GV-Redundant and Failover Server User Manual(RFSV1
GV-Redundant and Failover Server User Manual(RFSV1
GV-Redundant and Failover Server User Manual(RFSV1
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1.1.3 Optimal Network Requirements<br />
1<br />
Introduction<br />
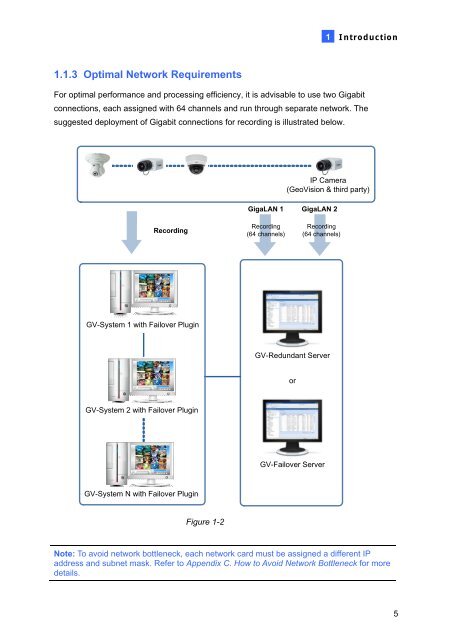
For optimal performance <strong>and</strong> processing efficiency, it is advisable to use two Gigabit<br />
connections, each assigned with 64 channels <strong>and</strong> run through separate network. The<br />
suggested deployment of Gigabit connections for recording is illustrated below.<br />
Recording<br />
<strong>GV</strong>-System 1 with <strong>Failover</strong> Plugin<br />
<strong>GV</strong>-System 2 with <strong>Failover</strong> Plugin<br />
<strong>GV</strong>-System N with <strong>Failover</strong> Plugin<br />
Figure 1-2<br />
GigaLAN 1<br />
Recording<br />
(64 channels)<br />
IP Camera<br />
(GeoVision & third party)<br />
<strong>GV</strong>-<strong>Redundant</strong> <strong>Server</strong><br />
or<br />
GigaLAN 2<br />
Recording<br />
(64 channels)<br />
<strong>GV</strong>-<strong>Failover</strong> <strong>Server</strong><br />
Note: To avoid network bottleneck, each network card must be assigned a different IP<br />
address <strong>and</strong> subnet mask. Refer to Appendix C. How to Avoid Network Bottleneck for more<br />
details.<br />
5