Metodos-Numericos-Basicos-Para-Ingenieria
Metodos-Numericos-Basicos-Para-Ingenieria
Metodos-Numericos-Basicos-Para-Ingenieria
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Asesorías en Matemáticas, Física e Ingeniería<br />
Métodos numéricos básicos para ingeniería<br />
7<br />
Algoritmo 1.2: Polinomios de Lagrange en Matlab<br />
Entradas: valor a interpolar x, vectores conteniendo los puntos X y Y.<br />
Salidas: valor interpolado y.<br />
function [y]=PoliLagrange(x,X,Y)<br />
y=0;<br />
for i=1:numel(X)<br />
L=1;<br />
for j=1:numel(X)<br />
if j~=i<br />
L=L*(x-X(j))/(X(i)-X(j));<br />
end<br />
end<br />
y=y+L*Y(i);<br />
end<br />
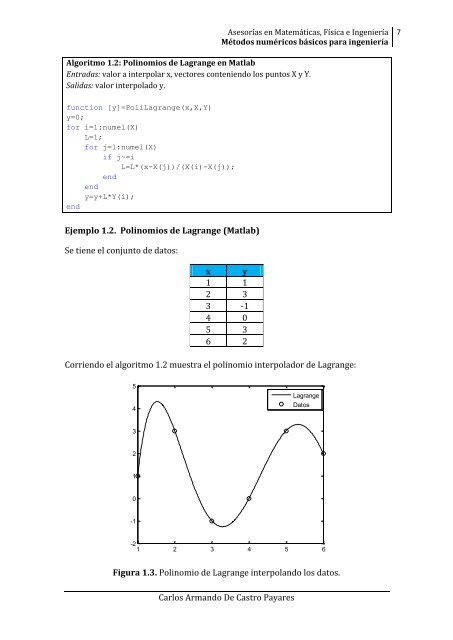
Ejemplo 1.2. Polinomios de Lagrange (Matlab)<br />
Se tiene el conjunto de datos:<br />
x y<br />
1 1<br />
2 3<br />
3 -1<br />
4 0<br />
5 3<br />
6 2<br />
Corriendo el algoritmo 1.2 muestra el polinomio interpolador de Lagrange:<br />
5<br />
4<br />
Lagrange<br />
Datos<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
0<br />
-1<br />
-2<br />
1 2 3 4 5 6<br />
Figura 1.3. Polinomio de Lagrange interpolando los datos.<br />
Carlos Armando De Castro Payares