Bauhaus Luftfahrt Jahrbuch 2018
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
53<br />
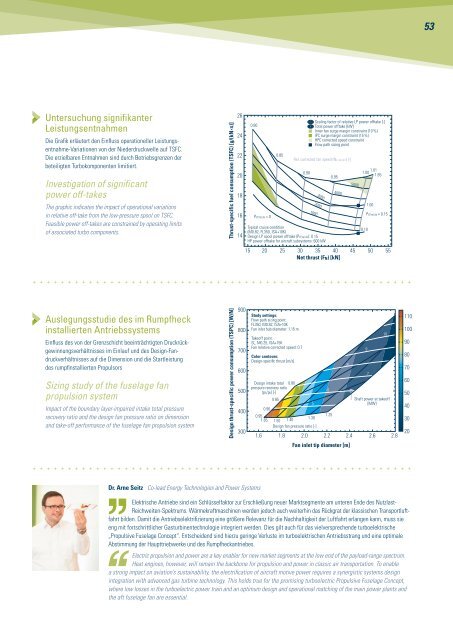
Untersuchung signifikanter<br />
Leistungsentnahmen<br />
Die Grafik erläutert den Einfluss operationeller Leistungsentnahme-Variationen<br />
von der Niederdruckwelle auf TSFC.<br />
Die erzielbaren Entnahmen sind durch Betriebsgrenzen der<br />
beteiligten Turbokomponenten limitiert.<br />
Investigation of significant<br />
power off-takes<br />
The graphic indicates the impact of operational variations<br />
in relative off-take from the low-pressure spool on TSFC.<br />
Feasible power off-takes are constrained by operating limits<br />
of associated turbo components.<br />
Thrust-specific fuel consumption (TSFC) [g/(kN x s)]<br />
26<br />
24<br />
22<br />
20<br />
18<br />
16<br />
14<br />
0.80<br />
PLP,rel,ds = 0<br />
0.85<br />
Rel. corrected fan speed (NL,rel,corr) [-]<br />
0.90<br />
1000<br />
Typical cruise condition<br />
(M0.82, FL350, ISA+10K)<br />
Design LP spool power offtake (PLP,rel,ds): 0.15<br />
HP power offtake for aircraft subsystems: 600 kW<br />
Scaling factor of relative LP power offtake [-]<br />
Total power offtake [kW]<br />
Inner fan surge margin constraint (10 %)<br />
IPC surge margin constraint (15 %)<br />
HPC corrected speed constraint<br />
Flow path sizing point<br />
3000<br />
2000<br />
0.95<br />
4000<br />
5000<br />
1.00 1.01<br />
1.65<br />
0.10<br />
1.00<br />
PLP,rel,ds = 0.15<br />
15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55<br />
Net thrust (FN) [kN]<br />
+ + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + +<br />
Auslegungsstudie des im Rumpfheck<br />
installierten Antriebssystems<br />
Einfluss des von der Grenzschicht beeinträchtigten Druckrückgewinnungsverhältnisses<br />
im Einlauf und des Design-Fandruckverhältnisses<br />
auf die Dimension und die Startleistung<br />
des rumpfinstallierten Propulsors<br />
Sizing study of the fuselage fan<br />
propulsion system<br />
Impact of the boundary layer-impaired intake total pressure<br />
recovery ratio and the design fan pressure ratio on dimension<br />
and take-off performance of the fuselage fan propulsion system<br />
Design thrust-specific power consumption (TSPC) [W/N]<br />
900<br />
800<br />
700<br />
600<br />
500<br />
400<br />
300<br />
Study settings:<br />
Flow path sizing point:<br />
FL350, M0.82, ISA+10K<br />
Fan inlet hub diameter: 1.15 m<br />
Takeoff point:<br />
SL, M0.25, ISA+15K<br />
Fan relative corrected speed: 0.7<br />
Color contours:<br />
Design-specific thrust [m/s]<br />
Design intake total 0.80<br />
pressure recovery ratio 7<br />
(p2/p0) [-]<br />
0.90<br />
0.95<br />
1.65<br />
0.85<br />
1.50 1.40<br />
1.30<br />
Design fan pressure ratio [-]<br />
5<br />
1.25<br />
Shaft power at takeoff<br />
[MW]<br />
1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8<br />
6<br />
8<br />
9<br />
7<br />
10<br />
110<br />
100<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
Fan inlet tip diameter [m]<br />
+ + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + +<br />
Dr. Arne Seitz Co-lead Energy Technologies and Power Systems<br />
Elektrische Antriebe sind ein Schlüsselfaktor zur Erschließung neuer Marktsegmente am unteren Ende des Nutzlast-<br />
Reichweiten-Spektrums. Wärmekraftmaschinen werden jedoch auch weiterhin das Rückgrat der klassischen Transportluftfahrt<br />
bilden. Damit die Antriebselektrifizierung eine größere Relevanz für die Nachhaltigkeit der <strong>Luftfahrt</strong> erlangen kann, muss sie<br />
eng mit fortschrittlicher Gasturbinentechnologie integriert werden. Dies gilt auch für das vielversprechende turboelektrische<br />
„Propulsive Fuselage Concept“. Entscheidend sind hierzu geringe Verluste im turboelektrischen Antriebsstrang und eine optimale<br />
Abstimmung der Haupttriebwerke und des Rumpfheckantriebes.<br />
Electric propulsion and power are a key enabler for new market segments at the low end of the payload-range spectrum.<br />
Heat engines, however, will remain the backbone for propulsion and power in classic air transportation. To enable<br />
a strong impact on aviation’s sustainability, the electrification of aircraft motive power requires a synergistic systems design<br />
integration with advanced gas turbine technology. This holds true for the promising turboelectric Propulsive Fuselage Concept,<br />
where low losses in the turboelectric power train and an optimum design and operational matching of the main power plants and<br />
the aft fuselage fan are essential.