Gas Laws
Gas Laws
Gas Laws
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
These three gas laws can be combined in one combined gas law. This law<br />
can be expressed as follows.<br />
If PV/T equals a constant, k, then PV/T for a sample of gas under one<br />
set of conditions equals PV/T under another set of conditions, assuming<br />
the amount of gas remains the same.<br />
Therefore, the combined gas law can be expressed by the following<br />
mathematical equation. This equation can be used to solve problems in<br />
which pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas vary. Only the molar<br />
quantity of the gas must be constant.<br />
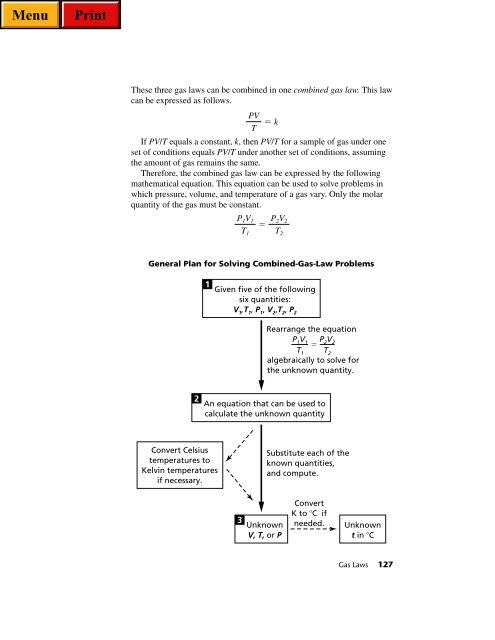
General Plan for Solving Combined-<strong>Gas</strong>-Law Problems<br />
2<br />
1<br />
Convert Celsius<br />
temperatures to<br />
Kelvin temperatures<br />
if necessary.<br />
P 1V 1<br />
T 1<br />
Given five of the following<br />
six quantities:<br />
V 1 ,T 1 , P 1 , V 2 ,T 2 , P 2<br />
Rearrange the equation<br />
P1V1 P2V2 <br />
T1 T2 algebraically to solve for<br />
the unknown quantity.<br />
An equation that can be used to<br />
calculate the unknown quantity<br />
3<br />
PV<br />
T<br />
k<br />
P 2V 2<br />
T 2<br />
Unknown<br />
V, T, or P<br />
Substitute each of the<br />
known quantities,<br />
and compute.<br />
Convert<br />
K to C if<br />
needed.<br />
Unknown<br />
t in C<br />
<strong>Gas</strong> <strong>Laws</strong> 127