- Page 1 and 2: Junos ® OS BGP Configuration Guide
- Page 3 and 4: Table of Contents Part 1 Overview A
- Page 5 and 6: Chapter 6 BGP BFD Configuration . .
- Page 7 and 8: Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 9 and 10: Part 3 Administration Chapter 15 BG
- Page 11 and 12: List of Figures Part 1 Overview Cha
- Page 13 and 14: List of Tables Part 2 Configuration
- Page 15 and 16: About the Documentation • Documen
- Page 17 and 18: Documentation Conventions Table 1:
- Page 19 and 20: Documentation Feedback We encourage
- Page 21 and 22: PART 1 Overview Copyright © 2012,
- Page 23 and 24: CHAPTER 1 Introduction to BGP Copyr
- Page 25 and 26: External and Internal BGP Related D
- Page 27 and 28: Open Messages Update Messages Copyr
- Page 29 and 30: Depending on whether nondeterminist
- Page 31 and 32: Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 33 and 34: CHAPTER 2 BGP Reference Supported B
- Page 35 and 36: PART 2 Configuration Copyright © 2
- Page 37: CHAPTER 3 Basic BGP Configuration
- Page 41 and 42: unit 9 { description to-C; family i
- Page 43 and 44: Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 45 and 46: Sample Output 0/0/0/0 0/0/0/0 10.10
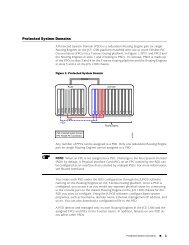
- Page 47 and 48: CLI Quick Configuration Figure 4: T
- Page 49 and 50: Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 51 and 52: Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 53 and 54: Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 55 and 56: Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 57 and 58: Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 59 and 60: user@R1:E> show bgp group Group Typ
- Page 61 and 62: Understanding Internal BGP Peering
- Page 63 and 64: When a device peers with a remote d
- Page 65 and 66: Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 67 and 68: Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 69 and 70: Step-by-Step Procedure } } Copyrigh
- Page 71 and 72: Verification Confirm that the confi
- Page 73 and 74: Groups: 1 Peers: 2 Down peers: 0 Ta
- Page 75 and 76: Step-by-Step Procedure set logical-
- Page 77 and 78: [edit logical-systems A protocols o
- Page 79 and 80: Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 81 and 82: Action From the operational mode, e
- Page 83 and 84: Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 85 and 86: CHAPTER 4 BGP Path Attribute Config
- Page 87 and 88: CLI Quick Configuration • Configu
- Page 89 and 90:
4. Configure a policy that accepts
- Page 91 and 92:
3. Configure OSPF. [edit protocols
- Page 93 and 94:
[edit protocols bgp group internal]
- Page 95 and 96:
Step-by-Step Procedure Configuring
- Page 97 and 98:
user@R1> show route protocol bgp in
- Page 99 and 100:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 101 and 102:
• Configuration on page 82 • Ve
- Page 103 and 104:
Device R2 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 u
- Page 105 and 106:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 107 and 108:
Results From configuration mode, co
- Page 109 and 110:
[edit policy-options policy-stateme
- Page 111 and 112:
user@R4# set export send-direct use
- Page 113 and 114:
to 12.12.12.2 via fe-1/2/0.1 192.16
- Page 115 and 116:
set routing-options router-id 192.1
- Page 117 and 118:
Results From configuration mode, co
- Page 119 and 120:
user@R2# set autonomous-system 123
- Page 121 and 122:
Other useful options for this scena
- Page 123 and 124:
[edit protocols bgp group external]
- Page 125 and 126:
Checking the Active Path From Devic
- Page 127 and 128:
• Configuration on page 108 • V
- Page 129 and 130:
CLI Quick Configuration To quickly
- Page 131 and 132:
Device R6 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 u
- Page 133 and 134:
6. Configure OSPF. [edit protocols
- Page 135 and 136:
user@R1> show route advertising-pro
- Page 137 and 138:
The Junos operating system (Junos O
- Page 139 and 140:
NOTE: If you configure the local AS
- Page 141 and 142:
set protocols bgp group ext type ex
- Page 143 and 144:
Step-by-Step Procedure route 10.1.0
- Page 145 and 146:
Step-by-Step Procedure Configuring
- Page 147 and 148:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 149 and 150:
192.168.0.3/32 *[BGP/170] 01:46:40,
- Page 151 and 152:
CLI Quick Configuration Configurati
- Page 153 and 154:
} } fe-1/2/1 { unit 5 { family inet
- Page 155 and 156:
Understanding the Accumulated IGP A
- Page 157 and 158:
CLI Quick Configuration The network
- Page 159 and 160:
set protocols bgp group internal ne
- Page 161 and 162:
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1 int
- Page 163 and 164:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 165 and 166:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 167 and 168:
4. Enable AIGP. [edit protocols bgp
- Page 169 and 170:
Step-by-Step Procedure } Copyright
- Page 171 and 172:
user@PE4# set router-id 10.9.9.4 us
- Page 173 and 174:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 175 and 176:
user@PE1# set group internal neighb
- Page 177 and 178:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 179 and 180:
6. Enable the policies. [edit polic
- Page 181 and 182:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 183 and 184:
user@PE3# set policy-statement SET_
- Page 185 and 186:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 187 and 188:
} } export SET_EXPORT_ROUTES; peer-
- Page 189 and 190:
AIGP: 25 * 99.0.0.0/24 (1 entry, 1
- Page 191 and 192:
Nexthop: 10.100.1.4 Localpref: 100
- Page 193 and 194:
Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 195 and 196:
CHAPTER 5 BGP Policy Configuration
- Page 197 and 198:
user@host# set term injectterm1 2.
- Page 199 and 200:
Solution If you configure policy tr
- Page 201 and 202:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 203 and 204:
advertise-peer-as; NOTE: The route
- Page 205 and 206:
[edit protocols bgp group cisco-pee
- Page 207 and 208:
direct connection of the two EBGP p
- Page 209 and 210:
Step-by-Step Procedure set routing-
- Page 211 and 212:
Step-by-Step Procedure router-id 19
- Page 213 and 214:
user@E# set local-address 192.168.6
- Page 215 and 216:
--- 10.10.10.14 ping statistics ---
- Page 217 and 218:
Table 4: Default Route Preference V
- Page 219 and 220:
CLI Quick Configuration Topology In
- Page 221 and 222:
user@R1# show interfaces fe-1/2/0 {
- Page 223 and 224:
• BGP Configuration Overview Exam
- Page 225 and 226:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 227 and 228:
CLI Quick Configuration Device R1 h
- Page 229 and 230:
set routing-options static route 19
- Page 231 and 232:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 233 and 234:
Example: Removing Private AS Number
- Page 235 and 236:
CLI Quick Configuration Configurati
- Page 237 and 238:
peer-as 200; } } } user@ISP# show r
- Page 239 and 240:
Action From configuration mode on D
- Page 241 and 242:
CHAPTER 6 BGP BFD Configuration Exa
- Page 243 and 244:
CLI Quick Configuration NOTE: BFD i
- Page 245 and 246:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 247 and 248:
file bgp-bfd; flag bfd detail; } lo
- Page 249 and 250:
Aug 15 17:07:25 trace_on: Tracing t
- Page 251 and 252:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 253 and 254:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 255 and 256:
show bfd session detail show bfd se
- Page 257 and 258:
CHAPTER 7 BGP Load Balancing Config
- Page 259 and 260:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 261 and 262:
export loadbal; } If you are done c
- Page 263 and 264:
also supported on logical systems a
- Page 265 and 266:
Step-by-Step Procedure set interfac
- Page 267 and 268:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 269 and 270:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 271 and 272:
type internal; local-address 10.255
- Page 273 and 274:
Action 1. From configuration mode,
- Page 275 and 276:
• Three of the BGP-enabled device
- Page 277 and 278:
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 int
- Page 279 and 280:
user@R1# set group rr type internal
- Page 281 and 282:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 283 and 284:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 285 and 286:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 287 and 288:
Step-by-Step Procedure } Copyright
- Page 289 and 290:
Step-by-Step Procedure } Copyright
- Page 291 and 292:
2. Configure BGP on Router R7’s i
- Page 293 and 294:
unit 84 { family inet { address 10.
- Page 295 and 296:
Verifying That Router R4 Is Receivi
- Page 297 and 298:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 299 and 300:
CHAPTER 8 IBGP Scaling Configuratio
- Page 301 and 302:
However, as clusters become large,
- Page 303 and 304:
CLI Quick Configuration Figure 29:
- Page 305 and 306:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 307 and 308:
Step-by-Step Procedure } } Copyrigh
- Page 309 and 310:
Step-by-Step Procedure } } Copyrigh
- Page 311 and 312:
passive; } interface fe-0/0/0.4; in
- Page 313 and 314:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 315 and 316:
Action From operational mode, enter
- Page 317 and 318:
Figure 30: BGP Confederations Sub-A
- Page 319 and 320:
Border Device in Sub-AS 64513 Step-
- Page 321 and 322:
Sample Output Table inet.0 Bit: 100
- Page 323 and 324:
CHAPTER 9 BGP Security Configuratio
- Page 325 and 326:
This example includes the following
- Page 327 and 328:
The start time of each key must be
- Page 329 and 330:
13:08:02.408249 Out IP 172.16.2.2.1
- Page 331 and 332:
CLI Quick Configuration • Configu
- Page 333 and 334:
encryption { algorithm 3des-cbc; ke
- Page 335 and 336:
CLI Quick Configuration Figure 34:
- Page 337 and 338:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 339 and 340:
tcp4 0 0 10.10.10.1.179 10.10.10.2.
- Page 341 and 342:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 343 and 344:
CLI Quick Configuration Requirement
- Page 345 and 346:
Results From configuration mode, co
- Page 347 and 348:
CHAPTER 10 BGP Flap Configuration
- Page 349 and 350:
Overview When a router or switch is
- Page 351 and 352:
Step-by-Step Procedure Step-by-Step
- Page 353 and 354:
2. Run the show bgp summary command
- Page 355 and 356:
Table 5: Damping Parameters (contin
- Page 357 and 358:
oute-filter 192.168.0.0/16 orlonger
- Page 359 and 360:
CHAPTER 11 Multiprotocol BGP Config
- Page 361 and 362:
; prefix-limit { maximum number; te
- Page 363 and 364:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 365 and 366:
For a list of hierarchy levels at w
- Page 367 and 368:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 369 and 370:
oute ::ffff:192.168.20.0/120 next-h
- Page 371 and 372:
Meaning The various occurrences of
- Page 373 and 374:
Table 6: Flow Route Match Condition
- Page 375 and 376:
Validating Flow Routes The Junos OS
- Page 377 and 378:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 379 and 380:
the less specific matching conditio
- Page 381 and 382:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 383 and 384:
Results From configuration mode, co
- Page 385 and 386:
Step-by-Step Procedure The followin
- Page 387 and 388:
Verifying Routes Purpose Look at th
- Page 389 and 390:
196.1.68/24,* 0 0 196.1.69/24,* 0 0
- Page 391 and 392:
CHAPTER 12 BGP CLNS Configuration E
- Page 393 and 394:
Verifying the Neighbor Status Purpo
- Page 395 and 396:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 397 and 398:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 399 and 400:
CHAPTER 13 BGP Monitoring Configura
- Page 401 and 402:
Step-by-Step Procedure configuratio
- Page 403 and 404:
• state—State transitions • t
- Page 405 and 406:
Step-by-Step Procedure Step-by-Step
- Page 407 and 408:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 409 and 410:
CHAPTER 14 BGP Configuration Statem
- Page 411 and 412:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 413 and 414:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 415 and 416:
accept-remote-nexthop Syntax accept
- Page 417 and 418:
Description Configure a limit to th
- Page 419 and 420:
advertise-external Syntax advertise
- Page 421 and 422:
advertise-peer-as Syntax advertise-
- Page 423 and 424:
aigp Syntax aigp [disable]; Hierarc
- Page 425 and 426:
aigp-originate Syntax aigp-originat
- Page 427 and 428:
Required Privilege Level Related Do
- Page 429 and 430:
as-override Syntax as-override; Hie
- Page 431 and 432:
authentication-algorithm • algori
- Page 433 and 434:
authentication-key-chain Syntax aut
- Page 435 and 436:
fd-liveness-detection (BGP) Syntax
- Page 437 and 438:
gp Syntax bgp { ... } Hierarchy Lev
- Page 439 and 440:
mp Related Documentation • Exampl
- Page 441 and 442:
Required Privilege Options cluster-
- Page 443 and 444:
description Syntax description text
- Page 445 and 446:
disable (BGP) Syntax disable; • t
- Page 447 and 448:
explicit-null Syntax explicit-null;
- Page 449 and 450:
family Syntax family { (inet | inet
- Page 451 and 452:
Release Information Statement intro
- Page 453 and 454:
graceful-restart Syntax graceful-re
- Page 455 and 456:
} advertise-default; external-paths
- Page 457 and 458:
hold-down-interval (BGP BFD Livenes
- Page 459 and 460:
hold-time (BGP) Syntax hold-time se
- Page 461 and 462:
import Syntax import [ policy-names
- Page 463 and 464:
inet-mdt (Signaling) Syntax signali
- Page 465 and 466:
iso-vpn Syntax iso-vpn { unicast {
- Page 467 and 468:
key-chain (BGP BFD Authentication)
- Page 469 and 470:
labeled-unicast Syntax labeled-unic
- Page 471 and 472:
local-address (BGP) Syntax local-ad
- Page 473 and 474:
local-as Syntax local-as autonomous
- Page 475 and 476:
Required Privilege Level Related Do
- Page 477 and 478:
log-updown • preference on page 4
- Page 479 and 480:
loops Syntax loops number; Hierarch
- Page 481 and 482:
loose-check (BGP BFD Authentication
- Page 483 and 484:
metric-out Syntax metric-out (metri
- Page 485 and 486:
minimum-interval (BGP BFD Liveness
- Page 487 and 488:
Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 489 and 490:
mtu-discovery Syntax mtu-discovery;
- Page 491 and 492:
multihop Syntax multihop { no-nexth
- Page 493 and 494:
multiplier (BGP BFD Liveness Detect
- Page 495 and 496:
accepted-prefix-limit { maximum num
- Page 497 and 498:
no-adaptation (BGP BFD Liveness Det
- Page 499 and 500:
no-aggregator-id Syntax no-aggregat
- Page 501 and 502:
no-nexthop-change (BGP Multihop) Sy
- Page 503 and 504:
Required Privilege out-delay Option
- Page 505 and 506:
passive Related Documentation Synta
- Page 507 and 508:
path-selection Syntax path-selectio
- Page 509 and 510:
peer-as Syntax peer-as autonomous-s
- Page 511 and 512:
precision-timers Syntax precision-t
- Page 513 and 514:
prefix-limit Syntax prefix-limit {
- Page 515 and 516:
eceive Syntax receive; Hierarchy Le
- Page 517 and 518:
Related Documentation resolve-vpn
- Page 519 and 520:
ib Syntax rib inet.3; Hierarchy Lev
- Page 521 and 522:
oute-target Syntax route-target { a
- Page 523 and 524:
session-mode Syntax session-mode (a
- Page 525 and 526:
tcp-mss Syntax tcp-mss segment-size
- Page 527 and 528:
Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 529 and 530:
traceoptions Syntax traceoptions {
- Page 531 and 532:
Required Privilege Level Related Do
- Page 533 and 534:
transmit-interval (BGP BFD Liveness
- Page 535 and 536:
type Syntax type type; Hierarchy Le
- Page 537 and 538:
vpn-apply-export Syntax vpn-apply-e
- Page 539 and 540:
PART 3 Administration Copyright ©
- Page 541 and 542:
CHAPTER 15 BGP Operational Commands
- Page 543 and 544:
clear bgp neighbor Syntax (EX Serie
- Page 545 and 546:
clear bgp table Syntax (EX Series S
- Page 547 and 548:
estart Syntax (EX Series Syntax res
- Page 549 and 550:
• ppp in Junos OS Release 7.5.
- Page 551 and 552:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 553 and 554:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 555 and 556:
Required Privilege Level Related Do
- Page 557 and 558:
show bgp bmp Syntax show bgp bmp Re
- Page 559 and 560:
Output Fields Table 9 on page 539 d
- Page 561 and 562:
Table 9: show bgp group Output Fiel
- Page 563 and 564:
Groups: 1 Peers: 3 External: 0 Inte
- Page 565 and 566:
show bgp group traffic-statistics S
- Page 567 and 568:
show bgp neighbor Syntax (EX Series
- Page 569 and 570:
Table 11: show bgp neighbor Output
- Page 571 and 572:
Table 11: show bgp neighbor Output
- Page 573 and 574:
Table 11: show bgp neighbor Output
- Page 575 and 576:
show bgp neighbor (CLNS) show bgp n
- Page 577 and 578:
show bgp neighbor (Layer 3 VPN) Cop
- Page 579 and 580:
show bgp neighbor neighbor-address
- Page 581 and 582:
show bgp replication Syntax show bg
- Page 583 and 584:
show bgp summary Syntax (EX Series
- Page 585 and 586:
Table 13: show bgp summary Output F
- Page 587 and 588:
show bgp summary (Layer 3 VPN) Copy
- Page 589 and 590:
Table 14: show policy damping Outpu
- Page 591 and 592:
show policy policy-name show policy
- Page 593 and 594:
Table 16: show policy conditions Ou
- Page 595 and 596:
Table 17: show policy damping Outpu
- Page 597 and 598:
Table 18: show route Output Fields
- Page 599 and 600:
show route destination-prefix 172.1
- Page 601 and 602:
show route active-path Syntax (EX S
- Page 603 and 604:
show route active-path extensive Co
- Page 605 and 606:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 607 and 608:
Table 19: show route advertising-pr
- Page 609 and 610:
show route advertising-protocol bgp
- Page 611 and 612:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 613 and 614:
List of Sample Output show route as
- Page 615 and 616:
via fxp2.0 [Direct/0] 2d 01:43:34 >
- Page 617 and 618:
show route brief Syntax (EX Series
- Page 619 and 620:
show route community Syntax (EX Ser
- Page 621 and 622:
show route community-name Syntax (E
- Page 623 and 624:
show route damping Syntax (EX Serie
- Page 625 and 626:
Table 20: show route damping Output
- Page 627 and 628:
show route damping history detail C
- Page 629 and 630:
Table 21: show route detail Output
- Page 631 and 632:
Table 21: show route detail Output
- Page 633 and 634:
Table 22: Next-hop Types Output Fie
- Page 635 and 636:
Table 23: State Output Field Values
- Page 637 and 638:
Sample Output show route detail use
- Page 639 and 640:
Age: 1:25:49 Metric: 1 Task: RSVP A
- Page 641 and 642:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 643 and 644:
show route exact Syntax (EX Series
- Page 645 and 646:
show route export Syntax (EX Series
- Page 647 and 648:
show route extensive Syntax (EX Ser
- Page 649 and 650:
Table 26: show route extensive Outp
- Page 651 and 652:
Table 26: show route extensive Outp
- Page 653 and 654:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 655 and 656:
State: Local AS: 69 Age: 1:34:06 T
- Page 657 and 658:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 659 and 660:
show route extensive (Access Route)
- Page 661 and 662:
show route flow validation Syntax (
- Page 663 and 664:
show route forwarding-table Syntax
- Page 665 and 666:
Required Privilege Level the main r
- Page 667 and 668:
Table 28: show route forwarding-tab
- Page 669 and 670:
show route forwarding-table detail
- Page 671 and 672:
show route forwarding-table extensi
- Page 673 and 674:
show route forwarding-table table d
- Page 675 and 676:
show route forwarding-table vpn Cop
- Page 677 and 678:
show route hidden detail show route
- Page 679 and 680:
show route inactive-path Syntax (EX
- Page 681 and 682:
show route inactive-path extensive
- Page 683 and 684:
show route inactive-prefix extensiv
- Page 685 and 686:
Table 29: show route instance Outpu
- Page 687 and 688:
show route instance detail (Gracefu
- Page 689 and 690:
show route instance detail (VPLS Ro
- Page 691 and 692:
show route next-hop Syntax (EX Seri
- Page 693 and 694:
show route next-hop extensive Copyr
- Page 695 and 696:
show route next-hop terse Copyright
- Page 697 and 698:
show route no-community Syntax (EX
- Page 699 and 700:
show route no-community terse Copyr
- Page 701 and 702:
Sample Output show route output add
- Page 703 and 704:
show route output interface extensi
- Page 705 and 706:
Required Privilege Level view • m
- Page 707 and 708:
show route protocol bgp extensive s
- Page 709 and 710:
show route protocol l2vpn extensive
- Page 711 and 712:
show route protocol ospf (Layer 3 V
- Page 713 and 714:
show route receive-protocol Syntax
- Page 715 and 716:
Table 30: show route receive-protoc
- Page 717 and 718:
show route receive-protocol bgp det
- Page 719 and 720:
show route receive-protocol bgp det
- Page 721 and 722:
show route table Syntax (EX Series
- Page 723 and 724:
Label operation: Push 182465 Protoc
- Page 725 and 726:
*[L2CKT/7] 00:50:47 > via so-0/1/2.
- Page 727 and 728:
show route table vpn-a.mdt.0 show r
- Page 729 and 730:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 731 and 732:
Table 31: show route terse Output F
- Page 733 and 734:
test policy Syntax test policy poli
- Page 735 and 736:
PART 4 Troubleshooting Copyright ©
- Page 737 and 738:
CHAPTER 16 Routing Protocol Process
- Page 739 and 740:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 741 and 742:
188 root 2 0 780K 600K select 0:00
- Page 743 and 744:
STACK segments, or the memory used
- Page 745 and 746:
PART 5 Index Copyright © 2012, Jun
- Page 747 and 748:
Index Symbols #, comments in config
- Page 749 and 750:
prefix-limit accepted..............
- Page 751 and 752:
G generated routes preferences.....
- Page 753 and 754:
O open messages, BGP...............
- Page 755 and 756:
show bgp replication command.......