Operating Instructions Dplmagic Marker Dplgenesis ... - ACI Laser
Operating Instructions Dplmagic Marker Dplgenesis ... - ACI Laser
Operating Instructions Dplmagic Marker Dplgenesis ... - ACI Laser
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Detailed Advanced Information<br />
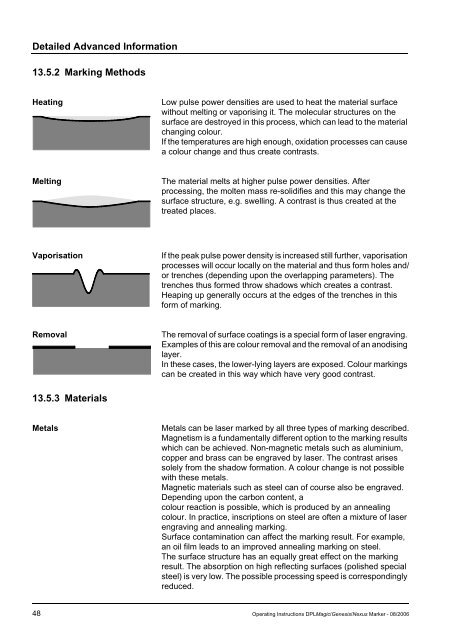
13.5.2 Marking Methods<br />
Heating Low pulse power densities are used to heat the material surface<br />
without melting or vaporising it. The molecular structures on the<br />
surface are destroyed in this process, which can lead to the material<br />
changing colour.<br />
If the temperatures are high enough, oxidation processes can cause<br />
a colour change and thus create contrasts.<br />
Melting The material melts at higher pulse power densities. After<br />
processing, the molten mass re-solidifies and this may change the<br />
surface structure, e.g. swelling. A contrast is thus created at the<br />
treated places.<br />
Vaporisation If the peak pulse power density is increased still further, vaporisation<br />
processes will occur locally on the material and thus form holes and/<br />
or trenches (depending upon the overlapping parameters). The<br />
trenches thus formed throw shadows which creates a contrast.<br />
Heaping up generally occurs at the edges of the trenches in this<br />
form of marking.<br />
Removal The removal of surface coatings is a special form of laser engraving.<br />
Examples of this are colour removal and the removal of an anodising<br />
layer.<br />
In these cases, the lower-lying layers are exposed. Colour markings<br />
can be created in this way which have very good contrast.<br />
13.5.3 Materials<br />
Metals Metals can be laser marked by all three types of marking described.<br />
Magnetism is a fundamentally different option to the marking results<br />
which can be achieved. Non-magnetic metals such as aluminium,<br />
copper and brass can be engraved by laser. The contrast arises<br />
solely from the shadow formation. A colour change is not possible<br />
with these metals.<br />
Magnetic materials such as steel can of course also be engraved.<br />
Depending upon the carbon content, a<br />
colour reaction is possible, which is produced by an annealing<br />
colour. In practice, inscriptions on steel are often a mixture of laser<br />
engraving and annealing marking.<br />
Surface contamination can affect the marking result. For example,<br />
an oil film leads to an improved annealing marking on steel.<br />
The surface structure has an equally great effect on the marking<br />
result. The absorption on high reflecting surfaces (polished special<br />
steel) is very low. The possible processing speed is correspondingly<br />
reduced.<br />
48 <strong>Operating</strong> <strong>Instructions</strong> DPLMagic/Genesis/Nexus <strong>Marker</strong> - 08/2006