grippers & rack and pinion rotary actuators - Industrial and Bearing ...
grippers & rack and pinion rotary actuators - Industrial and Bearing ...
grippers & rack and pinion rotary actuators - Industrial and Bearing ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
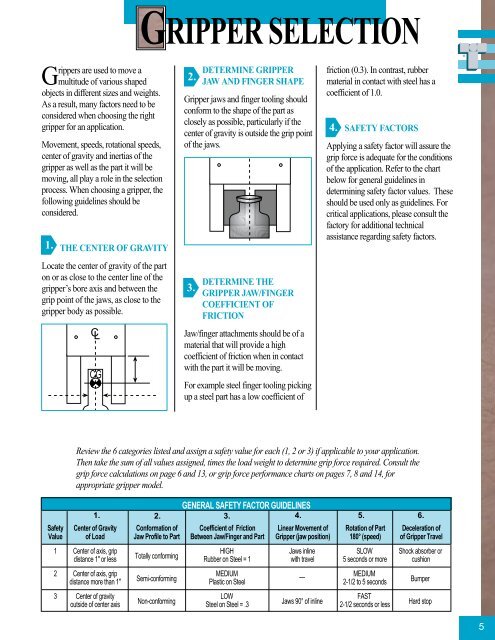
GRIPPER SELECTIONGrippers are used to move amultitude of various shapedobjects in different sizes <strong>and</strong> weights.As a result, many factors need to beconsidered when choosing the rightgripper for an application.Movement, speeds, rotational speeds,center of gravity <strong>and</strong> inertias of thegripper as well as the part it will bemoving, all play a role in the selectionprocess. When choosing a gripper, thefollowing guidelines should beconsidered.1.THE CENTER OF GRAVITYLocate the center of gravity of the parton or as close to the center line of thegripper’s bore axis <strong>and</strong> between thegrip point of the jaws, as close to thegripper body as possible.C LCG2.DETERMINE GRIPPERJAW AND FINGER SHAPEGripper jaws <strong>and</strong> finger tooling shouldconform to the shape of the part asclosely as possible, particularly if thecenter of gravity is outside the grip pointof the jaws.3.DETERMINE THEGRIPPER JAW/FINGERCOEFFICIENT OFFRICTIONJaw/finger attachments should be of amaterial that will provide a highcoefficient of friction when in contactwith the part it will be moving.For example steel finger tooling pickingup a steel part has a low coefficient offriction (0.3). In contrast, rubbermaterial in contact with steel has acoefficient of 1.0.4.SAFETY FACTORSApplying a safety factor will assure thegrip force is adequate for the conditionsof the application. Refer to the chartbelow for general guidelines indetermining safety factor values. Theseshould be used only as guidelines. Forcritical applications, please consult thefactory for additional technicalassistance regarding safety factors.Review the 6 categories listed <strong>and</strong> assign a safety value for each (1, 2 or 3) if applicable to your application.Then take the sum of all values assigned, times the load weight to determine grip force required. Consult thegrip force calculations on page 6 <strong>and</strong> 13, or grip force performance charts on pages 7, 8 <strong>and</strong> 14, forappropriate gripper model.GENERAL SAFETY FACTOR GUIDELINES1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.Safety Center of Gravity Conformation of Coefficient of Friction Linear Movement of Rotation of Part Deceleration ofValue of Load Jaw Profile to Part Between Jaw/Finger <strong>and</strong> Part Gripper (jaw position) 180° (speed) of Gripper Travel1 Center of axis, gripHIGH Jaws inline SLOW Shock absorber ordistance 1" or less Totally conforming Rubber on Steel = 1 with travel 5 seconds or more cushion2 Center of axis, gripMEDIUMSemi-conforming—MEDIUMdistance more than 1" Plastic on Steel 2-1/2 to 5 seconds3 Center of gravityLOWFASToutside of center axis Non-conformingSteel on Steel = .3 Jaws 90° of inline 2-1/2 seconds or lessBumperHard stop5