grippers & rack and pinion rotary actuators - Industrial and Bearing ...
grippers & rack and pinion rotary actuators - Industrial and Bearing ...
grippers & rack and pinion rotary actuators - Industrial and Bearing ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
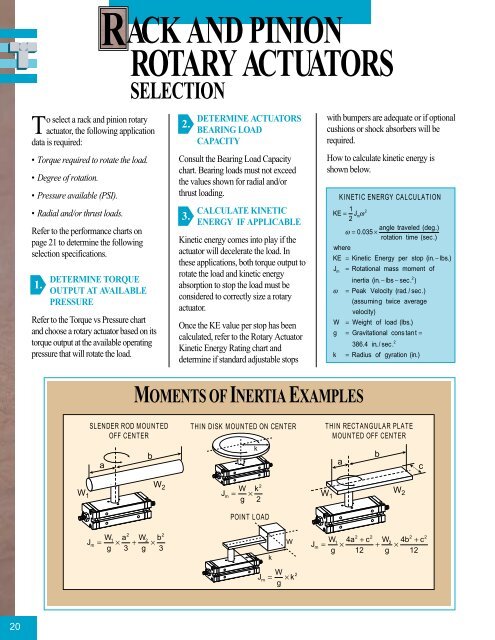
RACK AND PINIONROTARY ACTUATORSSELECTIONTo select a <strong>rack</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>pinion</strong> <strong>rotary</strong>actuator, the following applicationdata is required:• Torque required to rotate the load.• Degree of rotation.• Pressure available (PSI).• Radial <strong>and</strong>/or thrust loads.Refer to the performance charts onpage 21 to determine the followingselection specifications.1.DETERMINE TORQUEOUTPUT AT AVAILABLEPRESSURERefer to the Torque vs Pressure chart<strong>and</strong> choose a <strong>rotary</strong> actuator based on itstorque output at the available operatingpressure that will rotate the load.2.DETERMINE ACTUATORSBEARING LOADCAPACITYConsult the <strong>Bearing</strong> Load Capacitychart. <strong>Bearing</strong> loads must not exceedthe values shown for radial <strong>and</strong>/orthrust loading.3.CALCULATE KINETICENERGY IF APPLICABLEKinetic energy comes into play if theactuator will decelerate the load. Inthese applications, both torque output torotate the load <strong>and</strong> kinetic energyabsorption to stop the load must beconsidered to correctly size a <strong>rotary</strong>actuator.Once the KE value per stop has beencalculated, refer to the Rotary ActuatorKinetic Energy Rating chart <strong>and</strong>determine if st<strong>and</strong>ard adjustable stopswith bumpers are adequate or if optionalcushions or shock absorbers will berequired.How to calculate kinetic energy isshown below.KINETIC ENERGY CALCULATION1 2KE = Jmω2angle traveled (deg.)ω = 0.035 ×rotation time (sec.)whereKE = Kinetic Energy per stop ( in. −lbs.)Jm= Rotational mass moment of2inertia ( in. −lbs−sec. )ω = Peak Velocity ( rad. / sec.)( assuming twice averagevelocity)W = Weight of load ( lbs.)g = Gravitational cons tant=2386. 4 in. / sec.k = Radius of gyration ( in.)MOMENTS OF INERTIA EXAMPLESSLENDER ROD MOUNTEDOFF CENTERTHIN DISK MOUNTED ON CENTERTHIN RECTANGULAR PLATEMOUNTED OFF CENTERabkabcW 1W 2POINT LOAD2W kJ = mg× 2W 1W 222W1a W2bJm = × + ×g 3 g 32 2W W14a + c W24b+ cJm = × + ×g 12 g 12kWJm = × k2g2 220