final report - JRC IPTS - Sustainable Production and Consumption ...
final report - JRC IPTS - Sustainable Production and Consumption ...
final report - JRC IPTS - Sustainable Production and Consumption ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
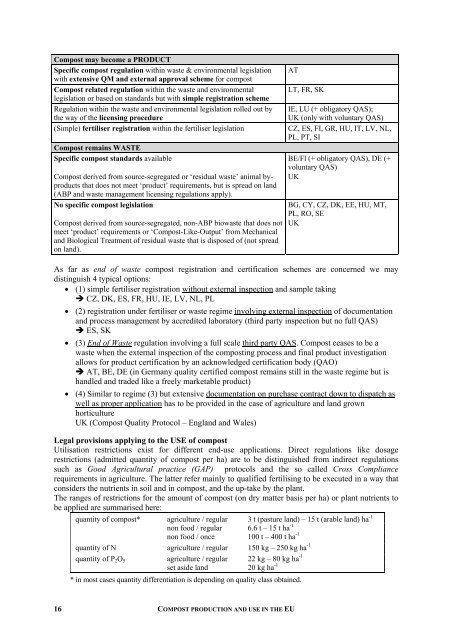
Compost may become a PRODUCT<br />
Specific compost regulation within waste & environmental legislation<br />
with extensive QM <strong>and</strong> external approval scheme for compost<br />
Compost related regulation within the waste <strong>and</strong> environmental<br />
legislation or based on st<strong>and</strong>ards but with simple registration scheme<br />
Regulation within the waste <strong>and</strong> environmental legislation rolled out by<br />
the way of the licensing procedure<br />
16<br />
AT<br />
COMPOST PRODUCTION AND USE IN THE EU<br />
LT, FR, SK<br />
IE, LU (+ obligatory QAS);<br />
UK (only with voluntary QAS)<br />
(Simple) fertiliser registration within the fertiliser legislation CZ, ES, FI, GR, HU, IT, LV, NL,<br />
PL, PT, SI<br />
Compost remains WASTE<br />
Specific compost st<strong>and</strong>ards available<br />
Compost derived from source-segregated or ‘residual waste’ animal byproducts<br />
that does not meet ‘product’ requirements, but is spread on l<strong>and</strong><br />
(ABP <strong>and</strong> waste management licensing regulations apply).<br />
No specific compost legislation<br />
Compost derived from source-segregated, non-ABP biowaste that does not<br />
meet ‘product’ requirements or ‘Compost-Like-Output’ from Mechanical<br />
<strong>and</strong> Biological Treatment of residual waste that is disposed of (not spread<br />
on l<strong>and</strong>).<br />
BE/Fl (+ obligatory QAS), DE (+<br />
voluntary QAS)<br />
UK<br />
BG, CY, CZ, DK, EE, HU, MT,<br />
PL, RO, SE<br />
UK<br />
As far as end of waste compost registration <strong>and</strong> certification schemes are concerned we may<br />
distinguish 4 typical options:<br />
• (1) simple fertiliser registration without external inspection <strong>and</strong> sample taking<br />
� CZ, DK, ES, FR, HU, IE, LV, NL, PL<br />
• (2) registration under fertiliser or waste regime involving external inspection of documentation<br />
<strong>and</strong> process management by accredited laboratory (third party inspection but no full QAS)<br />
� ES, SK<br />
• (3) End of Waste regulation involving a full scale third party QAS. Compost ceases to be a<br />
waste when the external inspection of the composting process <strong>and</strong> <strong>final</strong> product investigation<br />
allows for product certification by an acknowledged certification body (QAO)<br />
� AT, BE, DE (in Germany quality certified compost remains still in the waste regime but is<br />
h<strong>and</strong>led <strong>and</strong> traded like a freely marketable product)<br />
• (4) Similar to regime (3) but extensive documentation on purchase contract down to dispatch as<br />
well as proper application has to be provided in the case of agriculture <strong>and</strong> l<strong>and</strong> grown<br />
horticulture<br />
UK (Compost Quality Protocol – Engl<strong>and</strong> <strong>and</strong> Wales)<br />
Legal provisions applying to the USE of compost<br />
Utilisation restrictions exist for different end-use applications. Direct regulations like dosage<br />
restrictions (admitted quantity of compost per ha) are to be distinguished from indirect regulations<br />
such as Good Agricultural practice (GAP) protocols <strong>and</strong> the so called Cross Compliance<br />
requirements in agriculture. The latter refer mainly to qualified fertilising to be executed in a way that<br />
considers the nutrients in soil <strong>and</strong> in compost, <strong>and</strong> the up-take by the plant.<br />
The ranges of restrictions for the amount of compost (on dry matter basis per ha) or plant nutrients to<br />
be applied are summarised here:<br />
quantity of compost* agriculture / regular 3 t (pasture l<strong>and</strong>) – 15 t (arable l<strong>and</strong>) ha -1<br />
non food / regular 6.6 t – 15 t ha -1<br />
non food / once 100 t – 400 t ha -1<br />
quantity of N agriculture / regular 150 kg – 250 kg ha -1<br />
quantity of P2O5 agriculture / regular 22 kg – 80 kg ha -1<br />
set aside l<strong>and</strong> 20 kg ha -1<br />
* in most cases quantity differentiation is depending on quality class obtained.