- Page 2 and 3: About the Tutorial C++ is a middle-
- Page 4 and 5: Enumerated Types ..................
- Page 6 and 7: Function Declarations .............
- Page 8 and 9: Structures as Function Arguments ..
- Page 10 and 11: Data Encapsulation Example ........
- Page 12 and 13: My First CGI program ..............
- Page 14 and 15: C++ The ANSI standard has been stab
- Page 16 and 17: C++ C++ Compiler: This is an actual
- Page 18 and 19: 3. BASIC SYNTAX C++ When we conside
- Page 20 and 21: C++ add(x, y); A block is a set of
- Page 22 and 23: C++ ??= # ??/ \ ??' ^ ??( [ ??) ] ?
- Page 24 and 25: C++ cout
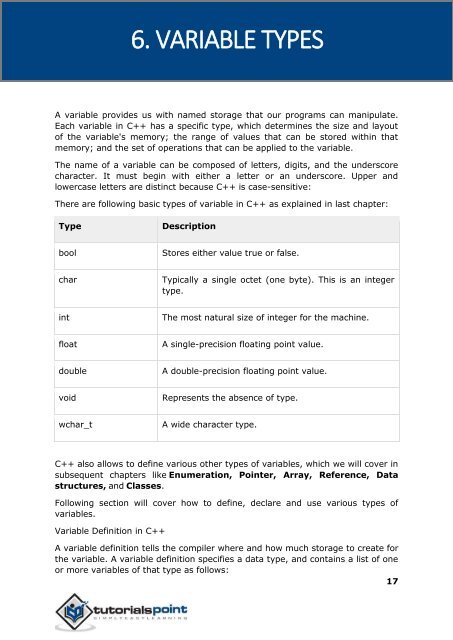
- Page 26 and 27: C++ The following table shows the v
- Page 30 and 31: C++ type variable_list; Here, type
- Page 32 and 33: C++ Same concept applies on functio
- Page 34 and 35: C++ Global Variables Global variabl
- Page 36 and 37: 8. CONSTANTS/LITERALS C++ Constants
- Page 38 and 39: C++ \a Alert or bell \b Backspace \
- Page 40 and 41: C++ } cout
- Page 42 and 43: C++ j = 50000; i = j; cout
- Page 44 and 45: C++ The static storage class instru
- Page 46 and 47: C++ extern int count; void write_ex
- Page 48 and 49: C++ ++ Increment operator, increase
- Page 50 and 51: C++ operand is greater than or equa
- Page 52 and 53: C++ Line 5 - b is either greater th
- Page 54 and 55: C++ Bitwise operator works on bits
- Page 56 and 57: C++ c = ~a; // -61 = 1100 0011 cout
- Page 58 and 59: C++ Copy and paste the following C+
- Page 60 and 61: C++ Condition ? X : Y Conditional o
- Page 62 and 63: C++ int b = 10; int c = 15; int d =
- Page 64 and 65: C++ do...while loop Like a ‘while
- Page 66 and 67: C++ } return 0; When the above code
- Page 68 and 69: C++ { } cout
- Page 70 and 71: C++ } When the above code is compil
- Page 72 and 73: C++ 2 is prime 3 is prime 5 is prim
- Page 74 and 75: C++ Example #include using namespa
- Page 76 and 77: C++ Example #include using namespa
- Page 78 and 79:
C++ Example #include using namespa
- Page 80 and 81:
C++ the ‘for’ loop are required
- Page 82 and 83:
C++ for equality against a list of
- Page 84 and 85:
C++ When the above code is compiled
- Page 86 and 87:
C++ An if can have zero to many e
- Page 88 and 89:
C++ switch(expression){ case consta
- Page 90 and 91:
C++ case 'D' : cout
- Page 92 and 93:
C++ C++ specifies that at least 256
- Page 94 and 95:
14. FUNCTIONS C++ A function is a g
- Page 96 and 97:
C++ Calling a Function While creati
- Page 98 and 99:
C++ in the call. This means that ch
- Page 100 and 101:
C++ temp = *x; /* save the value at
- Page 102 and 103:
C++ int main () { // local variable
- Page 104 and 105:
C++ Total value is :300 Total value
- Page 106 and 107:
C++ cout
- Page 108 and 109:
C++ double d = 200.374; // mathemat
- Page 110 and 111:
16. ARRAYS C++ C++ provides a data
- Page 112 and 113:
C++ for ( int j = 0; j < 10; j++ )
- Page 114 and 115:
C++ Multidimensioned arrays may be
- Page 116 and 117:
C++ Once you store the address of f
- Page 118 and 119:
C++ { . . . } Way-3 Formal paramete
- Page 120 and 121:
C++ . . } Second point to remember
- Page 122 and 123:
C++ 110
- Page 124 and 125:
C++ int main () { char greeting[6]
- Page 126 and 127:
C++ strcat( str1, str2): HelloWorld
- Page 128 and 129:
18. POINTERS C++ C++ pointers are e
- Page 130 and 131:
C++ // print the address stored in
- Page 132 and 133:
C++ convention, if a pointer contai
- Page 134 and 135:
C++ int main () { int var[MAX] = {1
- Page 136 and 137:
C++ Address of var[1] = 0xbfce42d4
- Page 138 and 139:
C++ Above statement is valid and wi
- Page 140 and 141:
C++ char *names[MAX] = { "Zara Ali"
- Page 142 and 143:
C++ Passing Pointers to Functions C
- Page 144 and 145:
C++ } return avg; When the above co
- Page 146 and 147:
C++ 613357504 1377296355 1530315259
- Page 148 and 149:
C++ // declare simple variables int
- Page 150 and 151:
C++ int temp; temp = x; /* save the
- Page 152 and 153:
C++ vals[4] = 50 When returning a r
- Page 154 and 155:
C++ hours:minutes:seconds year\n\0.
- Page 156 and 157:
C++ using namespace std; int main(
- Page 158 and 159:
C++ using namespace std; int main(
- Page 160 and 161:
C++ Error message : Unable to read.
- Page 162 and 163:
C++ int }book; book_id; Accessing S
- Page 164 and 165:
C++ using namespace std; void print
- Page 166 and 167:
C++ #include #include using names
- Page 168 and 169:
C++ Now, you can use Books directly
- Page 170 and 171:
C++ Both of the objects Box1 and Bo
- Page 172 and 173:
C++ created previously. C++ friend
- Page 174 and 175:
C++ { public: double length; double
- Page 176 and 177:
C++ internal representation of a cl
- Page 178 and 179:
C++ A private member variable or fu
- Page 180 and 181:
C++ You will learn derived classes
- Page 182 and 183:
C++ Line::Line(void) { cout
- Page 184 and 185:
C++ Line line(10.0); // get initial
- Page 186 and 187:
C++ } cout
- Page 188 and 189:
C++ } cout
- Page 190 and 191:
C++ } *ptr = len; Line::Line(const
- Page 192 and 193:
C++ friend class ClassTwo; Consider
- Page 194 and 195:
C++ int main( ) { } cout
- Page 196 and 197:
C++ Constructor called. Box2 is equ
- Page 198 and 199:
C++ Let us try the following exampl
- Page 200 and 201:
C++ }; Box(double l=2.0, double b=2
- Page 202 and 203:
24. INHERITANCE C++ One of the most
- Page 204 and 205:
C++ Total area: 35 Access Control a
- Page 206 and 207:
C++ }; public: int getCost(int area
- Page 208 and 209:
C++ 25. OVERLOADING (OPERATOR & FUN
- Page 210 and 211:
C++ Box operator+(const Box&, const
- Page 212 and 213:
C++ cout
- Page 214 and 215:
C++ #include using namespace std;
- Page 216 and 217:
C++ Time(int h, int m){ hours = h;
- Page 218 and 219:
C++ class Box { double length; doub
- Page 220 and 221:
C++ } return 0; When the above code
- Page 222 and 223:
C++ } { cout and the stream insert
- Page 224 and 225:
C++ Second Distance :F : 5 I : 11 T
- Page 226 and 227:
C++ } T2.displayTime(); T2++; T2.di
- Page 228 and 229:
C++ The function call operator () c
- Page 230 and 231:
C++ int arr[SIZE]; public: safearay
- Page 232 and 233:
C++ static int i, j; public: void f
- Page 234 and 235:
C++ } When the above code is compil
- Page 236 and 237:
C++ return (width * height); } }; c
- Page 238 and 239:
C++ As you can see, each of the chi
- Page 240 and 241:
C++ Here, you don't need to underst
- Page 242 and 243:
C++ Designing Strategy Abstraction
- Page 244 and 245:
C++ defined after the public specif
- Page 246 and 247:
29. INTERFACES C++ An interface des
- Page 248 and 249:
C++ }; int getArea() { return (widt
- Page 250 and 251:
30. FILES AND STREAMS C++ So far, w
- Page 252 and 253:
C++ You read information from a fil
- Page 254 and 255:
C++ File Position Pointers Both ist
- Page 256 and 257:
C++ Throwing Exceptions Exceptions
- Page 258 and 259:
C++ Because we are raising an excep
- Page 260 and 261:
C++ struct MyException : public exc
- Page 262 and 263:
C++ double* pvalue = NULL; if( !(pv
- Page 264 and 265:
C++ class Box { public: Box() { cou
- Page 266 and 267:
C++ // second name space namespace
- Page 268 and 269:
C++ } return 0; If we compile and r
- Page 270 and 271:
34. TEMPLATES C++ Templates are the
- Page 272 and 273:
C++ #include #include #include #
- Page 274 and 275:
C++ } } If we compile and run above
- Page 276 and 277:
C++ test.p. Now, if you check test.
- Page 278 and 279:
C++ #if 0 /* This is commented part
- Page 280 and 281:
C++ Above line will be transformed
- Page 282 and 283:
36. SIGNAL HANDLING C++ Signals are
- Page 284 and 285:
C++ Going to sleep.... Going to sle
- Page 286 and 287:
37. MULTITHREADING C++ Multithreadi
- Page 288 and 289:
C++ } pthread_exit(NULL); int main
- Page 290 and 291:
C++ int i; } for( i=0; i < NUM_THRE
- Page 292 and 293:
C++ // Initialize and set thread jo
- Page 294 and 295:
38. WEB PROGRAMMING C++ What is CGI
- Page 296 and 297:
C++ Options All Here, I assume th
- Page 298 and 299:
C++ Variable Name Description CONTE
- Page 300 and 301:
C++ if ( value != 0 ){ cout
- Page 302 and 303:
C++ You can pass information by sim
- Page 304 and 305:
C++ First Name: Last Name: Her
- Page 306 and 307:
C++ cout
- Page 308 and 309:
C++ if( !fi->isEmpty() && fi != (*f
- Page 310 and 311:
C++ Passing Dropdown Box Data to CG
- Page 312 and 313:
C++ Domain: This is the domain
- Page 314 and 315:
C++ Cgicc cgi; const_cookie_iterato
- Page 316 and 317:
C++ #include #include #include #
- Page 318 and 319:
39. STL TUTORIAL C++ Hope you have
- Page 320 and 321:
C++ value of vec [1] = 1 value of v
- Page 322:
C++ The Localization library Exc