Temas de Pediatria - Nestlé
Temas de Pediatria - Nestlé
Temas de Pediatria - Nestlé
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
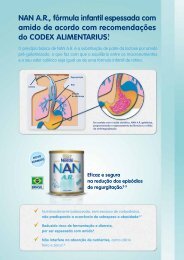
<strong>Temas</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>Pediatria</strong> nº 90<br />
AR-Bed(R)” in 3 weeks – 3 month old infants on<br />
regurgitation, associated symptoms andacid refl<br />
ux. Arch Dis Child 2010;95:26–30.<br />
36. Horwath A, Dzierchciarz P, Szajewska H. The<br />
effect of thickened feed interventions on gastroesophageal<br />
reflux in infants: systematic review<br />
and meta-analysis of randomized, control trials.<br />
Pediatrics 2008;122:e1268-e1277.<br />
37. Bosscher D, Van Caillie-Bertrand M, Deelstra H.<br />
Do thickening properties of locust bean gum affect<br />
the amount of calcium, iron and zinc available for<br />
absorption from infant formula In vitro studies.<br />
Int J Food Sci Nutr 2003;54:261–832.<br />
38. Chao H, Van<strong>de</strong>nplas Y. Effect of cereal-thicekned<br />
formula and upright positioning on regurgitation,<br />
gastric emptying and weight gain in infants with<br />
regurgitation. Nutrition 2007; 23(1): 23-8.<br />
39. Wenzl TG, Schnei<strong>de</strong>r S, Scheele F, Silny J, Heimann<br />
G, Skopnik H. Effects of thickene feeding<br />
on gastroesophageal reflux in infants: a placebocontrolled<br />
crossover study using intraluminal<br />
impedance. Pediatrics. 2003; 111(4): e355-9.<br />
40. Iacono G, Carroccio A, Cavataio F, et al. Gastroesophageal<br />
reflux and cow’s milk allergy in<br />
infants: a prospective study. J Allergy Clin Immunol<br />
1996;97:822–7.<br />
41. Nielsen RG, Bindslev-Jensen C, Kruse-An<strong>de</strong>rsen,<br />
S, Husby S. Severe Gastroesophageal Reflux<br />
Disease and Cow Milk Hypersensitivity in Infants<br />
and Children: Disease Associatio and Evaluation<br />
of a New Challenge Procedure. JPGN 2004; 39(4):<br />
383-91.<br />
42. Kaltenbach T, Crickett S, Gerson LB. Are lifestyle<br />
measures effective in patients with gastroesophageal<br />
reflux disease An evi<strong>de</strong>nce-based approach.<br />
Arch Intern Med. 2006 May 8;166(9):965-71.<br />
43. Salvatore S, Hauser B, Salvatoni A, Van<strong>de</strong>nplas Y.<br />
Oral ranitidine and duration of gastric pH > 4.0<br />
in infants with persisting reflux-symptoms. Acta<br />
Paediatr. 2006 Feb;95(2):176-81.<br />
44. Barron JJ, Tan H, Spalding J, et al. Proton pump<br />
inhibitor utilization patterns in infants. J Pediatr<br />
Gastroenterol Nutr 2007;45:421–7.<br />
45. Omari T, Haslam R, Lundborg P, Davidson, G.<br />
Effect of Omeprazole on Acid Gastroesophageal<br />
Reflux and Gastric Acidity in Preterm Infants With<br />
Pathological Acid Reflux. JPGN 2007;44(1):41-44.<br />
46. Canani RB, Cirillo P, Roggero P, et al. Therapy with<br />
gastric acidity inhibitors increases the risk of acute<br />
gastroenteritis and community-acquired pneumonia<br />
in children. Pediatrics 2006;117:e817–20.<br />
47. Guillet R, Stoll BJ, Cotten CM, et al. Association<br />
of H2-blocker therapy and higher inci<strong>de</strong>nce of<br />
necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight<br />
infants. Pediatrics 2006;117:e137–42.<br />
48. Gremse D, Winter H, Tolia V, et al. Pharmacokinetics<br />
and pharmacodynamics of lansoprazole<br />
in children with gastroesophageal reflux disease.<br />
J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2002;35(Suppl<br />
4):S319–26.<br />
49. Zhao J, Li J, Hamer-Maansson JE, et al. Pharmacokinetic<br />
properties of esomeprazole in children aged<br />
1 to 11 years with symptoms of gastroesophageal<br />
reflux disease: a randomized, open-label study.<br />
Clin Ther 2006;28:1868–76.<br />
50. Tounian P. Gastroesophageal reflux treatment:<br />
From therapeutic abstention to surgery. Arch Ped<br />
2009:16;1424-28.<br />
51. Winter HS. Gastroesophageal reflux in infants.<br />
www.uptodate.com (2010):1-12.<br />
52. Keady S. Update on drugs for gastro-oesophageal<br />
reflux disease. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed.<br />
2007 Aug;92(4):ep114-8.<br />
53. Hibbs AM, Lorch SA. Metocloprami<strong>de</strong> for the<br />
treatment of gastroesophagel reflux disease in<br />
infants a systematic review. Pediatrics. 2006<br />
Aug;118(2):746-52.<br />
54. Lee SL, Sydorak RM, Chiu VY, Hsu JW, Applebaum<br />
H, Haigh PI. Long-term antireflux medication use<br />
following pediatric Nissen fundoplication. Arch<br />
Surg. 2008 Sep;143(9):873-6.<br />
<strong>Nestlé</strong> Nutrition Institute<br />
23