The Nature of the Cooper Pair - University of Liverpool
The Nature of the Cooper Pair - University of Liverpool
The Nature of the Cooper Pair - University of Liverpool
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
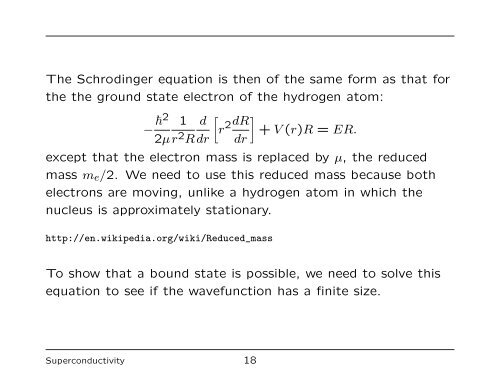
<strong>The</strong> Schrodinger equation is <strong>the</strong>n <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> same form as that for<br />
<strong>the</strong> <strong>the</strong> ground state electron <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> hydrogen atom:<br />
− �2 1<br />
2µ r2 d<br />
R dr<br />
�<br />
r 2dR<br />
dr<br />
�<br />
+ V (r)R = ER.<br />
except that <strong>the</strong> electron mass is replaced by µ, <strong>the</strong> reduced<br />
mass me/2. We need to use this reduced mass because both<br />
electrons are moving, unlike a hydrogen atom in which <strong>the</strong><br />
nucleus is approximately stationary.<br />
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reduced_mass<br />
To show that a bound state is possible, we need to solve this<br />
equation to see if <strong>the</strong> wavefunction has a finite size.<br />
Superconductivity 18