Management of stage Ⅳ rectal cancer - World Journal of ...
Management of stage Ⅳ rectal cancer - World Journal of ...
Management of stage Ⅳ rectal cancer - World Journal of ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
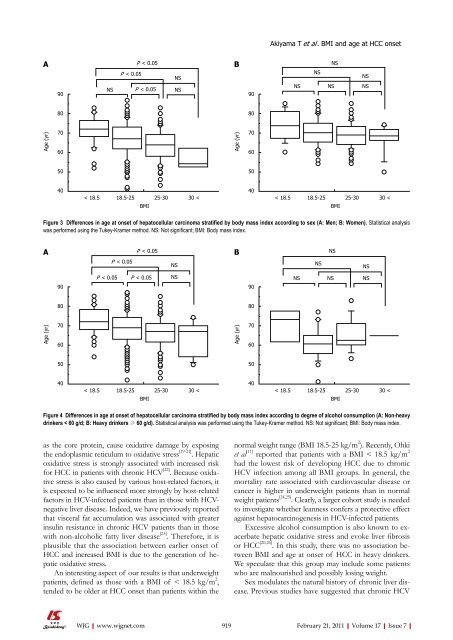
A<br />
Age (yr)<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
P < 0.05<br />
NS P < 0.05 NS<br />
as the core protein, cause oxidative damage by exposing<br />
the endoplasmic reticulum to oxidative stress [19-21] . Hepatic<br />
oxidative stress is strongly associated with increased risk<br />
for HCC in patients with chronic HCV [22] . Because oxidative<br />
stress is also caused by various host-related factors, it<br />
is expected to be influenced more strongly by host-related<br />
factors in HCV-infected patients than in those with HCVnegative<br />
liver disease. Indeed, we have previously reported<br />
that visceral fat accumulation was associated with greater<br />
insulin resistance in chronic HCV patients than in those<br />
with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [23] . Therefore, it is<br />
plausible that the association between earlier onset <strong>of</strong><br />
HCC and increased BMI is due to the generation <strong>of</strong> hepatic<br />
oxidative stress.<br />
An interesting aspect <strong>of</strong> our results is that underweight<br />
patients, defined as those with a BMI <strong>of</strong> < 18.5 kg/m 2 ,<br />
tended to be older at HCC onset than patients within the<br />
WJG|www.wjgnet.com<br />
P < 0.05<br />
NS<br />
< 18.5 18.5-25 25-30 30 <<br />
BMI<br />
Figure 3 Differences in age at onset <strong>of</strong> hepatocellular carcinoma stratified by body mass index according to sex (A: Men; B: Women). Statistical analysis<br />
was performed using the Tukey-Kramer method. NS: Not significant; BMI: Body mass index.<br />
A<br />
Age (yr)<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
P < 0.05<br />
P < 0.05<br />
< 18.5 18.5-25 25-30 30 <<br />
BMI<br />
NS<br />
P < 0.05 P < 0.05 NS<br />
B<br />
Age (yr)<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
NS<br />
NS NS NS<br />
< 18.5 18.5-25 25-30 30 <<br />
Figure 4 Differences in age at onset <strong>of</strong> hepatocellular carcinoma stratified by body mass index according to degree <strong>of</strong> alcohol consumption (A: Non-heavy<br />
drinkers < 60 g/d; B: Heavy drinkers ≥ 60 g/d). Statistical analysis was performed using the Tukey-Kramer method. NS: Not significant; BMI: Body mass index.<br />
B<br />
Age (yr)<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
Akiyama T et al . BMI and age at HCC onset<br />
NS<br />
normal weight range (BMI 18.5-25 kg/m 2 ). Recently, Ohki<br />
et al [11] reported that patients with a BMI < 18.5 kg/m 2<br />
had the lowest risk <strong>of</strong> developing HCC due to chronic<br />
HCV infection among all BMI groups. In general, the<br />
mortality rate associated with cardiovascular disease or<br />
<strong>cancer</strong> is higher in underweight patients than in normal<br />
weight patients [24,25] . Clearly, a larger cohort study is needed<br />
to investigate whether leanness confers a protective effect<br />
against hepatocarcinogenesis in HCV-infected patients.<br />
Excessive alcohol consumption is also known to exacerbate<br />
hepatic oxidative stress and evoke liver fibrosis<br />
or HCC [20,26] . In this study, there was no association between<br />
BMI and age at onset <strong>of</strong> HCC in heavy drinkers.<br />
We speculate that this group may include some patients<br />
who are malnourished and possibly losing weight.<br />
Sex modulates the natural history <strong>of</strong> chronic liver disease.<br />
Previous studies have suggested that chronic HCV<br />
919 February 21, 2011|Volume 17|Issue 7|<br />
NS<br />
BMI<br />
NS<br />
NS<br />
NS NS NS<br />
< 18.5 18.5-25 25-30 30 <<br />
BMI<br />
NS