Multivariate Gaussianization for Data Processing
Multivariate Gaussianization for Data Processing
Multivariate Gaussianization for Data Processing
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
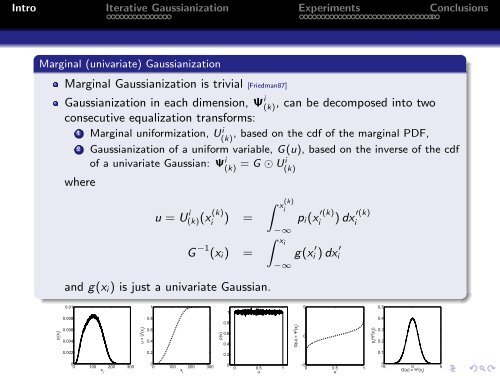
Intro Iterative <strong>Gaussianization</strong> Experiments ConclusionsMarginal (univariate) <strong>Gaussianization</strong>Marginal <strong>Gaussianization</strong> is trivial [Friedman87]<strong>Gaussianization</strong> in each dimension, Ψ i (k), can be decomposed into twoconsecutive equalization trans<strong>for</strong>ms:1 Marginal uni<strong>for</strong>mization, U(k) i , based on the cdf of the marginal PDF,2 <strong>Gaussianization</strong> of a uni<strong>for</strong>m variable, G(u), based on the inverse of the cdfof a univariate Gaussian: Ψ i (k) = G ⊙ Ui (k)whereu = U i (k)(x (k)i) =G −1 (x i ) =∫ x(k)i−∞∫ xi−∞p i (x ′(k)i) dx ′(k)ig(x i ′ ) dx i′and g(x i ) is just a univariate Gaussian.0.011150.5p i(x i)0.0080.0060.004u = U i (x i)0.80.60.4p(u)0.80.60.4G(u) = Ψ i (x i)0p i(Ψ i (x i))0.40.30.20.0020.20.20.100 100 200 300x i00 100 200 300x i00 0.5 1u−50 0.5 1u0−5 0 5G(u) = Ψ i (x i)