Encyclopedia of Homeopathy
Encyclopedia of Homeopathy
Encyclopedia of Homeopathy
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
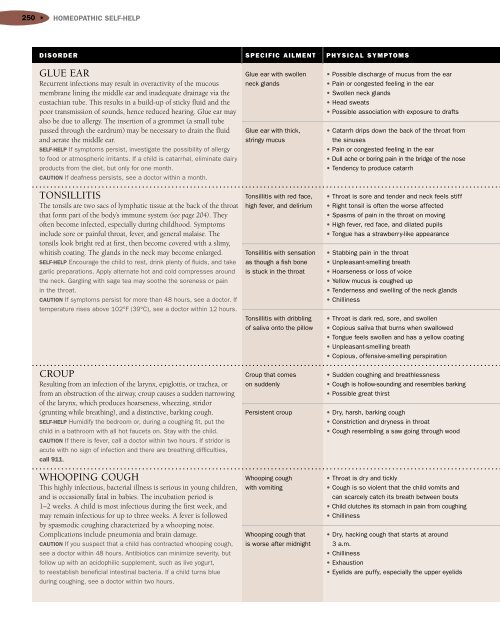
250 • HOMEOPATHIC SELF-HELPDISORDERGLUE EARRecurrent infections may result in overactivity <strong>of</strong> the mucousmembrane lining the middle ear and inadequate drainage via theeustachian tube. This results in a build-up <strong>of</strong> sticky fluid and thepoor transmission <strong>of</strong> sounds, hence reduced hearing. Glue ear mayalso be due to allergy. The insertion <strong>of</strong> a grommet (a small tubepassed through the eardrum) may be necessary to drain the fluidand aerate the middle ear.SELF-HELP If symptoms persist, investigate the possibility <strong>of</strong> allergyto food or atmospheric irritants. If a child is catarrhal, eliminate dairyproducts from the diet, but only for one month.CAUTION If deafness persists, see a doctor within a month.TONSILLITISThe tonsils are two sacs <strong>of</strong> lymphatic tissue at the back <strong>of</strong> the throatthat form part <strong>of</strong> the body’s immune system (see page 204). They<strong>of</strong>ten become infected, especially during childhood. Symptomsinclude sore or painful throat, fever, and general malaise. Thetonsils look bright red at first, then become covered with a slimy,whitish coating. The glands in the neck may become enlarged.SELF-HELP Encourage the child to rest, drink plenty <strong>of</strong> fluids, and takegarlic preparations. Apply alternate hot and cold compresses aroundthe neck. Gargling with sage tea may soothe the soreness or painin the throat.CAUTION If symptoms persist for more than 48 hours, see a doctor. Iftemperature rises above 102°F (39°C), see a doctor within 12 hours.CROUPResulting from an infection <strong>of</strong> the larynx, epiglottis, or trachea, orfrom an obstruction <strong>of</strong> the airway, croup causes a sudden narrowing<strong>of</strong> the larynx, which produces hoarseness, wheezing, stridor(grunting while breathing), and a distinctive, barking cough.SELF-HELP Humidify the bedroom or, during a coughing fit, put thechild in a bathroom with all hot faucets on. Stay with the child.CAUTION If there is fever, call a doctor within two hours. If stridor isacute with no sign <strong>of</strong> infection and there are breathing difficulties,call 911.WHOOPING COUGHThis highly infectious, bacterial illness is serious in young children,and is occasionally fatal in babies. The incubation period is1–2 weeks. A child is most infectious during the first week, andmay remain infectious for up to three weeks. A fever is followedby spasmodic coughing characterized by a whooping noise.Complications include pneumonia and brain damage.CAUTION If you suspect that a child has contracted whooping cough,see a doctor within 48 hours. Antibiotics can minimize severity, butfollow up with an acidophilic supplement, such as live yogurt,to reestablish beneficial intestinal bacteria. If a child turns blueduring coughing, see a doctor within two hours.SPECIFIC AILMENTGlue ear with swollenneck glandsGlue ear with thick,stringy mucusTonsillitis with red face,high fever, and deliriumTonsillitis with sensationas though a fish boneis stuck in the throatTonsillitis with dribbling<strong>of</strong> saliva onto the pillowCroup that comeson suddenlyPersistent croupWhooping coughwith vomitingWhooping cough thatis worse after midnightPHYSICAL SYMPTOMS• Possible discharge <strong>of</strong> mucus from the ear• Pain or congested feeling in the ear• Swollen neck glands• Head sweats• Possible association with exposure to drafts• Catarrh drips down the back <strong>of</strong> the throat fromthe sinuses• Pain or congested feeling in the ear• Dull ache or boring pain in the bridge <strong>of</strong> the nose• Tendency to produce catarrh• Throat is sore and tender and neck feels stiff• Right tonsil is <strong>of</strong>ten the worse affected• Spasms <strong>of</strong> pain in the throat on moving• High fever, red face, and dilated pupils• Tongue has a strawberry-like appearance• Stabbing pain in the throat• Unpleasant-smelling breath• Hoarseness or loss <strong>of</strong> voice• Yellow mucus is coughed up• Tenderness and swelling <strong>of</strong> the neck glands• Chilliness• Throat is dark red, sore, and swollen• Copious saliva that burns when swallowed• Tongue feels swollen and has a yellow coating• Unpleasant-smelling breath• Copious, <strong>of</strong>fensive-smelling perspiration• Sudden coughing and breathlessness• Cough is hollow-sounding and resembles barking• Possible great thirst• Dry, harsh, barking cough• Constriction and dryness in throat• Cough resembling a saw going through wood• Throat is dry and tickly• Cough is so violent that the child vomits andcan scarcely catch its breath between bouts• Child clutches its stomach in pain from coughing• Chilliness• Dry, hacking cough that starts at around3 a.m.• Chilliness• Exhaustion• Eyelids are puffy, especially the upper eyelids