ESC Textbook of Cardiovascular Imaging - sample
Discover the ESC Textbook of Cardiovascular Imaging 2nd edition
Discover the ESC Textbook of Cardiovascular Imaging 2nd edition
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
30<br />
chapter 1 conventional echocardiography—basic principles<br />
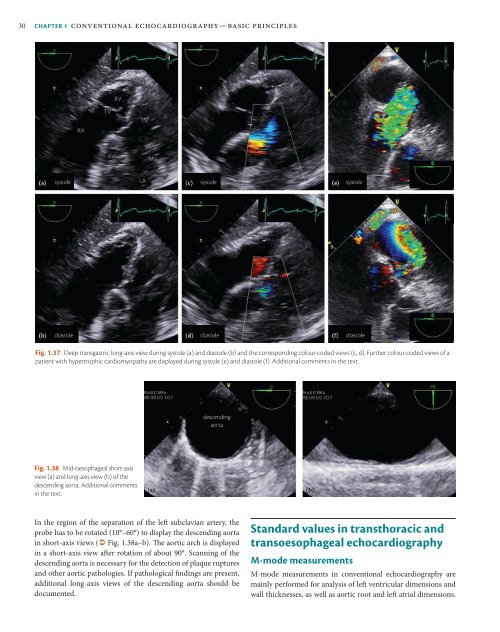
Fig. 1.37 Deep transgastric long-axis view during systole (a) and diastole (b) and the corresponding colour-coded views (c, d). Further colour-coded views <strong>of</strong> a<br />
patient with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy are displayed during systole (e) and diastole (f). Additional comments in the text.<br />
Fig. 1.38 Mid-oesophageal short-axis<br />
view (a) and long-axis view (b) <strong>of</strong> the<br />
descending aorta. Additional comments<br />
in the text.<br />
In the region <strong>of</strong> the separation <strong>of</strong> the left subclavian artery, the<br />
probe has to be rotated (10°–60°) to display the descending aorta<br />
in short-axis views ( Fig. 1.38a–b). The aortic arch is displayed<br />
in a short-axis view after rotation <strong>of</strong> about 90°. Scanning <strong>of</strong> the<br />
descending aorta is necessary for the detection <strong>of</strong> plaque ruptures<br />
and other aortic pathologies. If pathological findings are present,<br />
additional long-axis views <strong>of</strong> the descending aorta should be<br />
documented.<br />
Standard values in transthoracic and<br />
transoesophageal echocardiography<br />
M-mode measurements<br />
M-mode measurements in conventional echocardiography are<br />
mainly performed for analysis <strong>of</strong> left ventricular dimensions and<br />
wall thicknesses, as well as aortic root and left atrial dimensions.