DOWEX Ion Exchange Resins WATER CONDITIONING MANUAL
DOWEX Ion Exchange Resins WATER CONDITIONING MANUAL
DOWEX Ion Exchange Resins WATER CONDITIONING MANUAL
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Ion</strong> <strong>Exchange</strong> Cleaning Procedures<br />
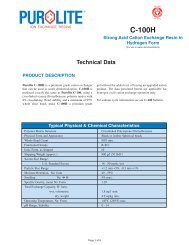
10.1.2 Removal of Barium, Strontium, and Calcium Sulfates from Cation <strong>Resins</strong><br />
Precipitation of BaSO4, SrSO4, and CaSO4 into a cation resin bed is a potential problem with H2SO4<br />
regeneration. Removal of the calcium with HCl is only partially effective because the solubility of CaSO4 in<br />
this media is also relatively low. A more effective treatment is to use a complexing agent for calcium<br />
removal:<br />
1. Carry out the normal regeneration sequence for the cation.<br />
2. Pass upflow one bed volume of 10% sodium citrate over 20–30 min.<br />
3. Leave to soak overnight with occasional air injection if possible to facilitate contact of the citrate with<br />
the resin.<br />
4. Displace/rinse the citrate downflow with minimum five bed volumes of deionized water.<br />
5. Backwash the resin and then carry out a double regeneration (same acid concentration, double<br />
injection time).<br />
Reference Document: Tech Facts 177-01832<br />
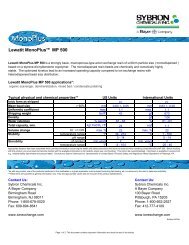
10.1.3 Removal of Iron from Anion <strong>Resins</strong><br />
Two possible cleaning procedures are as follows: Acid Wash with HCl at high concentration: The acid<br />
concentration should be increased gradually to avoid excessive osmotic stress to the resin:<br />
1. Exhaust the resin.<br />
2. Pass upflow one bed volume of 5% HCl solution with a contact time of 30 min.<br />
3. Pass upflow one bed volume of 10% HCl solution with a contact time of 30 min.<br />
4. Leave to soak for 2–4 h.<br />
5. Displace upflow with two to three bed volumes of water.<br />
6. Rinse out with three to five bed volumes of deionized water fast rinse (downflow).<br />
7. Double regenerate the resin (same NaOH concentration, double time).<br />
Reducing agent treatment: The same procedure can be used as for cation resins described above<br />
(Section 10.1.1).<br />
Reference Document: Tech Facts 177-01846<br />
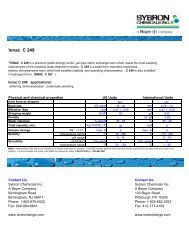
10.1.4 Removal of Calcium and Magnesium from Anion <strong>Resins</strong><br />
Calcium fouling can occur on anion resins if raw filtered water is used as the dilution source for the NaOH<br />
regenerant instead of decationized, softened, or deionized water. If calcium (and magnesium) are present<br />
in the NaOH, then they are likely to precipitate with the bicarbonates/carbonates that are being driven off<br />
of the exchange sites. The result is extremely prolonged rinse times, which render the ion exchange<br />
process inoperable.<br />
Calcium can also be deposited during brine cleaning of mixed bed anions (especially for primary working<br />
mixed beds), when a NaCl/NaOH mixture is introduced to remove organic fouling. If the cation component<br />
of the mixed bed is not regenerated prior to the brine treatment, the formation of Ca(OH)2 and Mg(OH)2<br />
can occur because the alkaline brine mixture is often prepared by introducing NaOH to the mixed bed<br />
vessel and adding salt pellets via the top manway. Therefore, it is critical to first regenerate the cation<br />
resin. The acid concentration should be increased gradually to avoid excessive osmotic stress to the<br />
resin:<br />
1. Exhaust the resin.<br />
2. Backwash the resin for approximately 15 min, with air injection if necessary.<br />
3. Pass upflow one bed volume of 2% HCl solution with a contact time of 30 min.<br />
4. Pass upflow one bed volume of 10% HCl solution.<br />
5. Leave to soak 4–16 h with occasional air injection to facilitate contacting of the acid with the resin.<br />
6. Displace/rinse the acid downflow with minimum five bed volumes of deionized water.<br />
7. Backwash the resin and then carry out a double regeneration (same caustic concentration, double<br />
injection time).<br />
<strong>DOWEX</strong> <strong>Ion</strong> <strong>Exchange</strong> <strong>Resins</strong> 58 Water Conditioning Manual