CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION 1.0 Chapter Overview - DSpace@UM
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION 1.0 Chapter Overview - DSpace@UM
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION 1.0 Chapter Overview - DSpace@UM
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
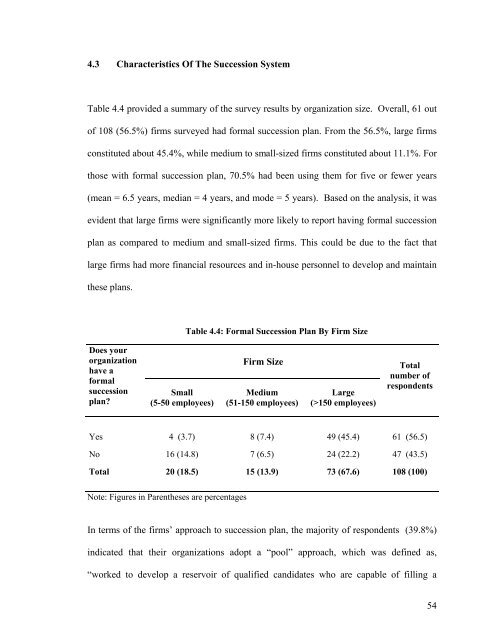
4.3 Characteristics Of The Succession SystemTable 4.4 provided a summary of the survey results by organization size. Overall, 61 outof 108 (56.5%) firms surveyed had formal succession plan. From the 56.5%, large firmsconstituted about 45.4%, while medium to small-sized firms constituted about 11.1%. Forthose with formal succession plan, 70.5% had been using them for five or fewer years(mean = 6.5 years, median = 4 years, and mode = 5 years). Based on the analysis, it wasevident that large firms were significantly more likely to report having formal successionplan as compared to medium and small-sized firms. This could be due to the fact thatlarge firms had more financial resources and in-house personnel to develop and maintainthese plans.Table 4.4: Formal Succession Plan By Firm SizeDoes yourorganizationhave aformalsuccessionplan?Small(5-50 employees)Firm SizeMedium(51-150 employees)Large(>150 employees)Totalnumber ofrespondentsYes 4 (3.7) 8 (7.4) 49 (45.4) 61 (56.5)No 16 (14.8) 7 (6.5) 24 (22.2) 47 (43.5)Total 20 (18.5) 15 (13.9) 73 (67.6) 108 (100)Note: Figures in Parentheses are percentagesIn terms of the firms’ approach to succession plan, the majority of respondents (39.8%)indicated that their organizations adopt a “pool” approach, which was defined as,“worked to develop a reservoir of qualified candidates who are capable of filling a54