- Page 1 and 2:
TRANSITION METAL-CATALYZED REACTION
- Page 3 and 4:
Transition Metal-Catalyzed Reaction
- Page 5 and 6:
List of Abbreviations Ac acetyl AcO
- Page 7 and 8:
Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction.
- Page 9 and 10:
Appendix A : X-ray crystal structur
- Page 11 and 12:
Table 4.8 Rh(I)-catalyzed cyclocarb
- Page 13 and 14:
List of Schemes Scheme 1.1 Three fo
- Page 15 and 16:
Scheme 3.24 Preparation of amide-te
- Page 17 and 18:
Scheme 4.16 Formation of bicyclo[5.
- Page 19 and 20:
1.0 Introduction 1.1 The Role of Di
- Page 21 and 22:
According to these guidelines, the
- Page 23 and 24:
Scheme 1.1 Three forms of diversity
- Page 25 and 26:
Another example from the Schreiber
- Page 27 and 28:
1.1.1 Transition Metal-Catalyzed Re
- Page 29 and 30:
37, , such reactions include transi
- Page 31 and 32:
the proximal olefin of allenyne 38
- Page 33 and 34:
2.0 Design and Synthesis of the Piv
- Page 35 and 36:
The allenic amino acid derivatives
- Page 37 and 38:
This protocol proved particularly u
- Page 39 and 40:
ZnCl2, which results in a Zn-chelat
- Page 41 and 42: Scheme 2.7 Synthesis of trisubstitu
- Page 43 and 44: THF), the yield was increased from
- Page 45 and 46: the terminus of the alkyne led to d
- Page 47 and 48: N-Alkylation of the glycine-derived
- Page 49 and 50: circumvent this issue, variants suc
- Page 51 and 52: BINAP as a chiral ligand to obtain
- Page 53 and 54: stereochemistry of the exocyclic ol
- Page 55 and 56: 3.2 Rhodium(I)-Catalyzed Allenic Cy
- Page 57 and 58: exocyclic olefin geometry is not re
- Page 59 and 60: 3.2.1 Preparation of Enol-ether Tri
- Page 61 and 62: Scheme 3.15 Synthesis of cycloisome
- Page 63 and 64: Scheme 3.17 Cycloisomerization of a
- Page 65 and 66: Scheme 3.19 Tandem cycloadditions o
- Page 67 and 68: Scheme 3.21 Intermolecular Diels-Al
- Page 69 and 70: attractive, since additional functi
- Page 71 and 72: increased yield of the triene (47%)
- Page 73 and 74: as an isobutyl-amide 155b was prepa
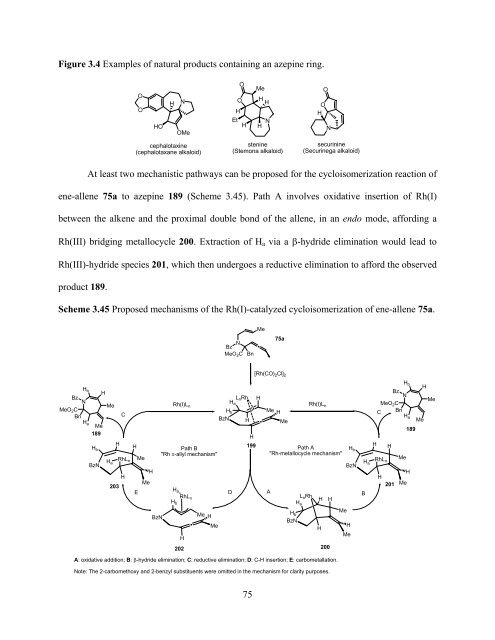
- Page 75 and 76: group) demonstrated that this cyclo
- Page 77 and 78: in 1M HCl/dioxane (1 : 1) for 1h, t
- Page 79 and 80: ppm (dd, J = 7.1, 4.6 Hz, 1H) assig
- Page 81 and 82: http://ccc.chem.pitt.edu/). Using f
- Page 83 and 84: Notably, exclusive cycloisomerizati
- Page 85 and 86: intermediate in the reaction we sou
- Page 87 and 88: epulsive dipole interactions (Schem
- Page 89 and 90: Table 3.4 Diels-Alder reactions of
- Page 91: allenic Alder-ene reaction, ene-all
- Page 95 and 96: species onto the proximal double bo
- Page 97 and 98: Scheme 3.49 Rh(I)-catalyzed ene rea
- Page 99 and 100: y Magnus 144 and it involves the in
- Page 101 and 102: usually is DMSO. Heating to 100 ºC
- Page 103 and 104: that require high pressures of CO.
- Page 105 and 106: In contrast to the Mo(CO)6-mediated
- Page 107 and 108: Scheme 4.15 Rh(I)-catalyzed allenic
- Page 109 and 110: 4.2 Rhodium(I)-Catalyzed Cyclocarbo
- Page 111 and 112: lack of double bond selectivity, si
- Page 113 and 114: Table 4.2 Cyclocarbonylation reacti
- Page 115 and 116: Notably, the allenic cyclocarbonyla
- Page 117 and 118: Scheme 4.22 Cyclocarbonylation reac
- Page 119 and 120: neat or in solution. This decomposi
- Page 121 and 122: the newly synthesized fulvenes (e.g
- Page 123 and 124: stereocenters and mixture of E/Z is
- Page 125 and 126: proximal double bond to give α-alk
- Page 127 and 128: the methyl ester and Ha are syn. Sc
- Page 129 and 130: that the major diastereomer in the
- Page 131 and 132: We were motivated to first examine
- Page 133 and 134: Scheme 4.42 Synthesis of pyrrole 29
- Page 135 and 136: periodic acid (H5IO6). 209 These hi
- Page 137 and 138: eaction failed to go to completion,
- Page 139 and 140: 4.5.2 Synthesis of a Library of Tri
- Page 141 and 142: diketones 312{1-3,1-2} in yields ra
- Page 143 and 144:
Figure 4.2 Distribution for physico
- Page 145 and 146:
tricyclic pyrrole 314{3,2,26} (Figu
- Page 147 and 148:
4.6 Synthesis of α-Alkylidene Cycl
- Page 149 and 150:
anched and linear carboxylic acid i
- Page 151 and 152:
eactivity of the species prepared i
- Page 153 and 154:
considerably lower than the ratio o
- Page 155 and 156:
diastereomer. Next, allenyne 328 wa
- Page 157 and 158:
Conclusions In summary, we have dem
- Page 159 and 160:
Experimental Section General Method
- Page 161 and 162:
General procedure A for esterificat
- Page 163 and 164:
F Bz N H 56f 2-Benzoylamino-3-(4-fl
- Page 165 and 166:
MeO2C Bz N H 58c 2-Benzoylamino-2-m
- Page 167 and 168:
MeO MeO2C Bz N H 58e 2-Benzoylamino
- Page 169 and 170:
mL) and MeOH (10 mL) instead of sat
- Page 171 and 172:
hexanes-EtOAc, 19 : 1 to 4 : 1, v/v
- Page 173 and 174:
which was immediately used in the C
- Page 175 and 176:
Boc TMS N H Bn 64f tert-Butyl-1-((4
- Page 177 and 178:
MeI (38 µL, 0.62 mmol). Yield 65a
- Page 179 and 180:
with brine and concentrated under v
- Page 181 and 182:
H MeO 2C • H Bn NHBoc tert-Butyl-
- Page 183 and 184:
TMS MeO 2C • 70 H H NHBoc 2-tert-
- Page 185 and 186:
185 (10), 141 (21), 57 (100); EI-HR
- Page 187 and 188:
dispersion in mineral oil, 1.0 mmol
- Page 189 and 190:
EI-HRMS calcd for C30H26NO3 m/z [M-
- Page 191 and 192:
CbzN MeO 2C Me 73h 2-[Benzyloxycarb
- Page 193 and 194:
CbzN MeO 2C Me 2-(Benzyloxycarbonyl
- Page 195 and 196:
dispersion in mineral oil, 3.85 mmo
- Page 197 and 198:
completion of the addition, the rea
- Page 199 and 200:
BzN MeO 2C S 74h 2-(Benzoylprop-2-y
- Page 201 and 202:
BzN MeO 2C Bn 75b 2-(Allylbenzoylam
- Page 203 and 204:
BzN MeO 2C TBSO 75e 2-(Benzoylbut-2
- Page 205 and 206:
Hz, 1H), 5.85 (s, 1H), 5.52 (dd, J
- Page 207 and 208:
1H), 3.69 (s, 3H), 1.58 (d, J = 7.1
- Page 209 and 210:
µmol), [Rh(CO)2Cl]2 (1 mg, 3 µmol
- Page 211 and 212:
1.25 (m, 6H), 0.88 (t, J = 6.9 Hz,
- Page 213 and 214:
6.72 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 0.5H), 6.68 (d
- Page 215 and 216:
BzN MeO2C Bn 122a Methyl-2-(N-(but-
- Page 217 and 218:
Bz N MeO2C Bn 1-Benzoyl-2-benzyl-4-
- Page 219 and 220:
13.9, 5.3 Hz, 1H), 2.51-2.47 (m, 1H
- Page 221 and 222:
15 min the solvent was removed unde
- Page 223 and 224:
Benzoyl chloride (0.169 mL, 1.46 mm
- Page 225 and 226:
mg, 0.11 mmol), [Rh(CO)2Cl]2 (4 mg,
- Page 227 and 228:
mL). kk The aqueous layer was extra
- Page 229 and 230:
ºC. After quenching the reaction b
- Page 231 and 232:
129.8, 129.0, 128.7, 128.4, 126.2,
- Page 233 and 234:
MeO 2C O O O N H N R 1 O N Ph [10c-
- Page 235 and 236:
The crude residue was purified by f
- Page 237 and 238:
14.4 Hz, 1H), 3.49-3.39 (m, 2H), 3.
- Page 239 and 240:
1H), 5.49 (dd, J = 17.3, 1.8 Hz, 1H
- Page 241 and 242:
was stirred at rt for 1 h when it w
- Page 243 and 244:
BzN HOOC 2-(N-(but-2-ynyl)benzamido
- Page 245 and 246:
°C and DIBAL-H (0.440 mL of a 1.0M
- Page 247 and 248:
129 (62), 91 (100); EI-HRMS calcula
- Page 249 and 250:
(d, J = 18.0 Hz, 1H), 4.14 (d, J =
- Page 251 and 252:
4.98 (dt, J = 7.7, 5.1 Hz, 1H), 4.1
- Page 253 and 254:
N Bz MeO2C OTBS 214 1-Benzoyl-2-(te
- Page 255 and 256:
270a (major diastereomer-eluting fi
- Page 257 and 258:
CDCl3): δ 7.42-7.17 (m, 13H), 7.04
- Page 259 and 260:
18.6 Hz, 1H), 4.34 (d, J = 18.0 Hz,
- Page 261 and 262:
Bz N MeO2C 2-Benzoyl-3,7-dimethyl-6
- Page 263 and 264:
v/v) afforded a mixture of compound
- Page 265 and 266:
(435 mg, 1.21 mmol), DMSO (429 µL,
- Page 267 and 268:
4.02 (s, 1H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 1.82 (s
- Page 269 and 270:
(207 mg, 96%) consisting of 287e (7
- Page 271 and 272:
procedure O, using: 74f (110 mg, 0.
- Page 273 and 274:
Bz N O H CO2Me BocN 287i 3-(2-Benzo
- Page 275 and 276:
4.17 (d, J = 15.0 Hz, 1H), 4.10 (d,
- Page 277 and 278:
137.1, 136.9, 130.4, 129.8, 128.5,
- Page 279 and 280:
H BzN MeO2C Bn H N C3H7 298b CO 2Me
- Page 281 and 282:
NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 172.3, 169.
- Page 283 and 284:
following the general procedure Q,
- Page 285 and 286:
H BzN MeO2C Bn H 5-Benzoyl-1,4-dibe
- Page 287 and 288:
119.9, 114.1, 109.9, 108.6, 73.0, 5
- Page 289 and 290:
4.11 (m, 1H), 4.07-3.98 (m, 1H), 3.
- Page 291 and 292:
126.8, 126.2, 109.0, 72.9, 58.7, 56
- Page 293 and 294:
NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 172.2, 169.
- Page 295 and 296:
3.0 Hz, 1H), 5.82-5.80 (m, 1H), 5.2
- Page 297 and 298:
87%). The diastereomeric ratio (288
- Page 299 and 300:
APPENDIX A: X-ray crystal structure
- Page 301 and 302:
APPENDIX B: X-ray crystal structure
- Page 303 and 304:
APPENDIX C: X-ray crystal structure
- Page 305 and 306:
APPENDIX D: X-ray crystal structure
- Page 307 and 308:
APPENDIX E: X-ray crystal structure
- Page 309 and 310:
APPENDIX F: QikProp property predic
- Page 311 and 312:
1 H and 13 C NMRs of 74b 293
- Page 313 and 314:
1 H and 13 C NMRs of 111a 295
- Page 315 and 316:
1 H and 13 C NMRs of 155a 297
- Page 317 and 318:
1 H and 13 C NMRs of 156a 299
- Page 319 and 320:
1 H and 13 C NMRs of 186b 301
- Page 321 and 322:
1 H and 13 C NMRs of 270h 303
- Page 323 and 324:
1 H and 13 C NMRs of 287b 305
- Page 325 and 326:
1 H and 13 C NMRs of 307 307
- Page 327 and 328:
1 H and 13 C NMRs of 308n 309
- Page 329 and 330:
10. (a) Burke, M. D.; Schreiber, S.
- Page 331 and 332:
Hu, Y. J. Comb. Chem. 2006, 8, 286.
- Page 333 and 334:
49. For reviews on reactions of all
- Page 335 and 336:
69. (a) Trost, B. M.; Lautens, M.;
- Page 337 and 338:
containing cross-conjugated trienes
- Page 339 and 340:
Vaillancourt, J.; Rasper, D. M.; Ta
- Page 341 and 342:
130. Oppolzer, W.; Snieckus, V. Ang
- Page 343 and 344:
149. (a) Hicks, F. A.; Buchwald, S.
- Page 345 and 346:
Maiese, W. M. J. Antibiot. 2000, 53
- Page 347 and 348:
192. The mechanism of decomposition
- Page 349 and 350:
Boger, D. L.; Boyce, C. W.; Labroli
- Page 351:
Generated Inhibitors of Human Mitog