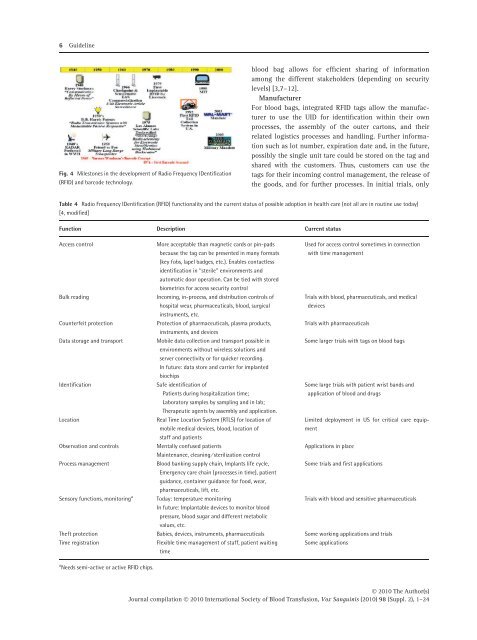
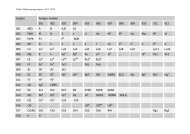
6 Guidel<strong>in</strong>eFig. 4 Milestones <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> development <strong>of</strong> Radio Frequency IDentification(<strong>RFID</strong>) and barcode technology.blood bag allows <strong>for</strong> efficient shar<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mationamong <strong>the</strong> different stakeholders (depend<strong>in</strong>g on securitylevels) [3,7–12].ManufacturerFor blood bags, <strong>in</strong>tegrated <strong>RFID</strong> tags allow <strong>the</strong> manufacturerto use <strong>the</strong> UID <strong>for</strong> identification with<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>ir ownprocesses, <strong>the</strong> assembly <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> outer cartons, and <strong>the</strong>irrelated logistics processes and handl<strong>in</strong>g. Fur<strong>the</strong>r <strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mationsuch as lot number, expiration date and, <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> future,possibly <strong>the</strong> s<strong>in</strong>gle unit tare could be stored on <strong>the</strong> tag andshared with <strong>the</strong> customers. Thus, customers can use <strong>the</strong>tags <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong>ir <strong>in</strong>com<strong>in</strong>g control management, <strong>the</strong> release <strong>of</strong><strong>the</strong> goods, and <strong>for</strong> fur<strong>the</strong>r processes. In <strong>in</strong>itial trials, onlyTable 4 Radio Frequency IDentification (<strong>RFID</strong>) functionality and <strong>the</strong> current status <strong>of</strong> possible adoption <strong>in</strong> health care (not all are <strong>in</strong> rout<strong>in</strong>e use today)[4, modified]Function Description Current statusAccess controlBulk read<strong>in</strong>gCounterfeit protectionData storage and transportIdentificationLocationObservation and controlsProcess managementSensory functions, monitor<strong>in</strong>g aMore acceptable than magnetic cards or p<strong>in</strong>-padsbecause <strong>the</strong> tag can be presented <strong>in</strong> many <strong>for</strong>mats(key fobs, lapel badges, etc.). Enables contactlessidentification <strong>in</strong> ‘‘sterile’’ environments andautomatic door operation. Can be tied with storedbiometrics <strong>for</strong> access security controlIncom<strong>in</strong>g, <strong>in</strong>-process, and distribution controls <strong>of</strong>hospital wear, pharmaceuticals, blood, surgical<strong>in</strong>struments, etc.Protection <strong>of</strong> pharmaceuticals, plasma products,<strong>in</strong>struments, and devicesMobile data collection and transport possible <strong>in</strong>environments without wireless solutions andserver connectivity or <strong>for</strong> quicker record<strong>in</strong>g.In future: data store and carrier <strong>for</strong> implantedbiochipsSafe identification <strong>of</strong>Patients dur<strong>in</strong>g hospitalization time;Laboratory samples by sampl<strong>in</strong>g and <strong>in</strong> lab;Therapeutic agents by assembly and application.Real Time Location System (RTLS) <strong>for</strong> location <strong>of</strong>mobile medical devices, blood, location <strong>of</strong>staff and patientsMentally confused patientsMa<strong>in</strong>tenance, clean<strong>in</strong>g ⁄ sterilization controlBlood bank<strong>in</strong>g supply cha<strong>in</strong>, Implants life cycle,Emergency care cha<strong>in</strong> (processes <strong>in</strong> time), patientguidance, conta<strong>in</strong>er guidance <strong>for</strong> food, wear,pharmaceuticals, lift, etc.Today: temperature monitor<strong>in</strong>gIn future: Implantable devices to monitor bloodpressure, blood sugar and different metabolicvalues, etc.<strong>Use</strong>d <strong>for</strong> access control sometimes <strong>in</strong> connectionwith time managementTrials with blood, pharmaceuticals, and medicaldevicesTrials with pharmaceuticalsSome larger trials with tags on blood bagsSome large trials with patient wrist bands andapplication <strong>of</strong> blood and drugsLimited deployment <strong>in</strong> US <strong>for</strong> critical care equipmentApplications <strong>in</strong> placeSome trials and first applicationsTrials with blood and sensitive pharmaceuticalsTheft protection Babies, devices, <strong>in</strong>struments, pharmaceuticals Some work<strong>in</strong>g applications and trialsTime registrationFlexible time management <strong>of</strong> staff, patient wait<strong>in</strong>g Some applicationstimea Needs semi-active or active <strong>RFID</strong> chips.Ó 2010 The Author(s)Journal compilation Ó 2010 International Society <strong>of</strong> Blood <strong>Transfusion</strong>, Vox Sangu<strong>in</strong>is (2010) 98 (Suppl. 2), 1–24
Guidel<strong>in</strong>e 7<strong>the</strong> red cell packs were fitted with tags, however <strong>for</strong> <strong>in</strong>tegratedtriple or quadruple systems <strong>the</strong> tag could be usedalso <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> whole blood. Plasma bags were fitted with tagslater <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> manufactur<strong>in</strong>g process to observe <strong>in</strong>activationsteps. A future comprehensive solution may need two <strong>RFID</strong>tags, one <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> red cells and one <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> plasma bag[3,8,11].DonationIf blood bag systems with <strong>in</strong>tegrated <strong>RFID</strong>-labels are notavailable, tags could be added at <strong>the</strong> collection site. Dur<strong>in</strong>g<strong>the</strong> donation process, <strong>the</strong> release <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> collection bag set,<strong>the</strong> bag tare (comparison <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> declared with <strong>the</strong> tare measuredat <strong>the</strong> donation site can detect loss <strong>of</strong> fluid) and expirationdate could be checked by <strong>the</strong> collection devices<strong>of</strong>tware. Relevant donation data such as user, time anddate, collection period, weight, and <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> future, possibly,unique lab tube numbers, etc. could be written to <strong>the</strong> tag.[3,8,11].When <strong>the</strong> Donation Number label is applied to <strong>the</strong> bagset at <strong>the</strong> po<strong>in</strong>t <strong>of</strong> collection, a simple hand-held comb<strong>in</strong>edbarcode and <strong>RFID</strong> reader may be used to read <strong>the</strong> ISBT 128Donation Number barcode [1] and program it and o<strong>the</strong>r relevant<strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation <strong>in</strong>to <strong>the</strong> <strong>RFID</strong> tag.Process<strong>in</strong>g<strong>RFID</strong> allows automatic identification <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> bags with<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>read range. Major improvements are possible, <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong>ability <strong>for</strong> bulk read<strong>in</strong>g and no need <strong>for</strong> l<strong>in</strong>e-<strong>of</strong>-sight <strong>for</strong>scann<strong>in</strong>g, which make it easy <strong>for</strong> employees to per<strong>for</strong>mconcurrent manual activities.Storage and distributionQuality and ⁄ or security checks, e.g. visual controls, specimens<strong>for</strong> content measur<strong>in</strong>g and so on are <strong>of</strong>ten registeredon paper sheets; <strong>the</strong>se could be monitored moreeasily and rules en<strong>for</strong>cement could be checked at severalpo<strong>in</strong>ts with<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> distribution cha<strong>in</strong>. Similar applicationsare used today <strong>for</strong> security and ma<strong>in</strong>tenance by companies<strong>in</strong> o<strong>the</strong>r <strong>in</strong>dustries. The addition <strong>of</strong> laboratory datato <strong>the</strong> tag (e.g. cross-match<strong>in</strong>g, antibody screen<strong>in</strong>g) couldalso <strong>of</strong>fer some significant process control benefits[3,7,9–11,13].Product turnover could be more easily managed toreduce outdat<strong>in</strong>g, and units required to meet specificcl<strong>in</strong>ical requirements could be more rapidly located and ⁄ orre-allocated, ei<strong>the</strong>r with<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> storage equipment or with amobile reader [3,8–11,13]. Such processes have been successfullyused <strong>in</strong> several libraries <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> management <strong>of</strong><strong>the</strong>ir collections.Dur<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> distribution process, bulk packag<strong>in</strong>g could bechecked <strong>for</strong> completeness and <strong>the</strong> transmission <strong>of</strong> shipment<strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation could be done rapidly us<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> <strong>RFID</strong> label.Receipt <strong>of</strong> bulk deliveries <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> hospital cl<strong>in</strong>ic laboratoriescould be significantly improved, allow<strong>in</strong>g pro<strong>of</strong>-<strong>of</strong>-deliveryreconciliation, and also provid<strong>in</strong>g a rapid means <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong><strong>in</strong>com<strong>in</strong>g components to be scanned and relevant dataloaded <strong>in</strong>to hospital <strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation systems [3,7–11].A far greater degree <strong>of</strong> automated monitor<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> productlocation may be possible with readers positioned <strong>in</strong> equipmentacross <strong>the</strong> cold distribution cha<strong>in</strong> where it is necessaryto know <strong>the</strong> storage temperature <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> products.However, <strong>the</strong>re are difficulties relat<strong>in</strong>g to <strong>the</strong> small rangesand <strong>the</strong> different storage temperatures. Monitor<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> everyshipment <strong>of</strong> bags is currently possible but is <strong>in</strong>efficient andexpensive. The use <strong>of</strong> semi-active labels with temperaturemonitor<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> shipp<strong>in</strong>g cartons allows products to be monitoreddur<strong>in</strong>g transportation [11]. The same label could beused <strong>in</strong> facilities without central temperature monitor<strong>in</strong>gsystems to observe <strong>the</strong> storage temperatures <strong>of</strong> red cells andplatelets. The low storage temperature <strong>of</strong> plasma can affect<strong>the</strong> shelf life <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> tag battery.3.3.3 Patient IdentificationPatient identification has relied upon direct <strong>in</strong>quiry <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>patient; referr<strong>in</strong>g to notes attached to <strong>the</strong> patient wristbandor per<strong>for</strong>m<strong>in</strong>g a bedside test to control <strong>the</strong> patient’sblood group. Verbal statements given <strong>in</strong> difficult situationsare <strong>of</strong>ten ambiguous; handwritten or pr<strong>in</strong>ted wristbandsand bedside test-cards can be <strong>in</strong>correctly applied or<strong>in</strong>terpreted.The use <strong>of</strong> automated identification technologies onwristbands is grow<strong>in</strong>g with l<strong>in</strong>ear barcodes, 2D barcodesand <strong>RFID</strong> bands available. The first trials with <strong>RFID</strong> wristbandsshowed <strong>the</strong> feasibility <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> technique [13–15], but<strong>the</strong>re are some technical issues with <strong>the</strong> use <strong>of</strong> <strong>RFID</strong> <strong>for</strong> thispurpose. For example, magnetic resonance imag<strong>in</strong>g techniquesand, <strong>for</strong> some k<strong>in</strong>d <strong>of</strong> <strong>RFID</strong> tags, x-ray irradiation,have been shown to destroy <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation on <strong>RFID</strong> tags.It will be essential to overcome this limitation.O<strong>the</strong>r potential applications <strong>of</strong> patient identification with<strong>RFID</strong> <strong>in</strong>clude bill<strong>in</strong>g functions, such as bed side charges <strong>for</strong>medication, supplies or special care functions; cafeteria services,telephone calls, and pay per view television. Additionalpossible applications are <strong>the</strong> track<strong>in</strong>g and ⁄ orguidance <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> patient through <strong>the</strong> hospital, <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>gaccess control and queue management, and specializedapplications <strong>for</strong> patient monitor<strong>in</strong>g and security, such aspsychiatry, dementia care and neonatology [16].3.3.4 <strong>Transfusion</strong> ManagementFor <strong>the</strong> collection <strong>of</strong> pre-transfusion blood samples and<strong>the</strong> transfusion <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> blood at <strong>the</strong> bedside, it is necessaryto use unique patient identification and tubes with prepr<strong>in</strong>tedunique sample numbers. With barcodes or <strong>RFID</strong>tags on <strong>the</strong> patient wristband, <strong>the</strong> sample tube, and <strong>the</strong>blood bag, it is possible to cross-check <strong>the</strong> collection <strong>of</strong>Ó 2010 The Author(s)Journal compilation Ó 2010 International Society <strong>of</strong> Blood <strong>Transfusion</strong>, Vox Sangu<strong>in</strong>is (2010) 98 (Suppl. 2), 1–24