CommScope® Enterprise Data Center Design Guide - Public ...
CommScope® Enterprise Data Center Design Guide - Public ...
CommScope® Enterprise Data Center Design Guide - Public ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
14<br />
www.commscope.com<br />
<strong>Data</strong> <strong>Center</strong> Network Architectures<br />
Today, there are three primary approaches in <strong>Data</strong> <strong>Center</strong>s for server networking:<br />
• Direct Connect (Centralized)<br />
• Zone Distribution (including End-of-Row, Middle-of-Row, etc)<br />
• Top-of-Rack (Distributed Electronics)<br />
Which approach you choose is largely determined by the server being deployed and<br />
operational objectives. Each design has its advantages and trade-offs and frequently larger<br />
data centers will house at least two, if not all three approaches to network architecture.<br />
Centralized Direct Connect<br />
The approach requires each server to be cabled back to the core switches. This provides a<br />
very efficient utilization of port switches and is easy to manage and add FOR SMALL SIZE data<br />
centers.<br />
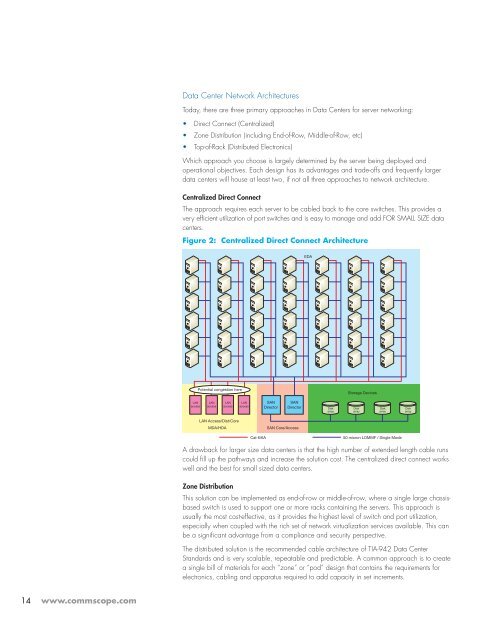
Figure 2: Centralized Direct Connect Architecture<br />
LAN<br />
access<br />
Potential congestion here<br />
LAN<br />
access<br />
LAN<br />
access<br />
LAN Access/Dist/Core<br />
MDA/HDA<br />
LAN<br />
access<br />
SAN<br />
Director<br />
SAN Core/Access<br />
EDA<br />
Storage Devices<br />
SAN<br />
Director Disk<br />
Disk<br />
Disk<br />
Disk<br />
array<br />
array<br />
array<br />
array<br />
Cat 6/6A 50 micron LOMMF / Single Mode<br />
A drawback for larger size data centers is that the high number of extended length cable runs<br />
could fill up the pathways and increase the solution cost. The centralized direct connect works<br />
well and the best for small sized data centers.<br />
Zone Distribution<br />
This solution can be implemented as end-of-row or middle-of-row, where a single large chassisbased<br />
switch is used to support one or more racks containing the servers. This approach is<br />
usually the most cost-effective, as it provides the highest level of switch and port utilization,<br />
especially when coupled with the rich set of network virtualization services available. This can<br />
be a significant advantage from a compliance and security perspective.<br />
The distributed solution is the recommended cable architecture of TIA-942 <strong>Data</strong> <strong>Center</strong><br />
Standards and is very scalable, repeatable and predictable. A common approach is to create<br />
a single bill of materials for each “zone” or “pod” design that contains the requirements for<br />
electronics, cabling and apparatus required to add capacity in set increments.