Microbiology and Spoilage Trail in Nile Perch (Lates niloticus), Lake ...
Microbiology and Spoilage Trail in Nile Perch (Lates niloticus), Lake ...
Microbiology and Spoilage Trail in Nile Perch (Lates niloticus), Lake ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Vibrionaceae at higher temperatures. Also there is still no selective or <strong>in</strong>dicative medium<br />
available for the Pseudomonas spp. which spoil some tropical <strong>and</strong> fresh water fish or for<br />
Photobacterium phosphoreum that spoil packed fresh fish. However there are some<br />
common used media <strong>in</strong> enumeration of some spoilage bacteria shown <strong>in</strong> table 9 below.<br />
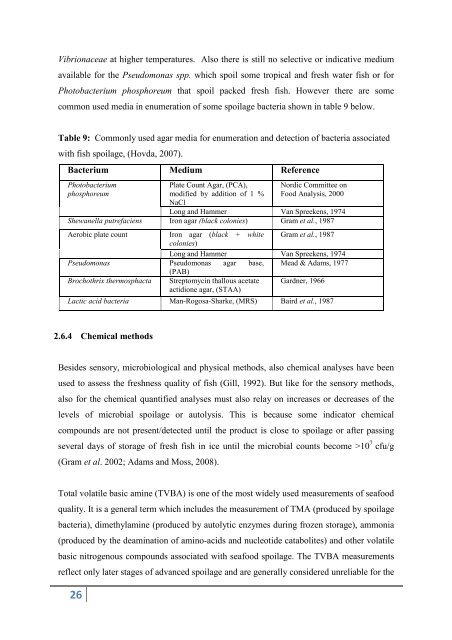
Table 9: Commonly used agar media for enumeration <strong>and</strong> detection of bacteria associated<br />
with fish spoilage, (Hovda, 2007).<br />
Bacterium Medium Reference<br />
Photobacterium<br />
phosphoreum<br />
26<br />
Plate Count Agar, (PCA),<br />
modified by addition of 1 %<br />
NaCl<br />
Nordic Committee on<br />
Food Analysis, 2000<br />
Long <strong>and</strong> Hammer Van Spreekens, 1974<br />
Shewanella putrefaciens Iron agar (black colonies) Gram et al., 1987<br />
Aerobic plate count Iron agar (black + white<br />
colonies)<br />
Gram et al., 1987<br />
Long <strong>and</strong> Hammer Van Spreekens, 1974<br />
Pseudomonas Pseudomonas<br />
(PAB)<br />
agar base, Mead & Adams, 1977<br />
Brochothrix thermosphacta Streptomyc<strong>in</strong> thallous acetate<br />
actidione agar, (STAA)<br />
Gardner, 1966<br />
Lactic acid bacteria Man-Rogosa-Sharke, (MRS) Baird et al., 1987<br />
2.6.4 Chemical methods<br />
Besides sensory, microbiological <strong>and</strong> physical methods, also chemical analyses have been<br />
used to assess the freshness quality of fish (Gill, 1992). But like for the sensory methods,<br />
also for the chemical quantified analyses must also relay on <strong>in</strong>creases or decreases of the<br />
levels of microbial spoilage or autolysis. This is because some <strong>in</strong>dicator chemical<br />
compounds are not present/detected until the product is close to spoilage or after pass<strong>in</strong>g<br />
several days of storage of fresh fish <strong>in</strong> ice until the microbial counts become >10 7 cfu/g<br />
(Gram et al. 2002; Adams <strong>and</strong> Moss, 2008).<br />
Total volatile basic am<strong>in</strong>e (TVBA) is one of the most widely used measurements of seafood<br />
quality. It is a general term which <strong>in</strong>cludes the measurement of TMA (produced by spoilage<br />
bacteria), dimethylam<strong>in</strong>e (produced by autolytic enzymes dur<strong>in</strong>g frozen storage), ammonia<br />
(produced by the deam<strong>in</strong>ation of am<strong>in</strong>o-acids <strong>and</strong> nucleotide catabolites) <strong>and</strong> other volatile<br />
basic nitrogenous compounds associated with seafood spoilage. The TVBA measurements<br />
reflect only later stages of advanced spoilage <strong>and</strong> are generally considered unreliable for the