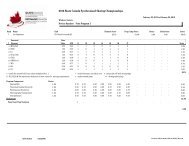
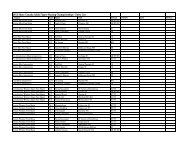
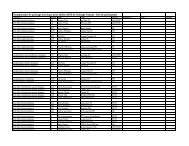
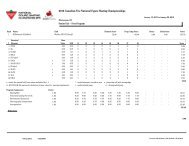
LONG-TERM ATHLETE DEVELOPMENT - Skate Canada
LONG-TERM ATHLETE DEVELOPMENT - Skate Canada
LONG-TERM ATHLETE DEVELOPMENT - Skate Canada
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
865 Sheord Road, Ottawa, Ontario K1J 1H9<br />
L O N G - T E R M Phone A613.747.1007 T H LI Toll E Free T1.888.747.2372 E D EI Fax V613.748.5718 E L OI Toll PFree MFax 1.877.211.2372 E N T<br />
What is Long-term Athlete Development?<br />
In general, long-term athlete development focuses<br />
on how participants and athletes are trained and<br />
develop skills and revolves around the essential role<br />
played by coaches in the process. It also recognizes<br />
the important supporting roles of parents/guardians,<br />
volunteers, officials, administrators, sponsors, sport<br />
medicine practitioners and sport scientists. Training the<br />
right components at the right stage of development<br />
is key to the success of all athletes, from beginners to<br />
Olympians. This document represents the first step in<br />
the redesign of long-term athlete development in our<br />
sport. Other components include: competition structure,<br />
coach training and development, officials’ training<br />
and development, sport leadership, sport facilities,<br />
equipment, technology, sport medicine and sport<br />
sciences.<br />
Photo: Jim Coveart<br />
At the heart of long-term athlete development is<br />
the concept of physical literacy which is defined as<br />
competency in fundamental movement skills (run,<br />
jump, throw, swim) as well as motor skills (ABC’s: agility,<br />
balance, coordination, speed) and fundamental sport<br />
skills (preferably before the age of 12). Historically, skills<br />
taught, learned, developed and acquired through the<br />
school system enhanced children’s abilities to acquire<br />
sport-specific skills more quickly.<br />
L o n g - Te r m A t h l e t e D e v e l o p m e n t<br />
O V E R V I E W O F<br />
N E X X I C E<br />
2009 World Champions<br />
5<br />
However, due to government cutbacks and a shift in<br />
core subject matters in school curricula we have created<br />
physically illiterate individuals. As a result, the ability to<br />
develop fundamental movement skills (running, jumping,<br />
throwing, adaptations to ice, snow, and water) as well<br />
as basic motor skills (balance, coordination, agility,<br />
speed, etc.) at an early age is becoming alarmingly non–<br />
existent.<br />
What is the Long-Term Athlete Development Model?<br />
The Long-Term Athlete Development Model (LTADM) is<br />
a guide or road map for every level of the organization<br />
to assist in making the best decisions in the interest<br />
of athlete development within our sport. This model<br />
addresses gaps in our process and removes roadblocks<br />
that result in lost members along the way.<br />
The LTADM provides a reference point for all coaches<br />
when developing annual and long-term training<br />
plans. It acts as a guide for all support team members<br />
when making athlete and program–related decisions.<br />
Furthermore, the LTADM directs the refinement<br />
and/or redesign of programs and administrative<br />
structures so as to maximize the development of all our<br />
participants regardless of their personal goals or stage of<br />
development.<br />
More specifically, the LTADM defines optimal training,<br />
competition and recovery programs based more on<br />
biological rather than solely chronological age. By<br />
incorporating knowledge gained from the field of<br />
exercise science and by tailoring sport development<br />
programs around basic principles of growth and<br />
maturation, especially during the critical early years of<br />
development, the LTADM capitalizes on opportunities<br />
in training athletes when bodies will respond the<br />
greatest to different training stimuli. At the same time,<br />
it emphasizes the intellectual, emotional and social<br />
development of the athlete in recognition of the fact<br />
that sport can play a positive role in child, youth and<br />
adolescent development and the creation of healthy,<br />
functional and productive individuals.