
242 • HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPDISORD
- Page 246 and 247:
244 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPEMOTION
- Page 248 and 249:
246 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPCHILDRE
- Page 250 and 251:
248 • HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPDISORD
- Page 252 and 253:
250 • HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPDISORD
- Page 254 and 255:
252 • HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPDISORD
- Page 256 and 257:
254 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPHEALTH
- Page 258 and 259:
256 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPWOMEN
- Page 260 and 261:
258 • HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPDISORD
- Page 262 and 263:
260 • HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPDISORD
- Page 264 and 265:
262 • HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPDISORD
- Page 266 and 267:
264 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPMEN’S
- Page 268 and 269:
266 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPHEALTH
- Page 270 and 271:
268 • HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPDISORD
- Page 272 and 273:
270 •HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPFIRST A
- Page 274 and 275:
272 • HOMEOPATHIC FIRST AIDAILMEN
- Page 276 and 277:
274 • HOMEOPATHIC FIRST AIDAILMEN
- Page 278 and 279:
276 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCEA-Z QUICK
- Page 280 and 281:
278 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCEALLIUM SA
- Page 282 and 283:
280 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCEARANEA DI
- Page 284 and 285:
282 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCEBACILLINU
- Page 286 and 287:
284 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCECADMIUM S
- Page 288 and 289:
286 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCECARCINOSI
- Page 290 and 291:
288 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCECIMEXAcan
- Page 292 and 293:
290 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCECRATAEGUS
- Page 294 and 295:
292 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCEEUPHORBIU
- Page 296 and 297:
294 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCEHEPAR SUL
- Page 298 and 299:
296 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCEKALI. PHO
- Page 300 and 301:
298 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCEMAG. CARB
- Page 302 and 303:
300 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCEMILLEFOLI
- Page 304 and 305:
302 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCEORIGANUMO
- Page 306 and 307:
304 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCEPYROGEN.P
- Page 308 and 309:
306 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCESANICULAA
- Page 310 and 311:
308 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCESTRAMONIU
- Page 312 and 313:
310 •A-Z QUICK REFERENCETUBERCULI
- Page 314 and 315:
312 • HOW TO FIND A PRACTITIONERH
- Page 316 and 317:
314 •BIBLIOGRAPHYBIBLIOGRAPHYThis
- Page 318 and 319:
316 • INDEXINDEXPage numbers in b
- Page 320 and 321:
318 •INDEXautonomic nervous syste
- Page 322 and 323:
320 •INDEXCausticum Hahnemanni (C
- Page 324 and 325:
322 •INDEXdelirium tremens 60Delp
- Page 326 and 327:
324 •INDEXGGalen 12Galipea cuspar
- Page 328 and 329:
326 •INDEXinsomnia 244-45Aconitum
- Page 330 and 331:
328 •INDEXMerc. iod. flav. 299see
- Page 332 and 333:
330 •INDEXPareira brava (Pareira)
- Page 334 and 335:
332 • INDEXSSabadilla 305see also
- Page 336 and 337:
334 • INDEXsweet marjoram see Ori
- Page 338:
336 •ACKNOWLEDGMENTSACKNOWLEDGMEN