BIOLOGY IN FOCUS
BIOLOGY IN FOCUS
BIOLOGY IN FOCUS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
CELLS AND THE CELL THEORY<br />
Cell structure and functioning<br />
Introduction: levels of organisation<br />
1.3<br />
Most living organisms that are seen<br />
every day consist of many cells and are<br />
termed multicellular. However, some<br />
living things consist of only one cell<br />
that carries out all of their life functions.<br />
These are said to be unicellular<br />
and can be seen with a microscope<br />
(e.g. Protists such as Euglena, Amoeba<br />
and Paramecium, living in pond water,<br />
and some disease-causing organisms<br />
such as bacteria) (see Fig. 1.11).<br />
The term ‘cell’ is therefore used to<br />
describe the basic unit of any organism,<br />
whether it is the only unit or one of<br />
many units making up an organism.<br />
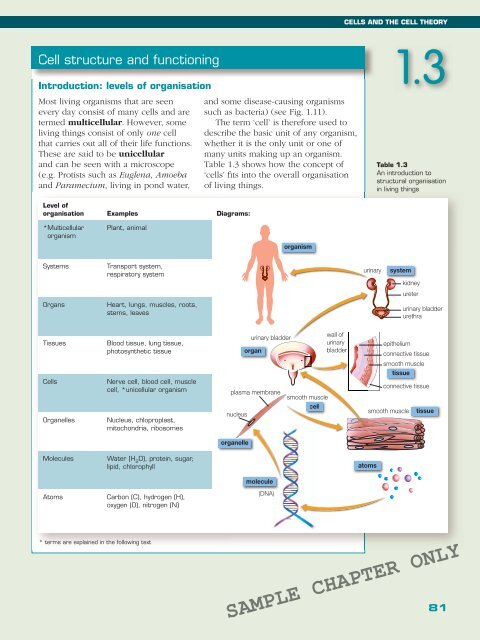
Table 1.3 shows how the concept of<br />
‘cells’ fits into the overall organisation<br />
of living things.<br />
Table 1.3<br />
An introduction to<br />
structural organisation<br />
in living things<br />
Level of<br />
organisation Examples Diagrams:<br />
* Multicellular<br />
organism<br />
Plant, animal<br />
organism<br />
Systems<br />
Transport system,<br />
respiratory system<br />
urinary<br />
system<br />
kidney<br />
ureter<br />
Organs<br />
Heart, lungs, muscles, roots,<br />
stems, leaves<br />
urinary bladder<br />
urethra<br />
Tissues<br />
Blood tissue, lung tissue,<br />
photosynthetic tissue<br />
urinary bladder<br />
organ<br />
wall of<br />
urinary<br />
bladder<br />
epithelium<br />
connective tissue<br />
smooth muscle<br />
tissue<br />
Cells<br />
Nerve cell, blood cell, muscle<br />
cell, *unicellular organism<br />
plasma membrane<br />
smooth muscle<br />
connective tissue<br />
Organelles<br />
Nucleus, chloproplast,<br />
mitochondria, ribosomes<br />
nucleus<br />
cell<br />
smooth muscle<br />
tissue<br />
organelle<br />
Molecules<br />
Water (H 2<br />
O), protein, sugar,<br />
lipid, chlorophyll<br />
atoms<br />
molecule<br />
Atoms<br />
Carbon (C), hydrogen (H),<br />
oxygen (O), nitrogen (N)<br />
(DNA)<br />
* terms are explained in the following text<br />
SAMPLE CHAPTER ONLY<br />
81