The Nature of the Cooper Pair - University of Liverpool
The Nature of the Cooper Pair - University of Liverpool
The Nature of the Cooper Pair - University of Liverpool
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
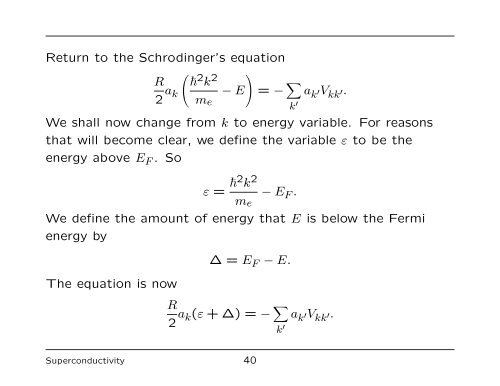
Return to <strong>the</strong> Schrodinger’s equation<br />
R<br />
2 a k<br />
� � 2 k 2<br />
me<br />
− E<br />
�<br />
= − �<br />
ak ′Vkk ′.<br />
We shall now change from k to energy variable. For reasons<br />
that will become clear, we define <strong>the</strong> variable ε to be <strong>the</strong><br />
energy above E F . So<br />
ε = �2 k 2<br />
me<br />
k ′<br />
− E F .<br />
We define <strong>the</strong> amount <strong>of</strong> energy that E is below <strong>the</strong> Fermi<br />
energy by<br />
<strong>The</strong> equation is now<br />
∆ = E F − E.<br />
R<br />
2 ak(ε + ∆) = − �<br />
Superconductivity 40<br />
k ′<br />
a k ′V kk ′.