DOWEX Ion Exchange Resins WATER CONDITIONING MANUAL
DOWEX Ion Exchange Resins WATER CONDITIONING MANUAL
DOWEX Ion Exchange Resins WATER CONDITIONING MANUAL
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Demineralization (Deionization) Process<br />
H2SO4 or HCl is usually used for cation resin regeneration at a rate of 2 to 4 ppm for each ppm of cation<br />
removed. Caustic soda (NaOH) is used at a rate of 1 to 2 ppm for each ppm of acid (e.g., HCl and H2SO4)<br />
removed by a weak base anion resin, or 2 to 3 ppm for each ppm of either strong or weak acid anion<br />
removed by a strong base anion resin. Mixed beds normally require 15–20% higher regenerant dosages<br />
than individual beds.<br />
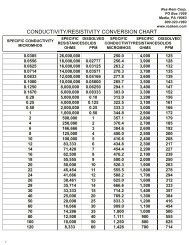
In Table 10, a typical water sample is analyzed before any treatment and after each of the three main<br />
steps in demineralization. The analyses indicate which constituents are removed from the water at each<br />
stage of the process.<br />
Constituent ppm as<br />
Table 10. Results of treatment by the demineralization process.<br />
Typical Raw<br />
Water<br />
Typical Strong<br />
Acid Cation<br />
Effluent after<br />
Degasification<br />
Typical Weak<br />
Base Anion<br />
Effluent after<br />
Degasification<br />
Typical Strong<br />
Base Anion<br />
Effluent<br />
Calcium CaCO3 150 Nil Nil Nil<br />
Magnesium CaCO3 50 Nil Nil Nil<br />
Sodium CaCO3 50 0–5 0–5 0–5<br />
Hydrogen CaCO3 0 100 0 0<br />
Total electrolyte CaCO3 250 100 0–5 0–5<br />
Bicarbonate CaCO3 150 0 0 0<br />
Carbonate CaCO3 0 0 0 0<br />
Hydroxide CaCO3 0 0 0 0–5<br />
Sulfate CaCO3 50 50 0 0<br />
Chloride CaCO3 50 50 0–5 0<br />
Nitrate CaCO3 0 0 0 0<br />
M Alk CaCO3 150 0 0–5 0–5<br />
P Alk CaCO3 0 0 0 0–5<br />
Carbon dioxide CO2 10 5 5 0<br />
pH — 7.5 2.0 7.0 7–9<br />
Silica SiO2 10 10 10 0–0.1<br />
7.3 Equipment Required<br />
A demineralization system may consist of a number of individual ion exchange units (e.g., a two-step<br />
system would involve a cation vessel and an anion vessel) or a single vessel containing a mixture of<br />
cation and anion exchange resins (mixed bed). Also required in any demineralization system are<br />
appropriate piping, valves, chemical regenerant storage, flow controls, and other accessories properly<br />
engineered for economical balance of resin capacity and chemical efficiency. The following illustrations<br />
show the basic types of demineralization processes and which of the constituents is removed by each of<br />
the demineralizing units.<br />
<strong>DOWEX</strong> <strong>Ion</strong> <strong>Exchange</strong> <strong>Resins</strong> 37 Water Conditioning Manual