CommScope® Enterprise Data Center Design Guide - Public ...
CommScope® Enterprise Data Center Design Guide - Public ...
CommScope® Enterprise Data Center Design Guide - Public ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
42<br />
www.commscope.com<br />
TABLE 9: TIA 568C LOMMF AND ISO’S OM PERFORMANCE STANDARDS<br />
Fiber Type or Name<br />
(ISO OM designation)<br />
Loose Tube Fiber Optic Cable Construction<br />
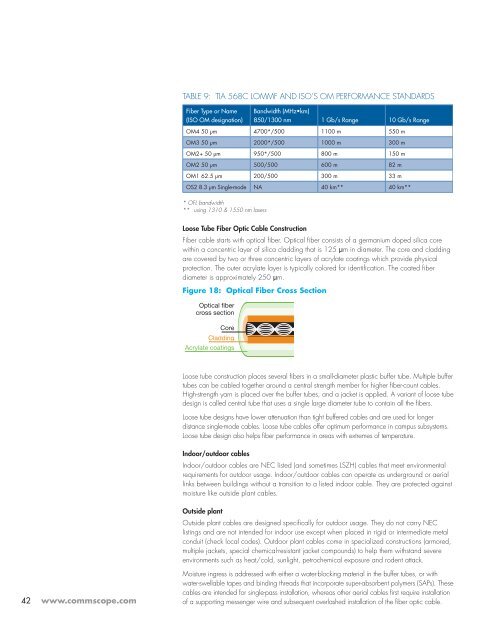
Fiber cable starts with optical fiber. Optical fiber consists of a germanium doped silica core<br />
within a concentric layer of silica cladding that is 125 µm in diameter. The core and cladding<br />
are covered by two or three concentric layers of acrylate coatings which provide physical<br />
protection. The outer acrylate layer is typically colored for identification. The coated fiber<br />
diameter is approximately 250 µm.<br />
Figure 18: Optical Fiber Cross Section<br />
Optical fiber<br />
cross section<br />
Core<br />
Cladding<br />
Acrylate coatings<br />
Bandwidth (MHz•km)<br />
850/1300 nm 1 Gb/s Range 10 Gb/s Range<br />
OM4 50 μm 4700*/500 1100 m 550 m<br />
OM3 50 μm 2000*/500 1000 m 300 m<br />
OM2+ 50 μm 950*/500 800 m 150 m<br />
OM2 50 μm 500/500 600 m 82 m<br />
OM1 62.5 μm 200/500 300 m 33 m<br />
OS2 8.3 μm Single-mode NA 40 km** 40 km**<br />
* OFL bandwidth<br />
** using 1310 & 1550 nm lasers<br />
Loose tube construction places several fibers in a small-diameter plastic buffer tube. Multiple buffer<br />
tubes can be cabled together around a central strength member for higher fiber-count cables.<br />
High-strength yarn is placed over the buffer tubes, and a jacket is applied. A variant of loose tube<br />
design is called central tube that uses a single large diameter tube to contain all the fibers.<br />
Loose tube designs have lower attenuation than tight buffered cables and are used for longer<br />
distance single-mode cables. Loose tube cables offer optimum performance in campus subsystems.<br />
Loose tube design also helps fiber performance in areas with extremes of temperature.<br />
Indoor/outdoor cables<br />
Indoor/outdoor cables are NEC listed (and sometimes LSZH) cables that meet environmental<br />
requirements for outdoor usage. Indoor/outdoor cables can operate as underground or aerial<br />
links between buildings without a transition to a listed indoor cable. They are protected against<br />
moisture like outside plant cables.<br />
Outside plant<br />
Outside plant cables are designed specifically for outdoor usage. They do not carry NEC<br />
listings and are not intended for indoor use except when placed in rigid or intermediate metal<br />
conduit (check local codes). Outdoor plant cables come in specialized constructions (armored,<br />
multiple jackets, special chemical-resistant jacket compounds) to help them withstand severe<br />
environments such as heat/cold, sunlight, petrochemical exposure and rodent attack.<br />
Moisture ingress is addressed with either a water-blocking material in the buffer tubes, or with<br />
water-swellable tapes and binding threads that incorporate super-absorbent polymers (SAPs). These<br />
cables are intended for single-pass installation, whereas other aerial cables first require installation<br />
of a supporting messenger wire and subsequent overlashed installation of the fiber optic cable.