november 2010 volume 1 number 2 - Advances in Electronics and ...
november 2010 volume 1 number 2 - Advances in Electronics and ...
november 2010 volume 1 number 2 - Advances in Electronics and ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
JANUSZ KLEBAN: PACKET DISPATCHING SCHEMES SUPPORTING UNIFORM AND NONUNIFORM TRAFFIC DISTRIBUTION PATTERNS 39<br />
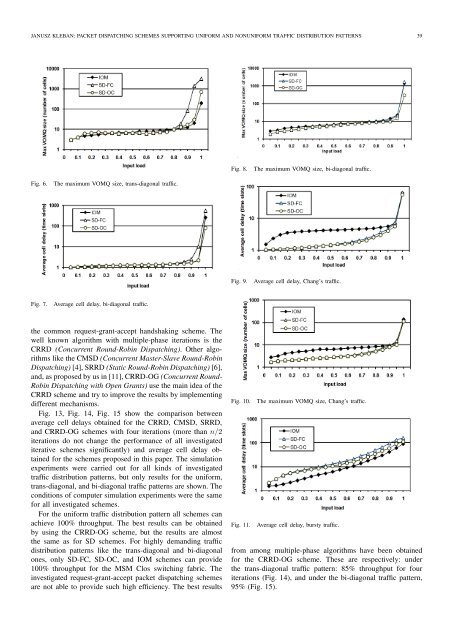
Fig. 6. The maximum VOMQ size, trans-diagonal traffic.<br />
Fig. 7. Average cell delay, bi-diagonal traffic.<br />
the common request-grant-accept h<strong>and</strong>shak<strong>in</strong>g scheme. The<br />
well known algorithm with multiple-phase iterations is the<br />
CRRD (Concurrent Round-Rob<strong>in</strong> Dispatch<strong>in</strong>g). Other algorithmslike<br />
the CMSD (ConcurrentMaster-Slave Round-Rob<strong>in</strong><br />
Dispatch<strong>in</strong>g)[4],SRRD(StaticRound-Rob<strong>in</strong>Dispatch<strong>in</strong>g)[6],<br />
<strong>and</strong>,asproposedbyus<strong>in</strong>[11],CRRD-OG(ConcurrentRound-<br />
Rob<strong>in</strong> Dispatch<strong>in</strong>gwith Open Grants) use the ma<strong>in</strong> idea of the<br />
CRRD scheme <strong>and</strong> try to improvethe results by implement<strong>in</strong>g<br />
different mechanisms.<br />
Fig. 13, Fig. 14, Fig. 15 show the comparison between<br />
average cell delays obta<strong>in</strong>ed for the CRRD, CMSD, SRRD,<br />
<strong>and</strong> CRRD-OG schemes with four iterations (more than n/2<br />
iterations do not change the performance of all <strong>in</strong>vestigated<br />
iterative schemes significantly) <strong>and</strong> average cell delay obta<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
for the schemes proposed <strong>in</strong> this paper. The simulation<br />
experiments were carried out for all k<strong>in</strong>ds of <strong>in</strong>vestigated<br />
traffic distribution patterns, but only results for the uniform,<br />
trans-diagonal, <strong>and</strong> bi-diagonal traffic patterns are shown. The<br />
conditions of computer simulation experiments were the same<br />
for all <strong>in</strong>vestigated schemes.<br />
For the uniform traffic distribution pattern all schemes can<br />
achieve 100% throughput. The best results can be obta<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
by us<strong>in</strong>g the CRRD-OG scheme, but the results are almost<br />
the same as for SD schemes. For highly dem<strong>and</strong><strong>in</strong>g traffic<br />
distribution patterns like the trans-diagonal <strong>and</strong> bi-diagonal<br />
ones, only SD-FC, SD-OC, <strong>and</strong> IOM schemes can provide<br />
100% throughput for the MSM Clos switch<strong>in</strong>g fabric. The<br />
<strong>in</strong>vestigated request-grant-accept packet dispatch<strong>in</strong>g schemes<br />
are not able to provide such high efficiency. The best results<br />
Fig. 8. The maximum VOMQ size, bi-diagonal traffic.<br />
Fig. 9. Average cell delay, Chang’s traffic.<br />
Fig. 10. The maximum VOMQ size, Chang’s traffic.<br />
Fig. 11. Average cell delay, bursty traffic.<br />
from among multiple-phase algorithms have been obta<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
for the CRRD-OG scheme. These are respectively: under<br />
the trans-diagonal traffic pattern: 85% throughput for four<br />
iterations (Fig. 14), <strong>and</strong> under the bi-diagonal traffic pattern,<br />
95% (Fig. 15).