Download this publication - AIDS Data Hub
Download this publication - AIDS Data Hub
Download this publication - AIDS Data Hub
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
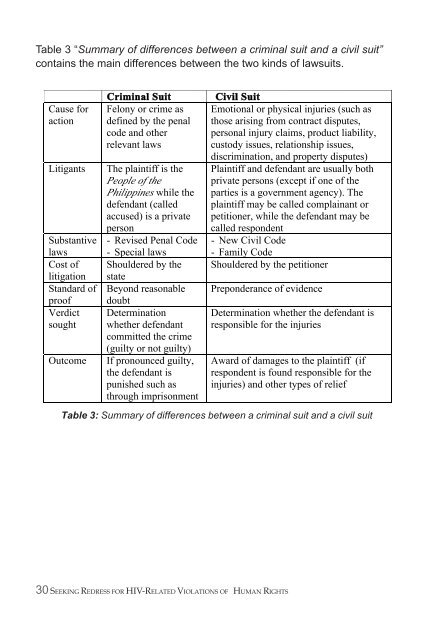
Table 3 “Summary of differences between a criminal suit and a civil suit”contains the main differences between the two kinds of lawsuits.Cause foractionLitigantsSubstantivelawsCost oflitigationStandard ofproofVerdictsoughtOutcomeCriminal SuitFelony or crime asdefined by the penalcode and otherrelevant lawsThe plaintiff is thePeople of thePhilippines while thedefendant (calledaccused) is a privateperson- Revised Penal Code- Special lawsShouldered by thestateBeyond reasonabledoubtDeterminationwhether defendantcommitted the crime(guilty or not guilty)If pronounced guilty,the defendant ispunished such asthrough imprisonmentCivil SuitEmotional or physical injuries (such asthose arising from contract disputes,personal injury claims, product liability,custody issues, relationship issues,discrimination, and property disputes)Plaintiff and defendant are usually bothprivate persons (except if one of theparties is a government agency). Theplaintiff may be called complainant orpetitioner, while the defendant may becalled respondent- New Civil Code- Family CodeShouldered by the petitionerPreponderance of evidenceDetermination whether the defendant isresponsible for the injuriesAward of damages to the plaintiff (ifrespondent is found responsible for theinjuries) and other types of reliefTable 3: Summary of differences between a criminal suit and a civil suit30 SEEKING REDRESS FOR HIV-RELATED VIOLATIONS OF HUMAN RIGHTS