DOWEX Ion Exchange Resins WATER CONDITIONING MANUAL
DOWEX Ion Exchange Resins WATER CONDITIONING MANUAL
DOWEX Ion Exchange Resins WATER CONDITIONING MANUAL
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Demineralization (Deionization) Process<br />
7.3.1 Equipment Sizing<br />
See Section 11.7.<br />
Note: CADIX can also be used to perform these calculations.<br />
7.4 Product Water Quality<br />
If it is a process water, it is likely that complete removal of carbon dioxide and silica is unnecessary. If so,<br />
a weak base anion resin is used. If removal of carbon dioxide and silica is required, a strong base anion<br />
resin is chosen. Demineralizers can produce waters with varied quality, depending on the type of system<br />
and the water supply. They usually produce water free of suspended solids. Determination of dissolved<br />
solids by evaporation will include any organic matter that may be present in the deionized water. Water<br />
quality is often measured in terms of the amount of suspended solids, dissolved solids concentration, and<br />
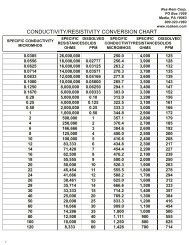
conductivity (µS/cm) or resistivity (MΩ.cm). Since conductivity is the reciprocal of resistivity, 1 µS/cm is<br />
equivalent to 1 MΩ.cm and represents approximately 0.5 ppm. A mixed bed unit is required if water purity<br />
in excess of 5 MΩ.cm is needed. The mixed bed may be the primary unit or a polishing unit following a<br />
multiple bed system.<br />
7.5 Product Water Quantity<br />
Usually, if the water demand is less than approximately 50 gpm (11.4 m 3 /h), the plant will benefit from the<br />
simplest piece of equipment at the expense of a higher chemical operating cost. For that reason, it is<br />
common to find mixed bed demineralizers widely used for small plant requirements because both the<br />
anion and cation resin can be contained in one unit and no degasifier is used. On the other hand, when<br />
plant demands exceed 200 gpm, it is almost certain that several units will be built into the demineralizer<br />
and one will probably be a degasifier.<br />
7.6 Other Demineralization Techniques<br />
The various ion exchange resin combinations indicated in the flow diagrams in Table 11 represent the<br />
majority of system designs employed today. Variations from these standard designs, however, are being<br />
increasingly utilized, especially those techniques that demonstrate significant chemical regenerant<br />
utilization improvements. Two of these techniques are outlined here.<br />
7.6.1 Counter-current Operation<br />
This term refers to the relative flow directions of the service and regeneration cycles. As opposed to the<br />
typical downflow service and regeneration of many systems, counter-current operation is typically<br />
downflow service and upflow regeneration. The primary advantage of counter-current operation is that<br />
very low leakage can be obtained at moderate regeneration levels, thus minimizing operating and waste<br />
disposal costs. Counter-current operation is also advantageous in softening.<br />
7.6.2 Layered Beds<br />
A layered bed of ion exchange resin involves the use of two cation resins or two anion resins in a single<br />
unit. A cation layered bed is composed of a weak acid resin upper layer and a strong acid resin lower<br />
layer, while an anion layered bed uses either a weak base resin upper layer with a strong base resin<br />
lower layer or a strong base resin upper layer and weak base resin lower layer depending on the density<br />
of the resins. In general, the use of layered beds allows some of the advantages of weak acid and weak<br />
base resins to be realized in the operation of a single cation or anion bed. Improved regenerant<br />
efficiencies and, in some cases, improved operating capacities over the corresponding strong acid or<br />
strong base units alone are attained. The layered bed concept is made possible by the density and<br />
particle size differences between the resins used. Upon exhaustion, the backwashing operation separates<br />
the resin layers that may have become partially mixed during service. In order for the full advantages of<br />
the weak acid and weak base resins to be realized, good resin separation is important.<br />
<strong>DOWEX</strong> <strong>Ion</strong> <strong>Exchange</strong> <strong>Resins</strong> 39 Water Conditioning Manual