Southern Blue Ridge: An Analysis of Matrix Forests - Conservation ...
Southern Blue Ridge: An Analysis of Matrix Forests - Conservation ...
Southern Blue Ridge: An Analysis of Matrix Forests - Conservation ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
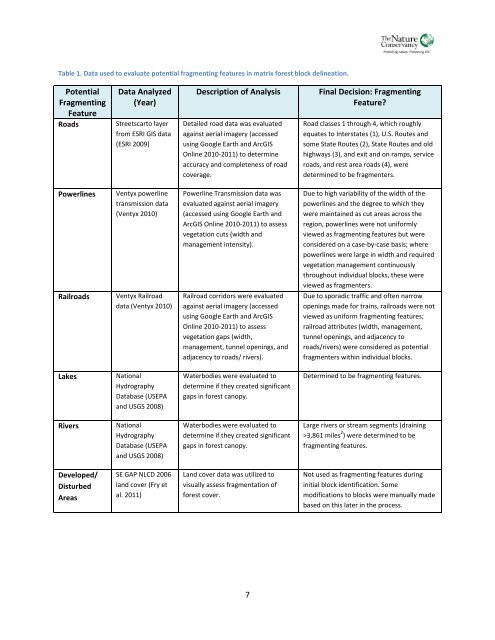
Table 1. Data used to evaluate potential fragmenting features in matrix forest block delineation.PotentialFragmentingFeatureRoadsData <strong>An</strong>alyzed(Year)Streetscarto layerfrom ESRI GIS data(ESRI 2009)Description <strong>of</strong> <strong>An</strong>alysisDetailed road data was evaluatedagainst aerial imagery (accessedusing Google Earth and ArcGISOnline 2010-2011) to determineaccuracy and completeness <strong>of</strong> roadcoverage.Final Decision: FragmentingFeature?Road classes 1 through 4, which roughlyequates to Interstates (1), U.S. Routes andsome State Routes (2), State Routes and oldhighways (3), and exit and on ramps, serviceroads, and rest area roads (4), weredetermined to be fragmenters.PowerlinesRailroadsVentyx powerlinetransmission data(Ventyx 2010)Ventyx Railroaddata (Ventyx 2010)Powerline Transmission data wasevaluated against aerial imagery(accessed using Google Earth andArcGIS Online 2010-2011) to assessvegetation cuts (width andmanagement intensity).Railroad corridors were evaluatedagainst aerial imagery (accessedusing Google Earth and ArcGISOnline 2010-2011) to assessvegetation gaps (width,management, tunnel openings, andadjacency to roads/ rivers).Due to high variability <strong>of</strong> the width <strong>of</strong> thepowerlines and the degree to which theywere maintained as cut areas across theregion, powerlines were not uniformlyviewed as fragmenting features but wereconsidered on a case-by-case basis; wherepowerlines were large in width and requiredvegetation management continuouslythroughout individual blocks, these wereviewed as fragmenters.Due to sporadic traffic and <strong>of</strong>ten narrowopenings made for trains, railroads were notviewed as uniform fragmenting features;railroad attributes (width, management,tunnel openings, and adjacency toroads/rivers) were considered as potentialfragmenters within individual blocks.LakesNationalHydrographyDatabase (USEPAand USGS 2008)Waterbodies were evaluated todetermine if they created significantgaps in forest canopy.Determined to be fragmenting features.RiversNationalHydrographyDatabase (USEPAand USGS 2008)Waterbodies were evaluated todetermine if they created significantgaps in forest canopy.Large rivers or stream segments (draining>3,861 miles 2 ) were determined to befragmenting features.Developed/DisturbedAreasSE GAP NLCD 2006land cover (Fry etal. 2011)Land cover data was utilized tovisually assess fragmentation <strong>of</strong>forest cover.Not used as fragmenting features duringinitial block identification. Somemodifications to blocks were manually madebased on this later in the process.7