full pdf of issue - Middle East Journal of Family Medicine
full pdf of issue - Middle East Journal of Family Medicine
full pdf of issue - Middle East Journal of Family Medicine
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
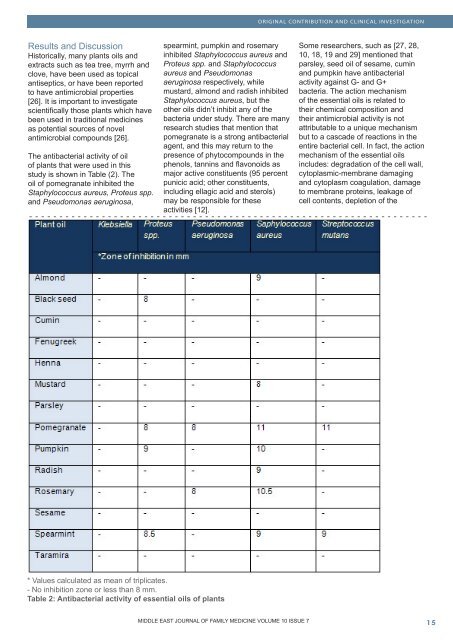
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION AND CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONResults and DiscussionHistorically, many plants oils andextracts such as tea tree, myrrh andclove, have been used as topicalantiseptics, or have been reportedto have antimicrobial properties[26]. It is important to investigatescientifically those plants which havebeen used in traditional medicinesas potential sources <strong>of</strong> novelantimicrobial compounds [26].The antibacterial activity <strong>of</strong> oil<strong>of</strong> plants that were used in thisstudy is shown in Table (2). Theoil <strong>of</strong> pomegranate inhibited theStaphylococcus aureus, Proteus spp.and Pseudomonas aeruginosa,spearmint, pumpkin and rosemaryinhibited Staphylococcus aureus andProteus spp. and Staphylococcusaureus and Pseudomonasaeruginosa respectively, whilemustard, almond and radish inhibitedStaphylococcus aureus, but theother oils didn’t inhibit any <strong>of</strong> thebacteria under study. There are manyresearch studies that mention thatpomegranate is a strong antibacterialagent, and this may return to thepresence <strong>of</strong> phytocompounds in thephenols, tannins and flavonoids asmajor active constituents (95 percentpunicic acid; other constituents,including ellagic acid and sterols)may be responsible for theseactivities [12].Some researchers, such as [27, 28,10, 18, 19 and 29] mentioned thatparsley, seed oil <strong>of</strong> sesame, cuminand pumpkin have antibacterialactivity against G- and G+bacteria. The action mechanism<strong>of</strong> the essential oils is related totheir chemical composition andtheir antimicrobial activity is notattributable to a unique mechanismbut to a cascade <strong>of</strong> reactions in theentire bacterial cell. In fact, the actionmechanism <strong>of</strong> the essential oilsincludes: degradation <strong>of</strong> the cell wall,cytoplasmic-membrane damagingand cytoplasm coagulation, damageto membrane proteins, leakage <strong>of</strong>cell contents, depletion <strong>of</strong> the* Values calculated as mean <strong>of</strong> triplicates.- No inhibition zone or less than 8 mm.Table 2: Antibacterial activity <strong>of</strong> essential oils <strong>of</strong> plantsMIDDLE MIDDLE EAST EAST JOURNAL JOURNAL OF OF FAMILY MEDICINE VOLUME • VOLUME 10 ISSUE 7, ISSUE 7 10 15