The Kolb Learning Style Inventory—Version 3.1 2005 - Whitewater ...
The Kolb Learning Style Inventory—Version 3.1 2005 - Whitewater ...
The Kolb Learning Style Inventory—Version 3.1 2005 - Whitewater ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Other Experiential <strong>Learning</strong> Assessment Instruments<br />
<strong>The</strong> <strong>Learning</strong> Skills Profi le<br />
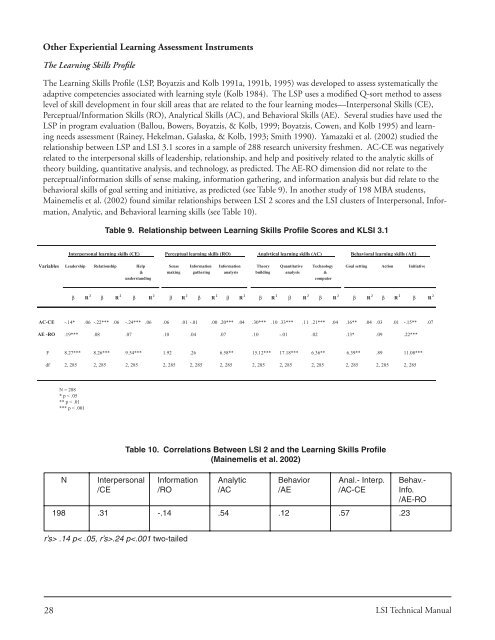
<strong>The</strong> <strong>Learning</strong> Skills Profi le (LSP, Boyatzis and <strong>Kolb</strong> 1991a, 1991b, 1995) was developed to assess systematically the<br />
adaptive competencies associated with learning style (<strong>Kolb</strong> 1984). <strong>The</strong> LSP uses a modifi ed Q-sort method to assess<br />
level of skill development in four skill areas that are related to the four learning modes—Interpersonal Skills (CE),<br />
Perceptual/Information Skills (RO), Analytical Skills (AC), and Behavioral Skills (AE). Several studies have used the<br />
LSP in program evaluation (Ballou, Bowers, Boyatzis, & <strong>Kolb</strong>, 1999; Boyatzis, Cowen, and <strong>Kolb</strong> 1995) and learning<br />
needs assessment (Rainey, Hekelman, Galaska, & <strong>Kolb</strong>, 1993; Smith 1990). Yamazaki et al. (2002) studied the<br />
relationship between LSP and LSI <strong>3.1</strong> scores in a sample of 288 research university freshmen. AC-CE was negatively<br />
related to the interpersonal skills of leadership, relationship, and help and positively related to the analytic skills of<br />
theory building, quantitative analysis, and technology, as predicted. <strong>The</strong> AE-RO dimension did not relate to the<br />
perceptual/information skills of sense making, information gathering, and information analysis but did relate to the<br />
behavioral skills of goal setting and initiative, as predicted (see Table 9). In another study of 198 MBA students,<br />
Mainemelis et al. (2002) found similar relationships between LSI 2 scores and the LSI clusters of Interpersonal, Information,<br />
Analytic, and Behavioral learning skills (see Table 10).<br />
Interpersonal learning skills (CE)<br />
N Interpersonal<br />
/CE<br />
Table 9. Relationship between <strong>Learning</strong> Skills Profi le Scores and KLSI <strong>3.1</strong><br />
Variables Leadership Relationship Help<br />
Sense Information Information <strong>The</strong>ory Quantitative Technology Goal setting<br />
&<br />
making gathering analysis building<br />
analysis<br />
&<br />
understanding computer<br />
β R 2 β R 2 β R 2 β R 2 β R 2 β R 2 β R 2 β R 2 β R 2 β R 2 β R 2 β R 2<br />
AC-CE -.14* .06 -.22*** .06 -.24*** .06 .06 .01 -.01 .00 .20*** .04 .30*** .10 .33*** .11 .21*** .04 .16** .04 .03 .01 -.15** .07<br />
AE -RO .19*** .08 .07 .10 .04 .07 .10 -.01 .02 .13* .09 .22***<br />
F 8.27*** 8.26*** 9.54*** 1.92 .26 6.58** 15.12*** 17.18*** 6.36** 6.39** .89 11.08***<br />
df 2, 285 2, 285 2, 285 2, 285 2, 285 2, 285 2, 285 2, 285 2, 285 2, 285 2, 285 2, 285<br />
N = 288<br />
* p < .05<br />
** p < .01<br />
*** p < .001<br />
Table 10. Correlations Between LSI 2 and the <strong>Learning</strong> Skills Profi le<br />
(Mainemelis et al. 2002)<br />
Information<br />
/RO<br />
Analytic<br />
/AC<br />
Behavior<br />
/AE<br />
Anal.- Interp.<br />
/AC-CE<br />
198 .31 -.14 .54 .12 .57 .23<br />
r’s> .14 p< .05, r’s>.24 p