IB Econ Chap 26 Terms of Trade - Sunny Hills High School
IB Econ Chap 26 Terms of Trade - Sunny Hills High School
IB Econ Chap 26 Terms of Trade - Sunny Hills High School
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
!!!!<br />
<strong>26</strong> . <strong>Terms</strong> <strong>of</strong> trade<br />
Agricultural policies in developed countries have had a<br />
damaging effect on world agricultural markets. Price support<br />
schemes in the EU and the US, for example, have led to<br />
relatively high prices there and over-production by domestic<br />
producers. These subsidies have also led to over-production.<br />
The over-production is then sold on the world markets, pushing<br />
down agricultural prices. For these reasons, developing<br />
countries <strong>of</strong>ten accuse the developed economies <strong>of</strong> "dumping"<br />
agricultural products on the world market and so ruining their<br />
own agricultural industries.<br />
With huge leaps in technology over the last 50 years, many<br />
products have become smaller. For example, computers that once<br />
took up a whole room are now replaced by laptop computers <strong>of</strong><br />
the same power; large tape recorders, the size <strong>of</strong> a suitcase, are<br />
now replaced by MP3 players the size <strong>of</strong> a cigarette lighter; and<br />
televisions, which were once housed in large cabinets, are now<br />
replaced by flat screens that require no such housing. This<br />
rniniaturisation <strong>of</strong> many products and the improvement in<br />
plastics technology has led to a fall in the demand for the<br />
commodities that were traditionally used to make and package<br />
these products.<br />
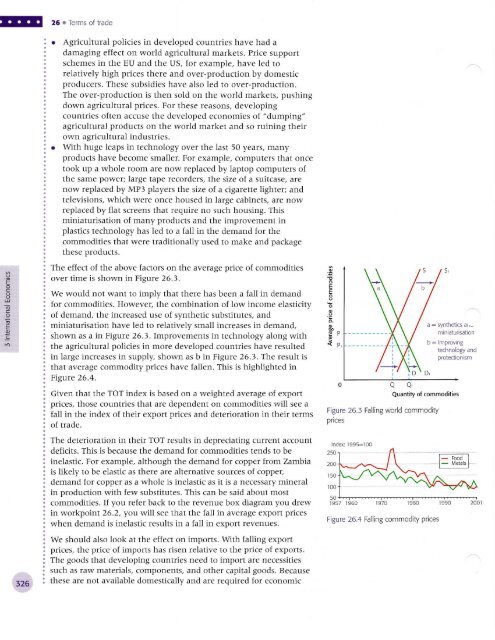
The effect <strong>of</strong> the above factors on the average price <strong>of</strong> commodities<br />
over time is shovrm in Figure <strong>26</strong>.3.<br />
We would not want to imply that there has been a fall in demand<br />
for commodities. However, the combination <strong>of</strong> low income elasticity<br />
<strong>of</strong> demand, the increased use <strong>of</strong> synthetic substitutes, and<br />
miniaturisation have led to relatively small increases in demand,<br />
shown as a in Figure <strong>26</strong>.3. Improvements in technology along with<br />
the agricultural policies in more developed countries have resulted<br />
in large increases in supply, showr as b in Figue <strong>26</strong>.). The result is<br />
that average commodity prices have fallen. This is highlighted in<br />
Figre <strong>26</strong>.4.<br />
Given that the TOT index is based on a weighted average <strong>of</strong> export<br />
prices, those countries that are dependent on commodities will see a<br />
fall in the index <strong>of</strong> their export prices and deterioration in their terms<br />
<strong>of</strong> trade.<br />
The deterioration in their TOT resr ts in depreciating current account<br />
deficits. This is because the demand for commodities tends to be<br />
inelastic. For example, although the dernand for copper from Zambia<br />
is likely to be elastic as there are alternative sources <strong>of</strong> copper,<br />
demand for copper as a whole is inelastic as it is a necessary mineral<br />
in production with few substitutes. This can be said about most<br />
commodities. If you refer back to the revenue box diagram you drew<br />
in workpoint <strong>26</strong>.2, you will see that the fall in average export prices<br />
when demand is inelastic results in a fall in expon revenues.<br />
We should also look at the eIlect on imports. with falling export<br />
prices, the price <strong>of</strong> imports has risen relative to the price <strong>of</strong> erT)orts.<br />
The goods that developing countries need to import are necessities<br />
such as raw materials, components, and other capital goods. Because<br />
these are not available domestically and are required for economic<br />
.9<br />
E<br />
E<br />
0Qa,<br />
Quanlity <strong>of</strong> commodities<br />
FiBure <strong>26</strong>.3 Falling world commodity<br />
prices<br />
lndexr 1995:loo<br />
25O r<br />
200<br />
r50<br />
100<br />
50+<br />
ti1ure <strong>26</strong>.4 Falling commodity prices<br />
a: synthetics ar,miniatuisation<br />
b = lmprovin8<br />
technology and<br />
proteclionism