Literacy Trends in Pakistan - UNESCO Islamabad
Literacy Trends in Pakistan - UNESCO Islamabad
Literacy Trends in Pakistan - UNESCO Islamabad
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
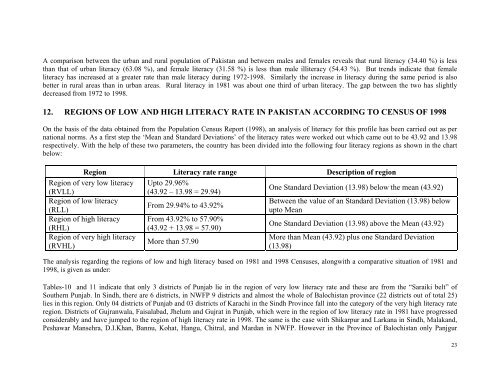
A comparison between the urban and rural population of <strong>Pakistan</strong> and between males and females reveals that rural literacy (34.40 %) is lessthan that of urban literacy (63.08 %), and female literacy (31.58 %) is less than male illiteracy (54.43 %). But trends <strong>in</strong>dicate that femaleliteracy has <strong>in</strong>creased at a greater rate than male literacy dur<strong>in</strong>g 1972-1998. Similarly the <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> literacy dur<strong>in</strong>g the same period is alsobetter <strong>in</strong> rural areas than <strong>in</strong> urban areas. Rural literacy <strong>in</strong> 1981 was about one third of urban literacy. The gap between the two has slightlydecreased from 1972 to 1998.12. REGIONS OF LOW AND HIGH LITERACY RATE IN PAKISTAN ACCORDING TO CENSUS OF 1998On the basis of the data obta<strong>in</strong>ed from the Population Census Report (1998), an analysis of literacy for this profile has been carried out as pernational norms. As a first step the ‘Mean and Standard Deviations’ of the literacy rates were worked out which came out to be 43.92 and 13.98respectively. With the help of these two parameters, the country has been divided <strong>in</strong>to the follow<strong>in</strong>g four literacy regions as shown <strong>in</strong> the chartbelow:Region <strong>Literacy</strong> rate range Description of regionRegion of very low literacy Upto 29.96%One Standard Deviation (13.98) below the mean (43.92)(RVLL)(43.92 – 13.98 = 29.94)Region of low literacyBetween the value of an Standard Deviation (13.98) belowFrom 29.94% to 43.92%(RLL)upto MeanRegion of high literacy From 43.92% to 57.90%One Standard Deviation (13.98) above the Mean (43.92)(RHL)(43.92 + 13.98 = 57.90)Region of very high literacyMore than Mean (43.92) plus one Standard DeviationMore than 57.90(RVHL)(13.98)The analysis regard<strong>in</strong>g the regions of low and high literacy based on 1981 and 1998 Censuses, alongwith a comparative situation of 1981 and1998, is given as under:Tables-10 and 11 <strong>in</strong>dicate that only 3 districts of Punjab lie <strong>in</strong> the region of very low literacy rate and these are from the “Saraiki belt” ofSouthern Punjab. In S<strong>in</strong>dh, there are 6 districts, <strong>in</strong> NWFP 9 districts and almost the whole of Balochistan prov<strong>in</strong>ce (22 districts out of total 25)lies <strong>in</strong> this region. Only 04 districts of Punjab and 03 districts of Karachi <strong>in</strong> the S<strong>in</strong>dh Prov<strong>in</strong>ce fall <strong>in</strong>to the category of the very high literacy rateregion. Districts of Gujranwala, Faisalabad, Jhelum and Gujrat <strong>in</strong> Punjab, which were <strong>in</strong> the region of low literacy rate <strong>in</strong> 1981 have progressedconsiderably and have jumped to the region of high literacy rate <strong>in</strong> 1998. The same is the case with Shikarpur and Larkana <strong>in</strong> S<strong>in</strong>dh, Malakand,Peshawar Mansehra, D.I.Khan, Bannu, Kohat, Hangu, Chitral, and Mardan <strong>in</strong> NWFP. However <strong>in</strong> the Prov<strong>in</strong>ce of Balochistan only Panjgur23