Pressure Support Ventilation - A New Triggered Venilation Mode for Neonates
Booklet about pressure support ventilation written by Jean Christophe Roze and Thomas Krueger.
Booklet about pressure support ventilation written by Jean Christophe Roze and Thomas Krueger.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
PRESSURE SUPPORT VENTILATION |<br />
PRESSURE SUPPORT VENTILATION IN PRACTICE<br />
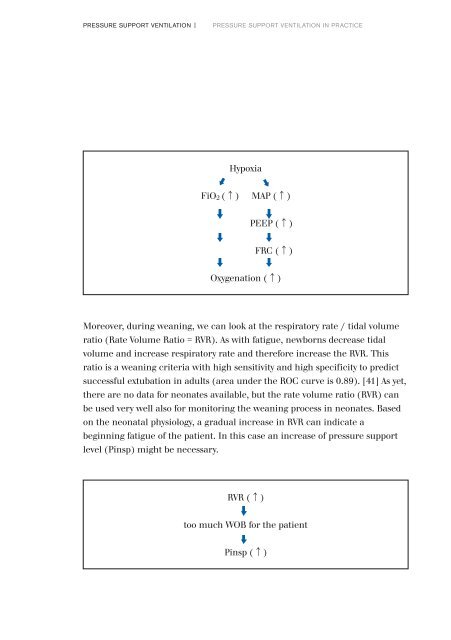
Hypoxia<br />
FiO 2 (↑)<br />
MAP (↑)<br />
PEEP (↑)<br />
FRC (↑)<br />
Oxygenation (↑)<br />
Moreover, during weaning, we can look at the respiratory rate / tidal volume<br />
ratio (Rate Volume Ratio = RVR). As with fatigue, newborns decrease tidal<br />
volume and increase respiratory rate and there<strong>for</strong>e increase the RVR. This<br />
ratio is a weaning criteria with high sensitivity and high specificity to predict<br />
successful extubation in adults (area under the ROC curve is 0.89). [41] As yet,<br />
there are no data <strong>for</strong> neonates available, but the rate volume ratio (RVR) can<br />
be used very well also <strong>for</strong> monitoring the weaning process in neonates. Based<br />
on the neonatal physiology, a gradual increase in RVR can indicate a<br />
beginning fatigue of the patient. In this case an increase of pressure support<br />
level (Pinsp) might be necessary.<br />
RVR (↑)<br />
too much WOB <strong>for</strong> the patient<br />
Pinsp (↑)