Tragflügelprofil für ein schnelles Standardklasse Segelflugzeug - IAG
Tragflügelprofil für ein schnelles Standardklasse Segelflugzeug - IAG
Tragflügelprofil für ein schnelles Standardklasse Segelflugzeug - IAG
Erfolgreiche ePaper selbst erstellen
Machen Sie aus Ihren PDF Publikationen ein blätterbares Flipbook mit unserer einzigartigen Google optimierten e-Paper Software.
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong><br />
<strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
0. Überblick<br />
1. Aufgabenstellung<br />
- Leistungs – Segelflug<br />
- Entwurfs – Idee<br />
- Auslegung<br />
- Anforderungen<br />
2. Das Profil<br />
- Die fs 34<br />
- Idealpolare<br />
- Holzwege<br />
- Umschlagsliniengestaltung<br />
- Endgültiger Entwurf<br />
3. Leistungsabschätzung<br />
- Handling<br />
- Vergleich mit Discus<br />
4. Ergebnis<br />
Profilseminar 2006 / 2007 Klemens Nübler
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong> <strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
1. Aufgabenstellung: Leistungs – Segelflug<br />
- versch. Wettbewerbsklassen<br />
- Standard-Klasse: 15 m Spannweite, starres Profil<br />
- typischer Flugverlauf<br />
50 %<br />
50 %<br />
KOMPROMISS<br />
- Idee: Optimierung zugunsten der Flugleistungen im Schnellflug<br />
+ evtl. Leistungsgewinn<br />
- anspruchsvoller<br />
1 / 13 Profilseminar 2006 / 2007 Klemens Nübler
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong> <strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
1. Aufgabenstellung: Auslegung<br />
Reibungswiderstand im Schnellflug groß -> kl<strong>ein</strong>e Fläche nötig<br />
-> hohe Streckung -> Induz. Widerstandszuwachs vertretbar<br />
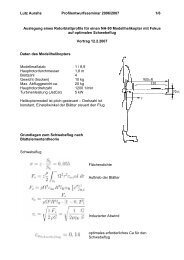
Discus 2 LS - 8 HoGeSe<br />
Flügelfläche [m 2 ] 10,16 10,5 8<br />
Leergewicht [kg] 240 275 220<br />
Abfluggewicht [kg] 340 375 320<br />
Flächenbelastung [kg/m 2 ] 33,5 35,7 40,0<br />
Streckung [-] 22,1 21,4 28,1<br />
Anforderungen:<br />
Flugzustand Güte v [km/h] Ca Re Cw,i<br />
Stall 80 1,59 7,62E+05 0,0286<br />
Kreisflug okay 100 1,02 9,52E+05 0,0117<br />
Streckenflug sehr gut 140 0,52 1,33E+06 0,0031<br />
160 0,40 1,52E+06 0,0018<br />
180 0,31 1,71E+06 0,0011<br />
- Ca,max = 1,6<br />
- Akzeptables Cw bei 100 km/h<br />
- Sehr geringes Cw zwischen 140 und 180 km/h<br />
2 / 13 Profilseminar 2006 / 2007 Klemens Nübler
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong><br />
<strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
0. Überblick<br />
1. Aufgabenstellung<br />
- Leistungs – Segelflug<br />
- Entwurfs – Idee<br />
- Auslegung<br />
- Anforderungen<br />
2. Das Profil<br />
- Die fs 34<br />
- Idealpolare<br />
- Holzwege<br />
- Umschlagsliniengestaltung<br />
- Endgültiger Entwurf<br />
3. Leistungsabschätzung<br />
- Handling<br />
- Vergleich mit Discus<br />
4. Ergebnis<br />
Profilseminar 2006 / 2007 Klemens Nübler
2. Das Profil: Die fs 34<br />
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong> <strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
Idee: Schnellflug-<strong>Segelflugzeug</strong> mit<br />
variabler Flügelfläche durch Fowlerklappe <strong>ein</strong>: 8 m^2<br />
Rennklasse<br />
Profil: DU94-VC-125<br />
Im Schnellflugbereich gleiches Auslegungsziel<br />
Aber: HoGeSe benötigt höheres Ca, max<br />
Projekt wurde nicht realisiert:<br />
Leistungsabschätzung ließ kaum Vorteile erwarten geg. Rennklasse<br />
Komplizierte Kinematik in dünnem Flügel<br />
3 / 13 Profilseminar 2006 / 2007 Klemens Nübler
2. Das Profil: Idealpolare<br />
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong> <strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
Dünnes Profil mit schmaler Laminardelle angestrebt<br />
5 / 13 Profilseminar 2006 / 2007 Klemens Nübler
2. Das Profil: Der Holzweg I<br />
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong> <strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
Zu starker HDA auf US -> Ablösung<br />
-> schöne LD<br />
Umschlagslinie OS <strong>ein</strong>igermaßen<br />
6 / 13 Profilseminar 2006 / 2007 Klemens Nübler
2. Das Profil: Der Holzweg II<br />
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong> <strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
Schlechte Umschlagsliniengestaltung OS<br />
-> schlechtes Ca, max<br />
6 / 13 Profilseminar 2006 / 2007 Klemens Nübler
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong> <strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
2. Das Profil: Umschlagsliniengestaltung OS<br />
NDA<br />
HDA<br />
2 Druckanstiege ergeben<br />
2 Auslegungsbereiche:<br />
- Lam. Lauflänge ~ 70 %<br />
- Turbulenzprofil mit hohen Ca<br />
Problem: Unterseite schlägt bei<br />
relativ hohen Ca um<br />
8 / 13 Profilseminar 2006 / 2007 Klemens Nübler
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong> <strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
2. Das Profil: Endgültiger Entwurf
2. Das Profil: Vergleich<br />
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong> <strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong>
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong><br />
<strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
0. Überblick<br />
1. Aufgabenstellung<br />
- Leistungs – Segelflug<br />
- Entwurfs – Idee<br />
- Auslegung<br />
- Anforderungen<br />
2. Das Profil<br />
- Die fs 34<br />
- Idealpolare<br />
- Holzwege<br />
- Umschlagsliniengestaltung<br />
- Endgültiger Entwurf<br />
3. Leistungsabschätzung<br />
- Handling<br />
- Vergleich mit Discus<br />
4. Ergebnis<br />
Profilseminar 2006 / 2007 Klemens Nübler
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong> <strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
3. Leistungsabschätzung: Handling<br />
Klappenausschlag:<br />
Verschiebung der Ca / alfa Kurve möglich<br />
K<strong>ein</strong>e großen Cw - Einbußen<br />
Überziehen:<br />
Grenzbereich: 10 km/h und 5°<br />
Abkippen vermutlich hart<br />
11 / 13 Profilseminar 2006 / 2007 Klemens Nübler
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong> <strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
3. Leistungsabschätzung: Vergleich mit Discus<br />
Profilpolare von Discus nicht verfügbar, aber Flugzeugpolare<br />
0<br />
0,5<br />
1<br />
1,5<br />
2<br />
2,5<br />
3<br />
3,5<br />
Rumpfwiderstand ?<br />
Flugzeugpolaren von Discus und HoGeSe<br />
50 100 150 200 250<br />
Aussagekraft<br />
Eingeschränkt !<br />
Discus HoGeSe<br />
12 / 13 Profilseminar 2006 / 2007 Klemens Nübler
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong><br />
<strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
0. Überblick<br />
1. Aufgabenstellung<br />
- Leistungs – Segelflug<br />
- Entwurfs – Idee<br />
- Auslegung<br />
- Anforderungen<br />
2. Das Profil<br />
- Die fs 34<br />
- Idealpolare<br />
- Holzwege<br />
- Umschlagsliniengestaltung<br />
- Endgültiger Entwurf<br />
3. Leistungsabschätzung<br />
- Handling<br />
- Vergleich mit Discus<br />
4. Ergebnis<br />
Profilseminar 2006 / 2007 Klemens Nübler
4. Ergebnis<br />
<strong>Tragflügelprofil</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>ein</strong> <strong>schnelles</strong> <strong>Standardklasse</strong> <strong>Segelflugzeug</strong><br />
Entwurf im Prinzip erfolgreich<br />
Entwurf mit 8 m^2 zu radikal<br />
bei guter Thermik vermutlich überlegen<br />
Praxistauglichkeit fragwürdig:<br />
-schwieriger zu fliegen<br />
-bei schwacher Thermik im Nachteil<br />
13 / 13 Profilseminar 2006 / 2007 Klemens Nübler