Airway Assessment
2cKbSEQ
2cKbSEQ
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
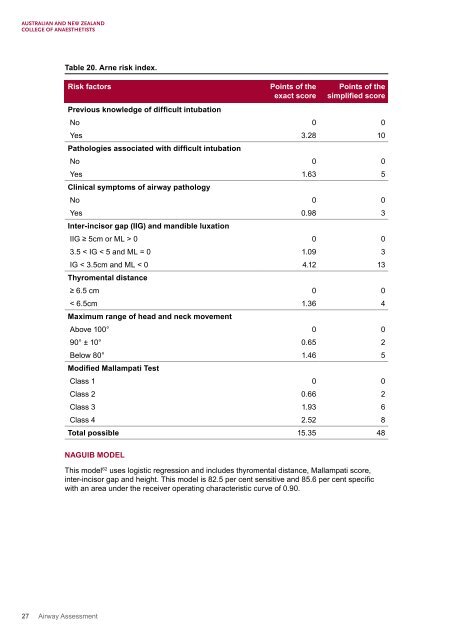
Table 20. Arne risk index.<br />
Risk factors<br />
Points of the<br />
exact score<br />
Points of the<br />
simplified score<br />
Previous knowledge of difficult intubation<br />
No 0 0<br />
Yes 3.28 10<br />
Pathologies associated with difficult intubation<br />
No 0 0<br />
Yes 1.63 5<br />
Clinical symptoms of airway pathology<br />
No 0 0<br />
Yes 0.98 3<br />
Inter-incisor gap (IIG) and mandible luxation<br />
IIG ≥ 5cm or ML > 0 0 0<br />
3.5 < IG < 5 and ML = 0 1.09 3<br />
IG < 3.5cm and ML < 0 4.12 13<br />
Thyromental distance<br />
≥ 6.5 cm 0 0<br />
< 6.5cm 1.36 4<br />
Maximum range of head and neck movement<br />
Above 100° 0 0<br />
90° ± 10° 0.65 2<br />
Below 80° 1.46 5<br />
Modified Mallampati Test<br />
Class 1 0 0<br />
Class 2 0.66 2<br />
Class 3 1.93 6<br />
Class 4 2.52 8<br />
Total possible 15.35 48<br />
NAGUIB MODEL<br />
This model 62 uses logistic regression and includes thyromental distance, Mallampati score,<br />
inter-incisor gap and height. This model is 82.5 per cent sensitive and 85.6 per cent specific<br />
with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.90.<br />
27 <strong>Airway</strong> <strong>Assessment</strong>