Chapter 105
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
1782 PART 5 ■ Anesthetic, Surgical, and Interventional Procedures: Considerations<br />
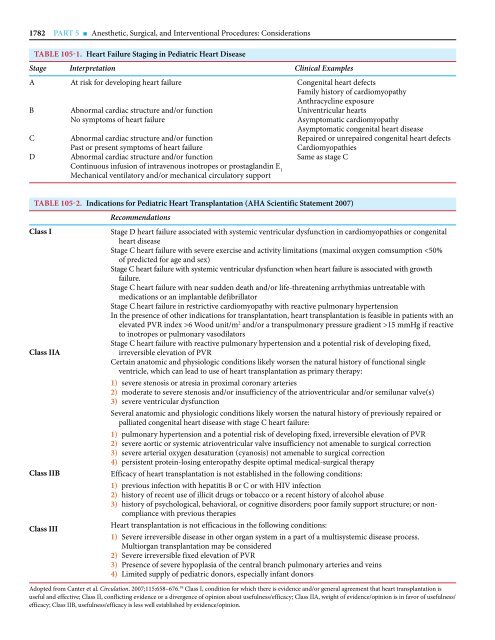
TABLE <strong>105</strong>-1. Heart Failure Staging in Pediatric Heart Disease<br />
Stage Interpretation Clinical Examples<br />
A<br />
B<br />
C<br />
D<br />
At risk for developing heart failure<br />
Abnormal cardiac structure and/or function<br />
No symptoms of heart failure<br />
Abnormal cardiac structure and/or function<br />
Past or present symptoms of heart failure<br />
Abnormal cardiac structure and/or function<br />
Continuous infusion of intravenous inotropes or prostaglandin E 1<br />
Mechanical ventilatory and/or mechanical circulatory support<br />
Congenital heart defects<br />
Family history of cardiomyopathy<br />
Anthracycline exposure<br />
Univentricular hearts<br />
Asymptomatic cardiomyopathy<br />
Asymptomatic congenital heart disease<br />
Repaired or unrepaired congenital heart defects<br />
Cardiomyopathies<br />
Same as stage C<br />
TABLE <strong>105</strong>-2. Indications for Pediatric Heart Transplantation (AHA Scientific Statement 2007)<br />
Class I<br />
Class IIA<br />
Class IIB<br />
Class III<br />
Recommendations<br />
Stage D heart failure associated with systemic ventricular dysfunction in cardiomyopathies or congenital<br />
heart disease<br />
Stage C heart failure with severe exercise and activity limitations (maximal oxygen comsumption 6 Wood unit/m 2 and/or a transpulmonary pressure gradient >15 mmHg if reactive<br />
to inotropes or pulmonary vasodilators<br />
Stage C heart failure with reactive pulmonary hypertension and a potential risk of developing fixed,<br />
irreversible elevation of PVR<br />
Certain anatomic and physiologic conditions likely worsen the natural history of functional single<br />
ventricle, which can lead to use of heart transplantation as primary therapy:<br />
1) severe stenosis or atresia in proximal coronary arteries<br />
2) moderate to severe stenosis and/or insufficiency of the atrioventricular and/or semilunar valve(s)<br />
3) severe ventricular dysfunction<br />
Several anatomic and physiologic conditions likely worsen the natural history of previously repaired or<br />
palliated congenital heart disease with stage C heart failure:<br />
1) pulmonary hypertension and a potential risk of developing fixed, irreversible elevation of PVR<br />
2) severe aortic or systemic atrioventricular valve insufficiency not amenable to surgical correction<br />
3) severe arterial oxygen desaturation (cyanosis) not amenable to surgical correction<br />
4) persistent protein-losing enteropathy despite optimal medical-surgical therapy<br />
Efficacy of heart transplantation is not established in the following conditions:<br />
1) previous infection with hepatitis B or C or with HIV infection<br />
2) history of recent use of illicit drugs or tobacco or a recent history of alcohol abuse<br />
3) history of psychological, behavioral, or cognitive disorders; poor family support structure; or non -<br />
compliance with previous therapies<br />
Heart transplantation is not efficacious in the following conditions:<br />
1) Severe irreversible disease in other organ system in a part of a multisystemic disease process.<br />
Multiorgan transplantation may be considered<br />
2) Severe irreversible fixed elevation of PVR<br />
3) Presence of severe hypoplasia of the central branch pulmonary arteries and veins<br />
4) Limited supply of pediatric donors, especially infant donors<br />
Adopted from Canter et al. Circulation. 2007;115:658–676. 59 Class I, condition for which there is evidence and/or general agreement that heart transplantation is<br />
useful and effective; Class II, conflicting evidence or a divergence of opinion about usefulness/efficacy; Class IIA, weight of evidence/opinion is in favor of usefulness/<br />
efficacy; Class IIB, usefulness/efficacy is less well established by evidence/opinion.