Rudolph MG
Rudolph MG
Rudolph MG
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006.24:419-466. Downloaded from arjournals.annualreviews.org<br />
by CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY on 04/04/10. For personal use only.<br />
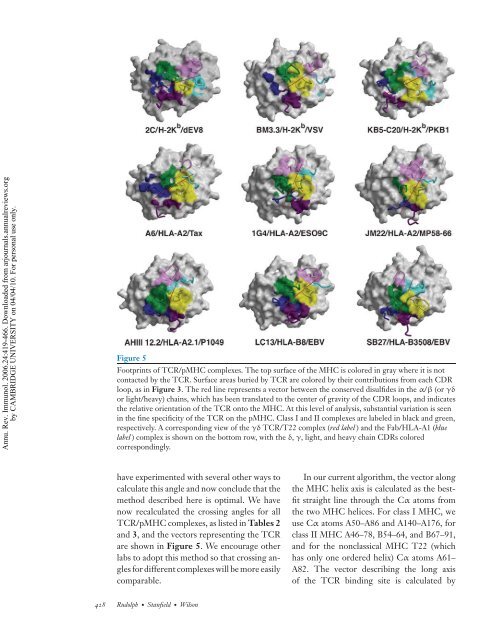
Figure 5<br />
Footprints of TCR/pMHC complexes. The top surface of the MHC is colored in gray where it is not<br />
contacted by the TCR. Surface areas buried by TCR are colored by their contributions from each CDR<br />
loop, as in Figure 3. The red line represents a vector between the conserved disulfides in the α/β (or γδ<br />
or light/heavy) chains, which has been translated to the center of gravity of the CDR loops, and indicates<br />
the relative orientation of the TCR onto the MHC. At this level of analysis, substantial variation is seen<br />
in the fine specificity of the TCR on the pMHC. Class I and II complexes are labeled in black and green,<br />
respectively. A corresponding view of the γδ TCR/T22 complex (red label ) and the Fab/HLA-A1 (blue<br />
label ) complex is shown on the bottom row, with the δ, γ, light, and heavy chain CDRs colored<br />
correspondingly.<br />
have experimented with several other ways to<br />
calculate this angle and now conclude that the<br />
method described here is optimal. We have<br />
now recalculated the crossing angles for all<br />
TCR/pMHC complexes, as listed in Tables 2<br />
and 3, and the vectors representing the TCR<br />
are shown in Figure 5. We encourage other<br />
labs to adopt this method so that crossing angles<br />
for different complexes will be more easily<br />
comparable.<br />
428 <strong>Rudolph</strong>· Stanfield· Wilson<br />
In our current algorithm, the vector along<br />
the MHC helix axis is calculated as the bestfit<br />
straight line through the Cα atoms from<br />
the two MHC helices. For class I MHC, we<br />
use Cα atoms A50–A86 and A140–A176, for<br />
class II MHC A46–78, B54–64, and B67–91,<br />
and for the nonclassical MHC T22 (which<br />
has only one ordered helix) Cα atoms A61–<br />
A82. The vector describing the long axis<br />
of the TCR binding site is calculated by