Eighth Condensed Phase and Interfacial Molecular Science (CPIMS)
Eighth Condensed Phase and Interfacial Molecular Science (CPIMS)
Eighth Condensed Phase and Interfacial Molecular Science (CPIMS)
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Model Catalysis by Size-Selected Cluster Deposition<br />
PI: Scott L. Anderson<br />
Chemistry Department, University of Utah<br />
315 S. 1400 E. Rm 2020<br />
Salt Lake City, UT 84112<br />
<strong>and</strong>erson@chem.utah.edu<br />
Program Scope<br />
The goal of our research is to explore correlations between supported cluster size, electronic <strong>and</strong><br />
morphological structure, the distributions of reactant binding sites, <strong>and</strong> catalytic activity, for model<br />
catalysts prepared using size-selected metal cluster deposition. The work to date has focused on catalysts<br />
with catalytically active metal clusters deposited on metal oxide supports, <strong>and</strong> on electrocatalysis by<br />
metal clusters on glassy carbon electrodes. We are also looking at effects of cluster size on Pd-catalyzed<br />
H2 splitting <strong>and</strong> uptake in metals.<br />
The experimental setup is quite flexible. The main instrument has a mass-selecting ion<br />
deposition beamline fed by a laser vaporization source that produces high fluxes at low deposition<br />
energies (~10 9 Pd10/sec in a 2 mm diameter spot at 1 eV/atom, for example). Typical samples with 0.1<br />
ML-equivalent of metal, deposited in the form of Mn + can be prepared in 10 – 20 minutes, <strong>and</strong> our<br />
analysis methods are also quite fast. Speed is important, because even in UHV these samples are highly<br />
efficient at collecting adventitious contaminants, due to substrate-mediated adsorption. Sample<br />
morphology is probed by low energy He + ion scattering (ISS), electronic structure is probed by x-ray <strong>and</strong><br />
UV photoelectron spectroscopy <strong>and</strong> ion neutralization spectroscopy (XPS, UPS, INS), <strong>and</strong> reactivity is<br />
studied using a differentially pumped mass spectrometer surrounded by a cluster of pulsed <strong>and</strong> cw gas<br />
inlets that can be used to dose the sample while various temperature programs are executed.<br />
The main UHV analysis chamber has a port in the bottom, equipped with a gate valve, a triple<br />
differential seal, <strong>and</strong> one of several interchangeable small chambers with their own pumping systems.<br />
When the sample is positioned in the lower chamber is it isolated from the main UHV system, enabling<br />
high pressures procedures such as film growth or in situ electrochemical studies.<br />
Recent Progress<br />
Strong Effects of Cluster Size <strong>and</strong> Air Exposure on Platinum Electrocatalysis<br />
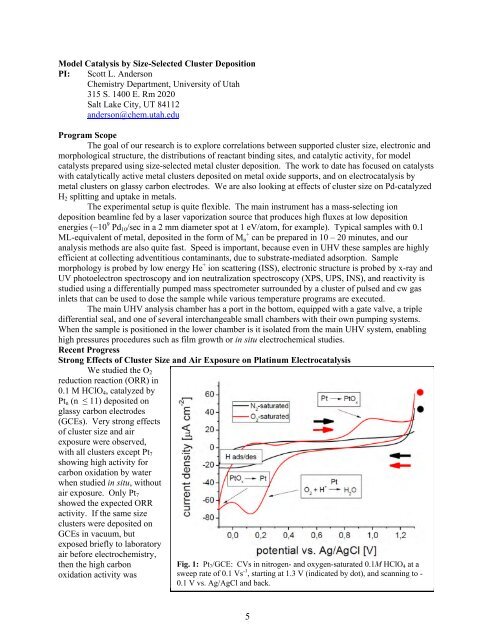
We studied the O2<br />
reduction reaction (ORR) in<br />
0.1 M HClO4, catalyzed by<br />
Ptn (n ≤ 11) deposited on<br />
glassy carbon electrodes<br />
(GCEs). Very strong effects<br />
of cluster size <strong>and</strong> air<br />
exposure were observed,<br />
with all clusters except Pt7<br />
showing high activity for<br />
carbon oxidation by water<br />
when studied in situ, without<br />
air exposure. Only Pt7<br />
showed the expected ORR<br />
activity. If the same size<br />
clusters were deposited on<br />
GCEs in vacuum, but<br />
exposed briefly to laboratory<br />
air before electrochemistry,<br />
then the high carbon<br />
oxidation activity was<br />
Fig. 1: Pt7/GCE: CVs in nitrogen- <strong>and</strong> oxygen-saturated 0.1M HClO4 at a<br />
sweep rate of 0.1 Vs -1 , starting at 1.3 V (indicated by dot), <strong>and</strong> scanning to -<br />
0.1 V vs. Ag/AgCl <strong>and</strong> back.<br />
5