Pressure Support Ventilation - A New Triggered Venilation Mode for Neonates
Booklet about pressure support ventilation written by Jean Christophe Roze and Thomas Krueger.
Booklet about pressure support ventilation written by Jean Christophe Roze and Thomas Krueger.
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
48|49<br />
7.3 MONITORING PRESSURE SUPPORT VENTILATION<br />
Be<strong>for</strong>e we consider monitoring of <strong>Pressure</strong> <strong>Support</strong> <strong>Ventilation</strong>, we first have<br />
to remember the physiological background of respiratory control of the<br />
neonate.<br />
7.3.1 PHYSIOLOGICAL BACKGROUND<br />
7.3.1.1 CHEMICAL CONTROL<br />
Although the role of chemical stimulation in the transition from intermittent<br />
breathing of the fetus to continuous breathing is questioned, [52] the role of<br />
PaCO 2 and PaO 2 on the control of breathing is well established in the<br />
newborn after birth. Immediately after birth, O 2 receptors are silent because<br />
of postnatal hyperoxia relative to fetal low PaO 2 (25-28 mmHg). Later, in case<br />
1200<br />
Minute <strong>Ventilation</strong> (ml/min/kg)<br />
900<br />
600<br />
30 Days<br />
2 Days<br />
D-22608-2010<br />
300<br />
0 2 4 6<br />
PaO 2 (torr)<br />
8 10<br />
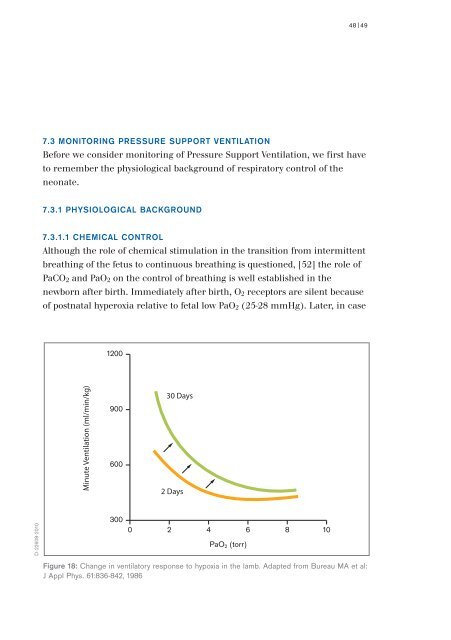
Figure 18: Change in ventilatory response to hypoxia in the lamb. Adapted from Bureau MA et al:<br />
J Appl Phys. 61:836-842, 1986