A State-Based Programming Model for Wireless Sensor Networks
A State-Based Programming Model for Wireless Sensor Networks
A State-Based Programming Model for Wireless Sensor Networks
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2.3. <strong>Sensor</strong> Nodes 23<br />
<strong>Sensor</strong>s<br />
Mirrors<br />
Analog I/O, DSP, Control<br />
Passive Transmitter with<br />
Corner-Cube Retroreflector<br />
1-2mm<br />
Interrogating<br />
Laser Beam<br />
Laser Lens Mirror<br />
Active Transmitter<br />
with Beam Steering<br />
Power Capacitor<br />
Solar Cell<br />
Thick-Film Battery<br />
Incoming Laser<br />
Communication<br />
Photodetector Photodetector and and Receiver<br />
Receiver<br />
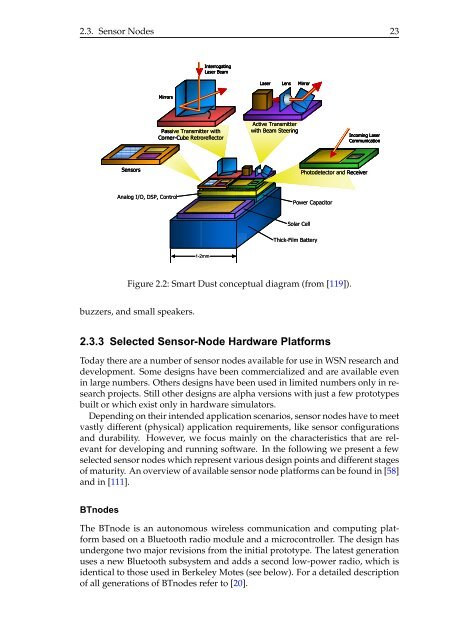
Figure 2.2: Smart Dust conceptual diagram (from [119]).<br />
buzzers, and small speakers.<br />
2.3.3 Selected <strong>Sensor</strong>-Node Hardware Plat<strong>for</strong>ms<br />
Today there are a number of sensor nodes available <strong>for</strong> use in WSN research and<br />
development. Some designs have been commercialized and are available even<br />
in large numbers. Others designs have been used in limited numbers only in research<br />
projects. Still other designs are alpha versions with just a few prototypes<br />
built or which exist only in hardware simulators.<br />
Depending on their intended application scenarios, sensor nodes have to meet<br />
vastly different (physical) application requirements, like sensor configurations<br />
and durability. However, we focus mainly on the characteristics that are relevant<br />
<strong>for</strong> developing and running software. In the following we present a few<br />
selected sensor nodes which represent various design points and different stages<br />
of maturity. An overview of available sensor node plat<strong>for</strong>ms can be found in [58]<br />
and in [111].<br />
BTnodes<br />
The BTnode is an autonomous wireless communication and computing plat<strong>for</strong>m<br />
based on a Bluetooth radio module and a microcontroller. The design has<br />
undergone two major revisions from the initial prototype. The latest generation<br />
uses a new Bluetooth subsystem and adds a second low-power radio, which is<br />
identical to those used in Berkeley Motes (see below). For a detailed description<br />
of all generations of BTnodes refer to [20].