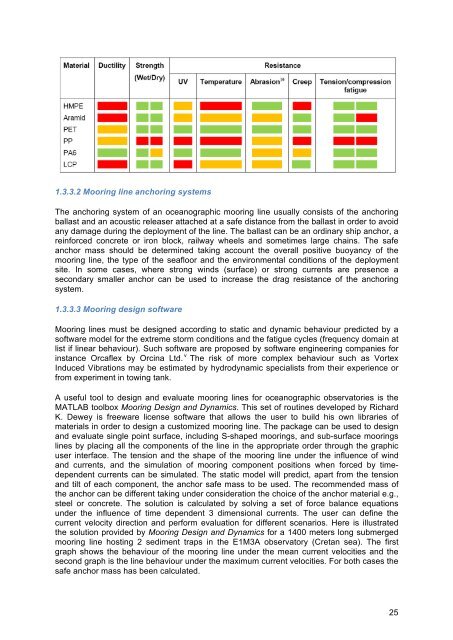
Handbook of best practices
Handbook%20of%20best%20practices
Handbook%20of%20best%20practices
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
1.3.3.2 Mooring line anchoring systems<br />
The anchoring system <strong>of</strong> an oceanographic mooring line usually consists <strong>of</strong> the anchoring<br />
ballast and an acoustic releaser attached at a safe distance from the ballast in order to avoid<br />
any damage during the deployment <strong>of</strong> the line. The ballast can be an ordinary ship anchor, a<br />
reinforced concrete or iron block, railway wheels and sometimes large chains. The safe<br />
anchor mass should be determined taking account the overall positive buoyancy <strong>of</strong> the<br />
mooring line, the type <strong>of</strong> the seafloor and the environmental conditions <strong>of</strong> the deployment<br />
site. In some cases, where strong winds (surface) or strong currents are presence a<br />
secondary smaller anchor can be used to increase the drag resistance <strong>of</strong> the anchoring<br />
system.<br />
1.3.3.3 Mooring design s<strong>of</strong>tware<br />
Mooring lines must be designed according to static and dynamic behaviour predicted by a<br />
s<strong>of</strong>tware model for the extreme storm conditions and the fatigue cycles (frequency domain at<br />
list if linear behaviour). Such s<strong>of</strong>tware are proposed by s<strong>of</strong>tware engineering companies for<br />
instance Orcaflex by Orcina Ltd. v The risk <strong>of</strong> more complex behaviour such as Vortex<br />
Induced Vibrations may be estimated by hydrodynamic specialists from their experience or<br />
from experiment in towing tank.<br />
A useful tool to design and evaluate mooring lines for oceanographic observatories is the<br />
MATLAB toolbox Mooring Design and Dynamics. This set <strong>of</strong> routines developed by Richard<br />
K. Dewey is freeware license s<strong>of</strong>tware that allows the user to build his own libraries <strong>of</strong><br />
materials in order to design a customized mooring line. The package can be used to design<br />
and evaluate single point surface, including S-shaped moorings, and sub-surface moorings<br />
lines by placing all the components <strong>of</strong> the line in the appropriate order through the graphic<br />
user interface. The tension and the shape <strong>of</strong> the mooring line under the influence <strong>of</strong> wind<br />
and currents, and the simulation <strong>of</strong> mooring component positions when forced by timedependent<br />
currents can be simulated. The static model will predict, apart from the tension<br />
and tilt <strong>of</strong> each component, the anchor safe mass to be used. The recommended mass <strong>of</strong><br />
the anchor can be different taking under consideration the choice <strong>of</strong> the anchor material e.g.,<br />
steel or concrete. The solution is calculated by solving a set <strong>of</strong> force balance equations<br />
under the influence <strong>of</strong> time dependent 3 dimensional currents. The user can define the<br />
current velocity direction and perform evaluation for different scenarios. Here is illustrated<br />
the solution provided by Mooring Design and Dynamics for a 1400 meters long submerged<br />
mooring line hosting 2 sediment traps in the E1M3A observatory (Cretan sea). The first<br />
graph shows the behaviour <strong>of</strong> the mooring line under the mean current velocities and the<br />
second graph is the line behaviour under the maximum current velocities. For both cases the<br />
safe anchor mass has been calculated.<br />
25