booklet format - inaf iasf bologna
booklet format - inaf iasf bologna
booklet format - inaf iasf bologna
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Temporal Data Analysis A.A. 2011/2012<br />
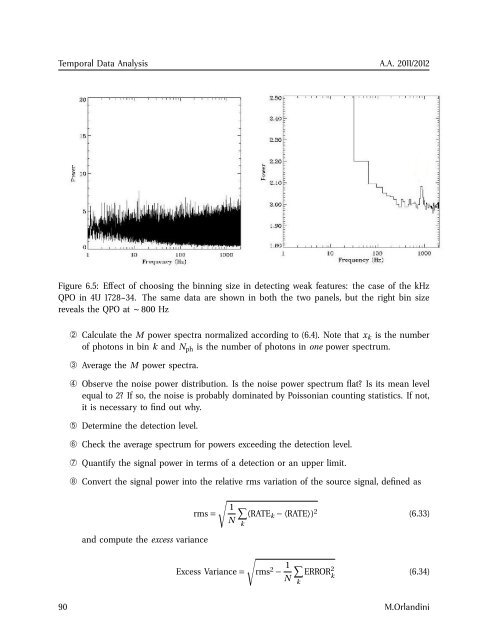
Figure 6.5: Effect of choosing the binning size in detecting weak features: the case of the kHz<br />
QPO in 4U 1728–34. The same data are shown in both the two panels, but the right bin size<br />
reveals the QPO at ∼ 800 Hz<br />
➁ Calculate the M power spectra normalized according to (6.4). Note that x k is the number<br />
of photons in bin k and N ph is the number of photons in one power spectrum.<br />
➂ Average the M power spectra.<br />
➃ Observe the noise power distribution. Is the noise power spectrum flat? Is its mean level<br />
equal to 2? If so, the noise is probably dominated by Poissonian counting statistics. If not,<br />
it is necessary to find out why.<br />
➄ Determine the detection level.<br />
➅ Check the average spectrum for powers exceeding the detection level.<br />
➆ Quantify the signal power in terms of a detection or an upper limit.<br />
➇ Convert the signal power into the relative rms variation of the source signal, defined as<br />
and compute the excess variance<br />
√<br />
1 ∑<br />
rms = (RATE k − 〈RATE〉) 2 (6.33)<br />
N<br />
k<br />
√<br />
Excess Variance = rms 2 − 1 ∑<br />
ERROR 2 (6.34)<br />
N<br />
k<br />
90 M.Orlandini<br />
k