The Nature of the Cooper Pair - University of Liverpool
The Nature of the Cooper Pair - University of Liverpool
The Nature of the Cooper Pair - University of Liverpool
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
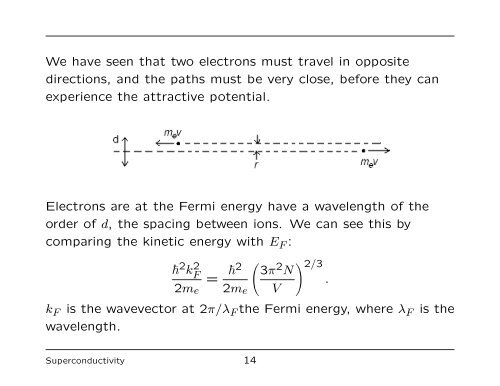
We have seen that two electrons must travel in opposite<br />
directions, and <strong>the</strong> paths must be very close, before <strong>the</strong>y can<br />
experience <strong>the</strong> attractive potential.<br />
Electrons are at <strong>the</strong> Fermi energy have a wavelength <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
order <strong>of</strong> d, <strong>the</strong> spacing between ions. We can see this by<br />
comparing <strong>the</strong> kinetic energy with E F :<br />
� 2 k 2 F<br />
2me<br />
= �2<br />
2me<br />
� �<br />
3π2 2/3<br />
N<br />
k F is <strong>the</strong> wavevector at 2π/λ F <strong>the</strong> Fermi energy, where λ F is <strong>the</strong><br />
wavelength.<br />
Superconductivity 14<br />
V<br />
.